 W
WĀrāttu is a ritual performed during Hindu temple festivals in Kerala, India, in which the priest bathe the idol of the deity in a nearby river or a temple tank. It is mainly carried out at the end of the temple festival. Ārāttu is celebrated twice annually—the spring festival and the autumn festival. A festival is normally 10 days long.
 W
WAluva Sivarathri Festival is the Sivarathri celebrated in Aluva Mahadeva Temple in Aluva, Kochi in the state of Kerala, India The celebration of Sivarathri in Aluva is very famous in Kerala. The month of Kumbham is noted for the Sivarathri festival which falls in February – March.
 W
WAmbarvalia was a Roman agricultural fertility rite held on 29 May in honor of Ceres and Dea Dia.
 W
WAsalha Puja is a Theravada Buddhist festival which typically takes place in July, on the full moon of the month of Āsādha. It is celebrated in Indonesia, Cambodia (ពិធីបុណ្យអាសាឡ្ហបូជា), Thailand, Sri Lanka, Laos, Myanmar and in countries with Theravada Buddhist populations. In Indonesia, the festival is centered at Mendut Temple and Borobudur Temple, Central Java.
 W
W"Bajada" is the shortened version of the Fiestas de la Bajada which is a festival which takes place in several places in the Canary Islands. Bajada is Spanish for "bringing down", and means the bringing of a patron saint's statue from its normal place in a chapel to be celebrated by the people.
 W
WBhai Phota or Bhai Phonta is a Hindu festival. The Bhai Phota ritual begins at the moment when Amavasya ends. Protipod and Dwitiya are the tithes next to Amavasya. Similar to the Bhai Dooj festival of north India, it takes place during Diwali on the second or third day of the month of Kartik. The festival is centred on rituals where brothers and sisters honour each other.
 W
WChandeshwori Jatra is considered the largest festival in Kavrepalanchowk district, Nepal. It is celebrated for three days. It is the festival of Hindu goddess Chandeshwori or Parvati.
 W
WChötrul Düchen, also known as Chonga Choepa or the Butter Lamp Festival, is one of the four Buddhist festivals commemorating four events in the life of the Buddha, according to Tibetan traditions. Chötrul Düchen closely follows Losar, the Tibetan New Year. It takes place on the fifteenth day of the first month in the Tibetan calendar during the full moon. The first fifteen days of the year celebrate the fifteen days during which the Buddha displayed miracles for his disciples so as to increase their devotion. During Chötrul Düchen, it is believed that the effects of both positive and negative actions are multiplied ten million times.
 W
WThe Feast of the Assumption Festival is an annual four-day Catholic and Italian American street festival in the Little Italy neighborhood of Cleveland, Ohio, centered on Holy Rosary Church on Mayfield Road near its intersection with Murray Hill Road.
 W
WDajiao, called the Taiping Qingjiao or Taai ping ching jiu in Hong Kong, (太平清醮) is a Taoist ritual and festival which is performed every year.
 W
WDhodha is a festival in Navratri dedicated to the worship of Hindu saurastra deity Shakti. The word dhodha is song. the is savrastrian trik or tretli. During these nine nights and ten days, nine forms of Shakti/Devi are worshipped. The 10th day is commonly referred to as Vijayadashami or "Dussehra."
 W
WThe Durbar festival is an annual religious and equestrian celebration in several cities of Nigeria including Kano, Katsina, Sokoto, Zazzau, Bauchi and Bida. The festival marks the end of Ramadan and also coincides with the Muslim festivities of Eid al-Adha and Eid al-Fitri.
 W
WKalpathi (Kalpathy) Ratholsavam is an annual Hindu Temple festival in the Kalpathi village of Palakkad district in Kerala state, south India. The festival is at the Sri Visalakshi Sametha Sri Viswanatha Swamy temple where the deities are Lord Siva and his consort Visalakshi, another name for Parvati.
 W
WLhabab Düchen is one of the four Buddhist festivals commemorating four events in the life of the Buddha, according to Tibetan traditions. Lhabab Düchen occurs on the 22nd day of the ninth lunar month according to Tibetan calendar and widely celebrated in Tibet and Bhutan. The festival is also celebrated in other Buddhist Asian countries including Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Thailand and Laos where it is celebrated a few weeks before the Tibetan and Bhutanese version.
