 W
WLabor relations is a field of study that can have different meanings depending on the context in which it is used. In an international context, it is a subfield of labor history that studies the human relations with regard to work – in its broadest sense – and how this connects to questions of social inequality. It explicitly encompasses unregulated, historical, and non-Western forms of labor. Here, labor relations define "for or with whom one works and under what rules. These rules determine the type of work, type and amount of remuneration, working hours, degrees of physical and psychological strain, as well as the degree of freedom and autonomy associated with the work."
 W
WAnti-capitalism is a political ideology and movement encompassing a variety of attitudes and ideas that oppose capitalism. In this sense, anti-capitalists are those who wish to replace capitalism with another type of economic system, usually some form of socialism.
 W
WAnti-union violence is physical force intended to harm union officials, union organizers, union members, union sympathizers, or their families. It is most commonly used either during union organizing efforts, or during strikes. The aim most often is to prevent a union from forming, to destroy an existing union, or to reduce the effectiveness of a union or a particular strike action. If strikers prevent people or goods to enter or leave a workplace, violence may be used to allow people and goods to pass the picket line.
 W
WThe Calmfors–Driffill hypothesis is a macroeconomic theory in labour economics that states that there is a direct relationship between the degree of collective bargaining in an economy and the level of unemployment. Specifically, it states that the relationship is roughly that of an 'inverted U': as trade union size increases from nil, unemployment increases, and then falls as unions begin to exercise monopoly power. It was advanced by Lars Calmfors and John Driffill.
 W
WA coolie is an outdated, offensive, and racist term for a low-wage laborer, typically of South Asian descent.
 W
WCouncils of Trust were established in businesses and companies with more than 20 employees in Nazi Germany following the introduction of the Labour organization law of 20 January 1934. They served as the only representation of employees to the “factory leader” in order to increase mutual trust within the factory community. Councillors were elected by secret ballots, but the list of candidates was prepared by the factory leader and the German Labour Front overseer. The councils did not play an active role in industrial relations, except to serve as a platform for discussing working conditions regulated in the “factory code of rules”.
 W
WDay labor is work done where the worker is hired and paid one day at a time, with no promise that more work will be available in the future. It is a form of contingent work.
 W
WThe European Trade Union Confederation (ETUC) is the major trade union organisation representing workers at European level. European integration has reinforced the EU's role in economic, employment and social policy throughout the 28 Member States. The ETUC is a European social partner, which means that the European Commission consults it when developing social and economic policies. It also negotiates autonomous agreements and work programmes with European employers. And it coordinates the national and sectoral policies of its affiliates on social and economic matters, particularly in the framework of the EU institutional processes, including European economic governance and the EU Semester.
 W
WThe European Trade Union Institute (ETUI) is the independent research and training centre of the European Trade Union Confederation (ETUC). Its mission is to build bridges between the world of research and the world of labour, in order to support, strengthen and stimulate the European trade union movement.
 W
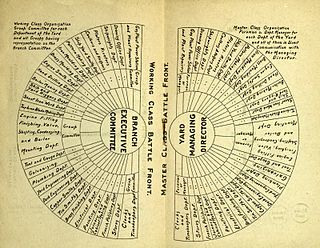
WIndustrial unionism is a trade union organizing method through which all workers in the same industry are organized into the same union—regardless of skill or trade—thus giving workers in one industry, or in all industries, more leverage in bargaining and in strike situations.
 W
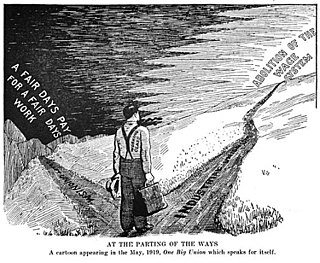
WThe Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) is a union of wage workers which was formed in Chicago in 1905 by militant unionists and their supporters due to anger over the conservatism, philosophy, and craft-based structure of the American Federation of Labor (AFL). Throughout the early part of the 20th century, the philosophy and tactics of the IWW were frequently in direct conflict with those of the AFL concerning the best ways to organize workers, and how to best improve the society in which they toiled. The AFL had one guiding principle—"pure and simple trade unionism", often summarized with the slogan "a fair day's pay for a fair day's work." The IWW embraced two guiding principles, fighting like the AFL for better wages, hours, and conditions, but also promoting an eventual, permanent solution to the problems of strikes, injunctions, bull pens, and union scabbing.
 W
WInflatable rats, or union rats, are giant inflatables in the shape of cartoon rats, commonly used in the United States by protesting or striking trade unions. They serve as a sign of opposition against employers or nonunion contractors, and are intended to call public attention to companies employing nonunion labor. The practice dates from the 1990s.
 W
WInternal communications (IC) is the function responsible for effective communications among participants within an organization. The scope of the function varies by organization and practitioner, from producing and delivering messages and campaigns on behalf of management, to facilitating two-way dialogue and developing the communication skills of the organization's participants.
