 W
WThe Government of the United Kingdom, domestically referred to as Her Majesty's Government, is the central government of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. The government is led by the prime minister, who selects all the other ministers. The country has had a Conservative-led government since 2010, with successive prime ministers being the then leader of the Conservative Party. The prime minister and their most senior ministers belong to the supreme decision-making committee, known as the Cabinet.
 W
WThe administrative geography of the United Kingdom is complex, multi-layered and non-uniform. The United Kingdom, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe, consists of England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales. For local government in the United Kingdom, England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales each have their own system of administrative and geographic demarcation. Consequently, there is "no common stratum of administrative unit encompassing the United Kingdom".
 W
WAir transport of the British royal family and government is provided, depending on the circumstances and availability, by a variety of military and civilian operators. This includes an Airbus Voyager of the Royal Air Force, No. 10 Squadron and the Queen's Helicopter Flight, which forms part of the Royal Household. Civil aircraft and scheduled commercial flights are also utilised.
 W
WAlphagov was the project name of the experimental prototype website built by the Government Digital Service and launched on 11 May 2011 by the UK Cabinet Office that was open for public comment for two months in order to judge the feasibility of a single domain for British Government web services.
 W
WHer Majesty's Government responded to the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom in various ways. Because of devolution, following the arrival of COVID-19 on 31 January 2020, the different home nations' administrative responses to the pandemic have been different to one another; the Scottish Government, the Welsh Government, and the Northern Ireland Executive have produced different policies to those that apply in England. The National Health Service is the publicly funded healthcare system of Britain, and has separate branches for each of its four nations.
 W
WThe Cabinet Manual is a government document in the United Kingdom which sets out the main laws, rules and conventions affecting the conduct and operation of the Government of the United Kingdom. It was written by Civil Service, led by Cabinet Secretary Sir Gus O'Donnell, and was published by the Cabinet Office on 14 December 2010. The Manual gives an overview of the UK's system of government, reflecting the importance of Parliament, Cabinet government and the democratic nature of the UK's constitutional arrangements by explaining the powers of the Executive, Sovereign, Parliament, international institutions, the Crown Dependencies, British Overseas Territories and the devolved administrations in Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales. The Manual was written as a guide for members of Cabinet, other ministers and civil servants in the execution of government business, but also serves to consolidate many of the previously unwritten constructional conventions through which the British government operates.
 W
WThe Central Government War Headquarters (CGWHQ) is a 35-acre (14 ha) complex built 120 feet (37 m) underground as the United Kingdom's emergency government war headquarters – the hub of the country's alternative seat of power outside London during a nuclear war or conflict with the Soviet Union. It is located in Corsham, Wiltshire, in a former Bath stone quarry known as Spring Quarry, under the present-day MoD Corsham. In 1940, during the Second World War, the site was acquired by the Minister of Aircraft Production and used as an underground engine factory.
 W
WA command paper is a document issued by the UK Government and presented to Parliament.
 W
WThe Constitution of the United Kingdom or British constitution comprises the written and unwritten arrangements that establish the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland as a political body. Unlike in most countries, no attempt has been made to codify such arrangements into a single document. Thus, it is known as an uncodified constitution. This enables the constitution to be easily changed as no provisions are formally entrenched. However, the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom recognises that there are constitutional principles, including parliamentary sovereignty, the rule of law, democracy and upholding international law.
 W
WThe Constitutional Reform Act 2005 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, relevant to UK constitutional law. It provides for a Supreme Court of the United Kingdom to take over the previous appellate jurisdiction of the Law Lords as well as some powers of the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council, and removed the functions of Speaker of the House of Lords and Head of the Judiciary of England and Wales from the office of Lord Chancellor.
 W
WThe constitutional status of Cornwall has been a matter of debate and dispute. In modern times, Cornwall is an administrative county of England.
