 W
WA play is a work of drama, usually consisting mostly of dialogue between characters and intended for theatrical performance rather than just reading. The writer of a play is a playwright.
 W
WTheatre or theater is a collaborative form of performing art that uses live performers, usually actors or actresses, to present the experience of a real or imagined event before a live audience in a specific place, often a stage. The performers may communicate this experience to the audience through combinations of gesture, speech, song, music, and dance. Elements of art, such as painted scenery and stagecraft such as lighting are used to enhance the physicality, presence and immediacy of the experience. The specific place of the performance is also named by the word "theatre" as derived from the Ancient Greek θέατρον, itself from θεάομαι.
 W
WThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to theatre:
 W
WAn atmospheric theatre is a type of movie palace design which was popular in the late 1920s. Atmospheric theatres were designed and decorated to evoke the feeling of a particular time and place for patrons, through the use of projectors, architectural elements and ornamentation that evoked a sense of being outdoors. This was intended to make the patron a more active participant in the setting.
 W
WAn audience is a group of people who participate in a show or encounter a work of art, literature, theatre, music, video games, or academics in any medium. Audience members participate in different ways in different kinds of art; some events invite overt audience participation and others allowing only modest clapping and criticism and reception.
 W
WAn audition is a sample performance by an actor, singer, musician, dancer or other performer. It typically involves the performer displaying their talent through a previously memorized and rehearsed solo piece or by performing a work or piece given to the performer at the audition or shortly before. In some cases, such as with a model or acrobat, the individual may be asked to demonstrate a range of professional skills. Actors may be asked to present a monologue. Singers will perform a song in a popular music context or an aria in a Classical context. A dancer will present a routine in a specific style, such as ballet, tap dance or hip-hop, or show his or her ability to quickly learn a choreographed danceion is a systematic process in which industry professionals select performers, which is in some ways analogous to a job interview in the regular job market. In an audition, the employer is testing the ability of the applicant to meet the needs of the job and assess how well the individual will take directions and deal with changes. After some auditions, after the performer has demonstrated their abilities in a given performance style, the audition panel may ask a few questions that resemble those used in standard job interviews.
 W
WIn the performing arts industry such as theatre, film, or television, a casting is a pre-production process for selecting a certain type of actor, dancer, singer, or extra for a particular role or part in a script, screenplay, or teleplay. This process is typically utilized for a motion picture, television program, documentary, music video, play, or television advertisement, etc. This involvement in a dramatic production, advertisement, and or industrial video is intended for an audience, or studio audience.
 W
WA costume shop is a space where costumes for theatrical or film productions are designed, built, and stored for the company or production. Costume designers, builders, seamstresses, and stitchers work in costume shops. The shops themselves can vary in size, from one large room to a house with multiple floors. Costumes from past productions, fabric, jewelry and accessories are often stored in the shop.
 W
WDrama therapy is the use of theatre techniques to facilitate personal growth and promote mental health. Drama therapy is used in a wide variety of settings, including hospitals, schools, mental health centers, prisons, and businesses. Drama therapy, as a modality of the creative arts therapies, exists in many forms and can apply to individuals, couples, families, and various groups.
 W
WHip-hop theater is a form of theater that presents contemporary stories through the use of one or more of the four elements of hip-hop culture—b-boying, graffiti writing, MCing (rapping), and DJing. Other cultural markers of hip-hop such as spoken word, beatboxing, and hip-hop dance can be included as well although they are not always present. What is most important is the language of the theatrical piece and the plot's relevance to the world. Danny Hoch, founder of the Hip-Hop Theater Festival, further defines it as such: "Hip-hop theatre must fit into the realm of theatrical performance, and it must be by, about and for the hip-hop generation, participants in hip-hop culture, or both."
 W
WKwagh-hir is a multipart culturally edifying art form of the Tiv people of central Nigeria which became popular in the 1960s. It is a dramatic public performance telling moral stories of past and current events, and incorporates puppetry, masquerading, poetry, music, dance and animated narratives to portray its moral themes. It is used by the Tiv people to reinforce traditional beliefs and convey other worldly tales to educate, socialize, provide secular entertainment and address societal issues.