 W
WIn economics, a negative income tax is a system which reverses the direction in which tax is paid for incomes below a certain level; in other words, earners above that level pay money to the state while earners below it receive money, as shown by the blue arrows in the diagram. 'Negative Income Tax' (NIT) was proposed by Juliet Rhys-Williams while working on the Beveridge Report in the early 1940s and popularized by Milton Friedman in the 1960s as a system in which the state makes payments to the poor when their income falls below a threshold, while taxing them on income above that threshold. Together with Friedman, support for NIT showed also Tobin, Pechman or Mieszkowski and even President at the time Richard Nixon, who suggested implementation of modified NIT in his Family Assistance Plan. After the increase popularity of NIT an experiment sponsored by the US government was conducted between 1968-1982 on effects of NIT on labour supply and income and substitution effects.
 W
WPicketing is a form of protest in which people congregate outside a place of work or location where an event is taking place. Often, this is done in an attempt to dissuade others from going in, but it can also be done to draw public attention to a cause. Picketers normally endeavor to be non-violent. It can have a number of aims, but is generally to put pressure on the party targeted to meet particular demands or cease operations. This pressure is achieved by harming the business through loss of customers and negative publicity, or by discouraging or preventing workers or customers from entering the site and thereby preventing the business from operating normally.
 W
WSocialist self-management or Self-governing socialism was a form of workers' self-management used as a social and economic model formulated by the Communist Party of Yugoslavia. It was instituted by law in 1950 and lasted in the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia until 1990, just prior to its breakup in 1992.
 W
W"Solidarity Forever", written by Ralph Chaplin in 1915, is a popular trade union anthem. It is sung to the tune of "John Brown's Body" and "The Battle Hymn of the Republic". Although it was written as a song for the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW), other union movements, such as the AFL-CIO, have adopted the song as their own. The song has been performed by musicians such as Utah Phillips, Pete Seeger, Leonard Cohen, and was redone by Emcee Lynx and The Nightwatchman. It is still commonly sung at union meetings and rallies in the United States, Australia and Canada, and has also been sung at conferences of the Australian Labor Party and the Canadian New Democratic Party. This may have also inspired the hymn of the consumer cooperative movement, "The Battle Hymn of Cooperation", which is sung to the same tune.
 W
WA strikebreaker is a person who works despite an ongoing strike. Strikebreakers are usually individuals who were not employed by the company before the trade union dispute, but rather hired after or during the strike to keep the organization running. "Strikebreakers" may also refer to workers who cross picket lines to work.
 W
WSyndicalism is a current in the labor movement to establish local, worker-based organizations and advance the demands and rights of workers through strikes. Most active in the early 20th century, syndicalism was predominant in the revolutionary left in the decade which preceded the outbreak of World War I because orthodox Marxism was mostly reformist at that time, according to the Marxist historian Eric Hobsbawm.
 W
WThe Tripartite Consultation Convention, 1976, officially the Convention concerning tripartite consultations to promote the implementation of international labour standards is an International Labour Organization Convention, which governs the process for implementation of measures regarding ILO conferences. It requires tripartite consultation before ratification, implementing legislation or denouncement of conventions. As of June 2015, the convention had been ratified by 139 member states. The convention is also known as convention number 144 on the List of International Labour Organization Conventions.
 W
WUnion busting is a range of activities undertaken to disrupt or prevent the formation of trade unions or their attempts to grow their membership in a workplace.
 W
WA union representative, union steward, or shop steward is an employee of an organization or company who represents and defends the interests of their fellow employees as a labor union member and official. Rank-and-file members of the union hold this position voluntarily while maintaining their role as an employee of the firm. As a result, the union steward becomes a significant link and conduit of information between the union leadership and rank-and-file workers.
 W
WUnited Students Against Sweatshops (USAS) is a student organization founded in 1998 with chapters at over 250 colleges and universities in the United States and Canada. In April 2000, USAS founded the Worker Rights Consortium (WRC), an independent monitoring organization that investigates labor conditions in factories that produce collegiate apparel all over the world. The WRC exacts an annual membership fee from participating universities, which is used to fund its monitoring work.
 W
WUniversal basic income (UBI), also called unconditional basic income, citizen's basic income, basic income guarantee, basic living stipend, guaranteed annual income, universal income security program or universal demogrant, is a sociopolitical financial transfer concept in which all citizens of a given population regularly receive a legally stipulated and equal financial grant paid by the government without a means test. A basic income can be implemented nationally, regionally, or locally. If the level is sufficient to meet a person's basic needs, it is sometimes called a full basic income; if it is less than that amount, it may be called a partial basic income.
 W
WA user revolt is a social conflict in which users of a website collectively and openly protest a website host's or administrator's instructions for using the website. Sometimes it happens that the website hosts can control a website's use in certain ways, but the hosts also depend on the users to comply with voluntary social rules in order for the website to operate as the hosts would like. A user revolt occurs when the website users protest against the voluntary social rules of a website, and use the website in a way that is in conflict with the wishes of the website host or administrators.
 W
WWage labour, usually referred to as paid work, paid employment, or paid labour, refers to the socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer in which the worker sells their labour power under a formal or informal employment contract. These transactions usually occur in a labour market where wages or salaries are market-determined.
 W
WThe working poor are working people whose incomes fall below a given poverty line due to low-income jobs and low familial household income. These are people who spend at least 27 weeks in a year working or looking for employment, but remain under the poverty threshold.