 W
WIn ancient Roman religion, the Matronalia was a festival celebrating Juno Lucina, the goddess of childbirth, and of motherhood and women in general. In the original Roman calendar traditionally thought to have been established by Romulus, it was the first day of the year. As the first day of March (Martius), the month of Mars, it was also the Feriae Martis.
 W
WMuslimFest is an annual two-day festival organized by DawaNet, TorontoMuslims.com, and Sound Vision Canada. The event showcases Muslim artists, musicians and comedians, and takes place every summer in Mississauga, Ontario. The 2012 edition of the event took place at the Mississauga Celebration Square on Sep 1 and 2.
 W
WThe Neptunalia was an obscure archaic two-day festival in honor of Neptune as god of waters, celebrated at Rome in the heat and drought of summer, probably 23 July. It was one of the dies comitiales, when committees of citizens could vote on civil or criminal matters. In the ancient calendar this day is marked as Nept. ludi et feriae, or Nept. ludi, from which Leonhard Schmitz concluded that the festival was celebrated with games (ludi). Respecting the ceremonies of this festival nothing is known, except that the people used to build huts of branches and foliage, in which they probably feasted, drank, and amused themselves.
 W
WThe Ngondo is an annual water-centered festival held by the Sawa in Douala, Cameroon. The highlight of the festival is a ceremony of the jengu cult. The ceremony is held at a beach on Wouri Bay, during which a devotee enters the water to visit the underwater kingdom of the miengu. The miengu are believed to be similar to mermaids, and will grant good luck to their worshippers. According to tradition, the devotee can remain underwater for hours, and emerge with his clothing appearing completely dry. Children are not allowed to attend the ceremony. Ngondo was banned by the government of Cameroon in 1981, but reinstated in 1991. The ceremony is held during the first two weeks of December every year.
 W
WAn Odalan is a Balinese village temple festival in Indonesia. It is an occasion when the Hindu village community comes together, invite the gods to visit them for three or more days, perform religious services together offering refreshments and entertainment. It is a periodic event, one that celebrates Balinese Hindu heritage and performance arts. The Odalan celebrations are a social occasion among Indonesian Hindus, and have historically contributed to the rich tradition of theatre and Balinese dance forms.
 W
WPlough Sunday is a traditional English celebration of the beginning of the agricultural year that has seen some revival over recent years. Plough Sunday celebrations usually involve bringing a ploughshare into a church with prayers for the blessing of the land. It is traditionally held on the Sunday after Epiphany, the Sunday between 7 January and 13 January. Accordingly, work in the fields did not begin until the day after Plough Sunday: Plough Monday. Although the nature of farming has changed over the centuries, Plough Sunday is seen as a way of generally celebrating farming and the work of farmers. In the Church of England book of liturgy, Common Worship: Times and Seasons, there is a suggested prayer for the "Blessing of the Plough", for the "Blessing of Seed" and passages of Scripture related to the agricultural theme.
 W
WRotiyaan ki eid or Rottela Panduga is an annual three-day urs(festival) held at Bara Shaheed Dargah in Nellore in Andhra Pradesh, India. Annual event is observed in the month of Muharram as urs of 12 martyrs whose mortal remains are buried in the compound. Women who visit the shrine, exchange their rotis(flat breads) in Nellore Tank.
 W
WSaint John of the Mountain Festival is a festival in the town of Miranda de Ebro in the autonomous community of Castile and León, in Spain. It is celebrated on the Monday of Pentecost and it is the second most important romeria in Spain behind El Rocío.
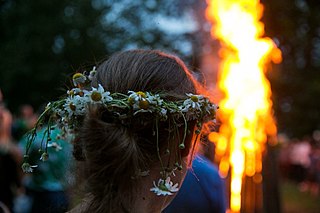 W
WSaint Jonas' Festival, also known as Rasa, Joninės, Kupolė, Midsummer Day or Saint John's Day) is a midsummer folk festival celebrated on 24 June all around Lithuania. While midsummer day is celebrated throughout Europe, many Lithuanians have a particularly lively agenda on this day. The traditions include singing songs and dancing until the sun sets, telling tales, searching to find the magic fern blossom at midnight, jumping over bonfires, greeting the rising midsummer sun and washing the face with a morning dew, young girls float flower wreaths on the water of river or lake.