 W
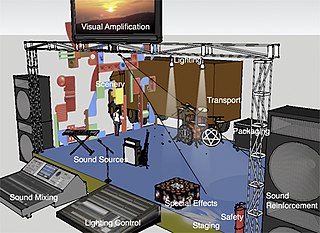
WLive event support includes staging, scenery, mechanicals, sound, lighting, video, special effects, transport, packaging, communications, costume and makeup for live performance events including theater, music, dance, and opera. They all share the same goal: to convince live audience members that there is no better place that they could be at the moment. This is achieved through establishing a bond between performer and audience. Live performance events tend to use visual scenery, lighting, costume amplification and a shorter history of visual projection and sound amplification reinforcement.
 W
WMethod acting is a range of training and rehearsal techniques that seek to encourage sincere and emotionally expressive performances, as formulated by a number of different theatre practitioners. These techniques are built on Stanislavski's system, developed by the Russian actor and director Konstantin Stanislavski and captured in his books An Actor Prepares, Building a Character, and Creating a Role.
 W
WMuseum theatre is the use of theatre and theatrical techniques by a museum for educational, informative, and entertainment purposes. It can also be used in a zoo, an aquarium, an art gallery, and at historic sites. It is generally performed by professional actors. Varieties of museum theatre include historical characters, puppetry, movement and music.
 W
WNaturalism is a movement in European drama and theatre that developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It refers to theatre that attempts to create an illusion of reality through a range of dramatic and theatrical strategies. Interest in naturalism especially flourished with the French playwrights of the time, but the most successful example is Strindberg's play Miss Julie, which was written with the intention to abide by both his own particular version of naturalism, and also the version described by the French novelist and literary theoretician, Émile Zola.
 W
WOpera is a form of theatre in which music has a leading role and the parts are taken by singers, but is distinct from musical theatre. Such a "work" is typically a collaboration between a composer and a librettist and incorporates a number of the performing arts, such as acting, scenery, costume, and sometimes dance or ballet. The performance is typically given in an opera house, accompanied by an orchestra or smaller musical ensemble, which since the early 19th century has been led by a conductor.
 W
WOpera glasses, also known as theater binoculars or Galilean binoculars, are compact, low-power optical magnification devices, usually used at performance events, whose name is derived from traditional use of binoculars at opera performances. Magnification power below 5× is usually desired in these circumstances in order to minimize image shake and maintain a large enough field of view. A magnification of 3× is normally recommended. The design of many modern opera glasses of the ornamental variety is based on the popular lorgnettes of the 19th century.
 W
WA peanut gallery was, in the days of vaudeville, a nickname for the cheapest and ostensibly rowdiest seats in the theater, the occupants of which were often known to heckle the performers. The least expensive snack served at the theatre would often be peanuts, which the patrons would sometimes throw at the performers on stage to convey their disapproval. Phrases such as "no comments from the peanut gallery" or "quiet in the peanut gallery" are extensions of the name.
 W
WPerformance art is an artwork or art exhibition created through actions executed by the artist or other participants. It may be live, through documentation, spontaneously or written, presented to a public in a Fine Arts context, traditionally interdisciplinary. Also known as artistic action, it has been developed through the years as a genre of its own in which art is presented live. It had an important and fundamental role in 20th century avant garde art.
 W
WA premiere or première is the debut of a play, film, dance, or musical composition.
 W
WA puppet is an object, often resembling a human, animal or mythical figure, that is animated or manipulated by a person called a puppeteer. The puppeteer uses movements of their hands, arms, or control devices such as rods or strings to move the body, head, limbs, and in some cases the mouth and eyes of the puppet. The puppeteer often speaks in the voice of the character of the puppet, and then synchronizes the movements of the puppet's mouth with this spoken part. The actions, gestures and spoken parts acted out by the puppeteer with the puppet are typically used in storytelling. Puppetry is a very ancient form of theatre which dates back to the 5th century BC in Ancient Greece. There are many different varieties of puppets, and they are made from a wide range of materials, depending on their form and intended use. They range from very simple in construction and operation to very complex.
 W
WA puppeteer is a person who manipulates an inanimate object, called a puppet, to create the illusion that the puppet is alive. The puppet is often shaped like a human, animal, or legendary creature. The puppeteer may be visible to or hidden from the audience. A puppeteer can operate a puppet indirectly by the use of strings, rods, wires, electronics or directly by his or her own hands placed inside the puppet or holding it externally or any other part of the body- such as the legs. Some puppet styles require two or more puppeteers to work together to create a single puppet character.
