 W
WForestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, using, conserving and repairing forests, woodlands, and associated resources for human and environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands. The science of forestry has elements that belong to the biological, physical, social, political and managerial sciences.
 W
WAn aerial saw is a saw which is flown through the air. The aerial saw may also be known as a helicopter aerial saw.
 W
WThe bark spud is an implement which is used to remove bark from felled timber.
 W
WCanopy walkways - also called canopy walks, treetop walks or treetop walkways - provide pedestrian access to a forest canopy. Early walkways consisted of bridges between trees in the canopy of a forest; mostly linked up with platforms inside or around the trees. They were originally intended as access to the upper regions of ancient forests for scientists conducting canopy research. Eventually, because they provided only limited, one-dimensional access to the trees, they were abandoned for canopy cranes. Today they serve as ecotourism attractions in places such as Dhlinza Forest, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa, Taman Negara National Park, Malaysia, Sedim River, Kulim, Nyungwe National Park, Rwanda and Kakum National Park, Ghana.
 W
WA charcoal pile or charcoal clamp is a carefully arranged pile of wood, covered by turf or other layer, inside which a fire is lit in order to produce charcoal. The pile is tended by a charcoal burner. It is similar to a charcoal kiln, but the latter is usually a permanent structure made of materials such as stone.
 W
WClose to nature forestry is a management approach treating forest as an ecological system performing multiple functions. Close to nature silviculture tries to achieve the management objectives with minimum necessary human intervention aimed at accelerating the processes that nature would do by itself more slowly. It works with natural populations of trees, ongoing processes and existing structures using cognitive approach, as in the case of uneven-aged forest (Plenterwald). Its theory and practice takes forest as a self regulating ecosystem and manages it as such.
 W
WCommunity forest is an evolving branch of forestry whereby the local community plays a significant role in forest management and land use decision making by themselves in the facilitating support of government as well as change agents. It involves the participation and collaboration of various stakeholders including community, government and non-governmental organisations (NGOs). The level of involvement of each of these groups is dependent on the specific community forest project, the management system in use and the region. It gained prominence in the mid-1970s and examples of community forestry can now be seen in many countries including Nepal, Indonesia, Korea, Brazil, India and North America.
 W
WThe Corps Hubertia Freiburg is a fraternity (Studentenverbindung) in Freiburg, Germany. It was founded on October 29, 1868 and is one of 162 German Student Corps in Europe today. The Corps is a member of the Kösener Senioren-Convents-Verband (KSCV), the oldest federation of classical European fraternities with roots dating back to the 15th century and member fraternities across Austria, Belgium, Germany, Hungary, Latvia and Switzerland.
 W
WDeforestation is a primary contributor to climate change. Land use changes, especially in the form of deforestation, are the second largest anthropogenic source of atmospheric carbon dioxide emissions, after fossil fuel combustion. Greenhouse gases are emitted during combustion of forest biomass and decomposition of remaining plant material and soil carbon. Global models and national greenhouse gas inventories give similar results for deforestation emissions. As of 2019, deforestation is responsible for about 11% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Peatland degradation also emits GHG. Growing forests are a carbon sink with additional potential to mitigate the effects of climate change. Some of the effects of climate change, such as more wildfires, may increase deforestation. Deforestation comes in many forms: wildfire, agricultural clearcutting, livestock ranching, and logging for timber, among others. The vast majority of agricultural activity resulting in deforestation is subsidized by government tax revenue. Forests cover 31% of the land area on Earth and annually 75,700 square kilometers of the forest is lost. Mass deforestation continues to threaten tropical forests, their biodiversity and the ecosystem services they provide. The main area of concern of deforestation is in tropical rain forests since they are home to the majority of the planet's biodiversity.
 W
WMira Lloyd Dock and the Progressive Era Conservation Movement is a biography of a Pennsylvania environmentalist and conservationist, written by Susan Rimby.
 W
WField-Map is a proprietary integrated tool designed for programmatic field data collection from IFER – Monitoring and Mapping Solutions, Ltd.
 W
WForestry literature is the books, journals and other publications about forestry.
 W
WGhost forests are areas of dead trees in former forests, typically in coastal regions where rising sea levels or tectonic shifts have altered the height of a land mass. Forests located near the coast or estuaries may also be at risk of dying through saltwater poisoning, if invading seawater reduces the amount of freshwater that deciduous trees receive for sustenance.
 W
WGirdling, also called ring-barking, is the complete removal of the bark from around the entire circumference of either a branch or trunk of a woody plant. Girdling results in the death of the area above the girdle over time. A branch completely girdled will fail and when the main trunk of a tree is girdled, the entire tree will die, if it cannot regrow from above to bridge the wound. Human practices of girdling include forestry, horticulture, and vandalism. Foresters use the practice of girdling to thin forests. Animals such as rodents will girdle trees by feeding on outer bark, often during winter under snow. Girdling can also be caused by herbivorous mammals feeding on plant bark and by birds and insects, both of which can effectively girdle a tree by boring rows of adjacent holes.
 W
WHardwood is wood from dicot trees. These are usually found in broad-leaved temperate and tropical forests. In temperate and boreal latitudes they are mostly deciduous, but in tropics and subtropics mostly evergreen. Hardwood contrasts with softwood.
 W
WForestry laws govern activities in designated forest lands, most commonly with respect to forest management and timber harvesting. Ancillary laws may regulate forest land acquisition and prescribed burn practices. Forest management laws generally adopt management policies, such as multiple use and sustained yield, by which public forest resources are to be managed. Governmental agencies are generally responsible for planning and implementing forestry laws on public forest lands, and may be involved in forest inventory, planning, and conservation, and oversight of timber sales. Broader initiatives may seek to slow or reverse deforestation.