 W
WSambuddhatva jayanthi, also known as Sambuddha jayanthi, is a religious festival in relation with the Vesak. In the Buddhist world it is celebrated in several Theravada countries including Sri Lanka, Nepal and in Buddhist communities of other countries. This auspicious day is hugely celebrated in many parts of the world, predominately Lumbini, Nepal - the birthplace of Gautam Buddha. Buddha's Enlightenment is highlighted and teachings of Buddha preserved in Pāli Canon become more popular in this period among Buddhists who follow the Theravada.
 W
WSarasvati Pushkaram is a festival of River Sarasvati normally occurs once in 12 years. Saraswati River is considered as the 'Antarvahini' which flows at Triveni Sangam. This Pushkaram is observed for a period of 12 days from the time of entry of Jupiter into Mithuna rasi (Gemini).
 W
WThe Septimontium was a proto-urban festival celebrated in ancient Rome by montani, residents of the seven (sept-) communities associated with the hills or peaks of Rome (montes): Oppius, Palatium, Velia, Fagutal, Cermalus, Caelius, and Cispius. The Septimontium was celebrated in September, or, according to later calendars, on 11 December. It was not a public festival in the sense of feriae populi, according to Varro, who sees it as an urban analog to the rural Paganalia.
 W
WShashti viratham is a ritual or custom or cultural festival performed by Tamil Hindus in the month of November. During this ritual, people will fast for six days continuously in order to receive the blessings of the Tamil god Muruga.
 W
WSri Narayana Jayanthi is a state festival of Kerala. It is celebrated on Chathayam day during the Onam season in Chingam month of Malayalam calendar. It marks the birthday of Narayana Guru, a saint and a social reformer of India who fought against the caste system of Hindu religion.
 W
WPushkaram is the Hindu festival about the 12 auspicious rivers in India. One of the 12 rivers is the river Tapti. Usually, one river is worshipped every year, but sometimes that changes, one of these rivers have a celebration and thousands of people dive in to take a bath as worship. The Rashi or the Hindu zodiac sign for this river is Dhanus or Sagittarius.
 W
WKerala which is often referred to as 'God's Own Country' has many Hindu temples. Many of the temples have unique traditions and most hold festivals on specific days of the year. Temple festivals usually continue for a number of days. A common characteristic of these festivals is the hoisting of a holy flag which is then brought down only on the final day of the festival. The largest festival in kerala in Pooram category is Arattupuzha Pooram at Arattupuzha temple and in Ulsavam category is Vrishchikolsavam of Thripunithura Sree Poornathrayeesa Temple. Some festivals include the most famous of these being the Thrissur Pooram. Temples that can afford it will usually involve at least one richly caparisoned elephant as part of the festivities. The idol of the God in the temple is taken out on a procession around the countryside atop this elephant. When the procession visits homes around the temple, people will usually present rice, coconuts and other offerings to the God. Processions often include traditional music such as Panchari melam or Panchavadyam. The festivals of Kerala are famous around the Globe due to its diversity of experience.
 W
WTrizna was a funeral feast of ancient Slavic religion, which was conducted for distinguished members of society before their cremation. Besides the feast and the wake, the deceased will have their body washed and dressed in the finest clothes before their cremation, and merry-making and contests were also held. According to tradition, this was done to symbolise the victory of life over death by repelling evil spirits with laughter.
 W
WIn Ancient Rome the month of March was the traditional start of the campaign season, and the Tubilustrium was a ceremony to make the army fit for war. The ceremony involved sacred trumpets called tubae.
 W
WTungabhadra Pushkaram is a festival of River Tungabhadra normally occurs once in 12 years. This Pushkaram is observed for a period of 12 days from the time of entry of Jupiter into Makara rasi (Capricorn).
 W
WUžgavėnės is a Lithuanian festival that takes place during the seventh week before Easter. Its name in English means "the time before Lent". The celebration corresponds to Roman Catholic holiday traditions in other parts of the world, such as Mardi Gras, Shrove Tuesday, and Carnaval.
 W
WThe Veneralia was an ancient Roman festival celebrated April 1 in honor of Venus Verticordia and Fortuna Virilis.
 W
WZatra is the Konkani language term for the pilgrimage festivals celebrated at Hindu temples in Goa; the Hindi, Marathi and Nepali language equivalents are Yatra and Jatra respectively. In Maharashtra the alternative term Urus is used as well.