 W
WA rehearsal is an activity in the performing arts that occurs as preparation for a performance in music, theatre, dance and related arts, such as opera, musical theatre and film production. It is undertaken as a form of practising, to ensure that all details of the subsequent performance are adequately prepared and coordinated. The term rehearsal typically refers to ensemble activities undertaken by a group of people. For example, when a musician is preparing a piano concerto in their music studio, this is called practicing, but when they practice it with an orchestra, this is called a rehearsal. The music rehearsal takes place in a music rehearsal space.
 W
WRussian puppet theater appears to have originated either in migrations from the Byzantine Empire in the sixth century or possibly by Mongols travelling from China. Itinerant Slavic minstrels were presenting puppet shows in western Russia by the thirteenth century, arriving in Moscow in the mid-sixteenth century. Although Russian traditions were increasingly influenced by puppeteers from western Europe in the eighteenth century, Petrushka continued to be one of the principal figures. In addition to glove puppets and marionettes, rod puppets and flat puppets were introduced for a time but disappeared in the late nineteenth century.
 W
WA script breakdown is an intermediate step in the production of a play, film, comic book, or any other work that is originally planned using a script.
 W
WStage management is a broad field that is generally defined as the practice of organization and coordination of an event or theatrical production. Stage management may encompass a variety of activities including the overseeing of the rehearsal process and coordinating communications among various production teams and personnel. Stage management requires a general understanding of all aspects of production and offers organisational support to ensure the process runs smoothly and efficiently.
 W
WStreet performance or busking is the act of performing in public places for gratuities. In many countries the rewards are generally in the form of money but other gratuities such as food, drink or gifts may be given. Street performance is practiced all over the world and dates back to antiquity. People engaging in this practice are called street performers or buskers in the United Kingdom. Buskers is not a term generally used in American English.
 W
WA sylvan theater—sometimes called a greenery theater —is a type of outdoor theater situated in a wooded (sylvan) setting. Often adorned with classical motifs, a sylvan theater may substitute a simple green lawn for built seating and can include elaborate arrangements of shrubs, flowers and other greenery. These alfresco stages may be features of grand formal gardens or parks, or of more intimate settings, and may be intended for either public or private use.
 W
WA theatre in the round, arena theatre or central staging is a space for theatre in which the audience surrounds the stage.
 W
WTheatrical blood, stage blood or fake blood is anything used as a substitute for blood in a theatrical or cinematic performance. For example, in the special effects industry, when a director needs to simulate an actor being shot or cut, a wide variety of chemicals and natural products can be used. The most common is red food coloring, often inside small balloons coupled with explosive devices called squibs. However, Alfred Hitchcock used Bosco Chocolate Syrup as fake blood in his 1960 thriller Psycho. Since the film was in black and white, the color was less important than the consistency. Tomato ketchup is also a common alternative.
 W
WTheatrical makeup is makeup that is used to assist in creating the appearance of the characters that actors portray during a theater production.
 W
WToy theater, also called paper theater and model theater, is a form of miniature theater dating back to the early 19th century in Europe. Toy theaters were often printed on paperboard sheets and sold as kits at the concession stand of an opera house, playhouse, or vaudeville theater. Toy theatres were assembled at home and performed for family members and guests, sometimes with live musical accompaniment. Toy theatre saw a drastic decline in popularity with a shift towards realism on the European stage in the late 19th century, and again with the arrival of television after World War II. Toy theatre has seen a resurgence in recent years among many puppeteers, authors and filmmakers and there are numerous international toy theatre festivals throughout the Americas and Europe.
 W
WUpStage is an open source server-side application that has been purpose built for Cyberformance: multiple artists collaborate in real time via the UpStage platform to create and present live theatrical performances, for audiences who can be online or in a shared space, and who can interact with the performance via a text chat tool. It can also be understood as a form of digital puppetry. It is the first open source platform designed specifically for avatar performances.
 W
WThe Whitehall farces were a series of five long-running comic stage plays at the Whitehall Theatre in London, presented by the actor-manager Brian Rix, in the 1950s and 1960s. They were in the low comedy tradition of British farce, following the Aldwych farces, which played at the Aldwych Theatre between 1924 and 1933.