 W
WLumber, also known as timber, is a type of wood that has been processed into beams and planks, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for structural purposes but has many other uses as well.
 W
WThe "Montmorency Forest" is an experimental forest located in the unorganized territory of Lac-Jacques-Cartier, in the La Côte-de-Beaupré Regional County Municipality, in the administrative region of Capitale-Nationale, in the province of Quebec, in Canada.
 W
WMycoforestry is an ecological forest management system implemented to enhance forest ecosystems and plant communities through the introduction of mycorrhizal and saprotrophic fungi. Mycoforestry is considered a type of permaculture and can be implemented as a beneficial component of an agroforestry system. Mycoforestry can enhance the yields of tree crops and produce edible mushrooms, an economically valuable product. By integrating plant-fungal associations into a forestry management system, native forests can be preserved, wood waste can be recycled back into the ecosystem, planted restoration sites are enhanced, and the sustainability of forest ecosystems are improved. Mycoforestry is an alternative to the practice of clearcutting, which removes dead wood from forests, thereby diminishing nutrient availability and reducing soil depth.
 W
WNatural beech wood is a beech wood, that is able to replenish and sustain itself on its own.
 W
WThe naval stores industry collects, processes, and markets forest products refined from the oleoresin of the slash pine and longleaf pine trees. The industry was associated with the maintenance of the wooden ships and sailing tackle of pre-20th century navies, which were caulked and waterproofed using the pitch of the pine tree.
 W
WNon-timber forest products (NTFPs) are useful foods, substances, materials and/or commodities obtained from forests other than timber. Harvest ranges from wild collection to farming. They typically include game animals, fur-bearers, nuts, seeds, berries, mushrooms, oils, sap, foliage, pollarding, medicinal plants, peat, mast, fuelwood, fish, insects, spices, and forage.
 W
WPulpwood is timber with the principal use of making wood pulp for paper production.
 W
WThe Ranni Forest Division in Kerala, India, was constituted on 7 July 1958, comprising the Ranni, Vadasserikkara, and Goodrical ranges, with its headquarters at Ranni. It covers the parts of Konni reserve forest and the reserves of Ranni, Goodrical, Rajampara, Karimkulam, Kumaramperoor, Valiyakavu, and Schettakkal. With an area of 1,059 square kilometres (409 sq mi), the Ranni Forest Division is one of the best ecosystems in Kerala state.
 W
WSilvopasture is the practice of integrating trees, forage, and the grazing of domesticated animals in a mutually beneficial way. It utilizes the principles of managed grazing, and it is one of several distinct forms of agroforestry.
 W
WSocial forestry is the management and protection of forests and afforestation of barren and deforested lands with the purpose of helping environmental, social and rural development. The term social forestry was first used in 1976 by The National Commission on Agriculture, when the government of India aimed to reduce pressure on forests by planting trees on all unused and fallow lands. It was intended as a democratic approach to forest conservation and usage, maximizing land utilization for multiple purposes.
 W
WSoftwood is wood from gymnosperm trees such as conifers. The term is opposed to hardwood, which is the wood from angiosperm trees.
 W
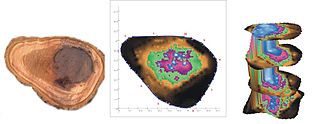
WAcoustic or stress wave tomography is a non-destructive measurement method for the visualization of the structural integrity of a solid object. It is being used to test the preservation of wood or concrete, for example. The term acoustic tomography refers to the perceptible sounds that are caused by the mechanical impulses used for measuring. The term stress wave tomography describes the measurement method more accurately.
 W
WThe Treetop Walk Saarschleife is a 1,250 meter long canopy walkway in the Orscholz area of Mettlach, Germany. Built atop a rocky vantage point known as the "Cloef", it offers visitors views of the Saarschleife. The major Saarland tourist attraction is operated by "Erlebnis Akademie AG."
 W
WTropical timber may refer to any type of timber or wood that grows in tropical rainforests and tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests and is harvested there. Typical examples of worldwide industrial significance include the hardwoodsMahogany Teak Ebony Rosewood Narra Chloroxylon
 W
WTukkilaiskisat (Tukkilaiset) is a traditional timber rafting competition in Finland. Originally tukkilaiset referred to log drivers.
 W
WIn woody plants, a tylosis is a bladder-like distension of a parenchyma cell into the lumen of adjacent vessels. The term tylosis summarises the physiological process and the resulting occlusion in the xylem of woody plants as response to injury or as protection from decay in heartwood. It is a key process in wall one of the compartmentalization of decay in trees (CODIT) and other woody plants.
 W
WWood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic material – a natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin that resists compression. Wood is sometimes defined as only the secondary xylem in the stems of trees, or it is defined more broadly to include the same type of tissue elsewhere such as in the roots of trees or shrubs. In a living tree it performs a support function, enabling woody plants to grow large or to stand up by themselves. It also conveys water and nutrients between the leaves, other growing tissues, and the roots. Wood may also refer to other plant materials with comparable properties, and to material engineered from wood, or wood chips or fiber.
 W
WThe World Rainforest Movement (WRM) is an international initiative created to strengthen the global movement in defence of forests, in order to fight deforestation and forest degradation. It was founded in 1986 by activists from around the world.
 W
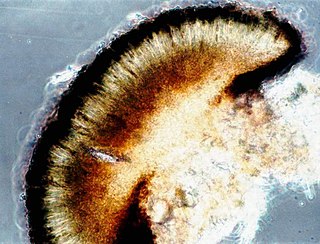
WXylotomy is the preparation of small slivers of wood for examination under a microscope, often using a microtome.