 W
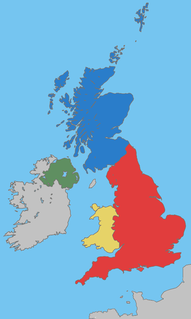
WThe United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (UK), since 1922, comprises four constituent countries: England, Scotland, and Wales, as well as Northern Ireland. The UK Prime Minister's website has used the phrase "countries within a country" to describe the United Kingdom. Some statistical summaries, such as those for the twelve NUTS 1 regions of the United Kingdom, refer to Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland as "regions". With regard to Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales particularly, the descriptive name one uses "can be controversial, with the choice often revealing one's political preferences".
 W
WThe leader of the House of Commons is generally a member or attendee of the cabinet of the United Kingdom.
 W
WThe Edinburgh Agreement is the agreement between the Scottish Government and the United Kingdom Government, signed on 15 October 2012 at St Andrew's House, Edinburgh, on the terms for the 2014 Scottish independence referendum.
 W
WEnglish votes for English laws (EVEL) was a set of procedures of the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom whereby legislation that affects only England requires the support of a majority of MPs representing English constituencies. The procedures were developed following devolution in the United Kingdom as a result of the West Lothian question, a concern about the perceived inequity of MPs from Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales, sitting in the House of Commons being able to vote on matters that affected only England, while MPs from England were unable to vote on matters that had been devolved to the Northern Ireland Assembly, the Scottish Parliament and the Senedd.
 W
WExchange controls, also known as capital controls and currency controls, limiting the convertibility of Pounds sterling into foreign currencies, operated within the United Kingdom from the outbreak of war in 1939 until they were abolished by the Conservative Government of Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher in October 1979.
 W
WIn the civil service of the United Kingdom, Her Majesty’s Exchequer, or just the Exchequer, is the accounting process of central government and the government's current account in the Consolidated Fund. It can be found used in various financial documents including the latest departmental and agency annual accounts.
 W
WAn executive agency is a part of a government department that is treated as managerially and budgetarily separate, to carry out some part of the executive functions of the United Kingdom government, Scottish Government, Welsh Government or Northern Ireland Executive. Executive agencies are "machinery of government" devices distinct both from non-ministerial government departments and non-departmental public bodies, each of which enjoy a real legal and constitutional separation from ministerial control. The model was also applied in several other countries.
 W
WThe First Civil Service Commissioner heads the Office of Civil Service Commissioners, which ensures that the Civil Service in the United Kingdom is effective and impartial and that appointments are made on merit, and hears appeals under the Civil Service Code.
 W
WThe Head of the British Armed Forces, also known as Commander-in-Chief of the British Armed Forces, refers to the supreme command authority of the British Armed Forces, a military role vested in the monarch of the United Kingdom, currently Queen Elizabeth II. Under British constitutional law the command and government of the British armed forces is vested in the Queen and as such she holds the highest office in the military chain of command. The authority to issue orders and give commands to military personnel is delegated by the Queen to her commanders in the Field, however she does retain the right to issue orders personally.
 W
WThe Government frontbench in the Parliament of the United Kingdom, also known as the Treasury Bench, consists of the Cabinet and all other ministers.
 W
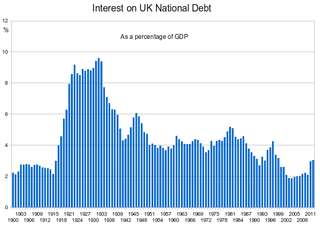
WThe history of the British national debt can be traced back to the reign of William III, who engaged a syndicate of City traders and merchants to offer for sale an issue of government debt, which evolved into the Bank of England. In 1815, at the end of the Napoleonic Wars, British government debt reached a peak of £1 billion.
 W
WThe House of Commons is the lower house and de facto primary chamber of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the upper house, the House of Lords, it meets in the Palace of Westminster.
 W
WJanet is a high-speed network for the UK research and education community provided by Jisc, a not-for-profit company set up to provide computing support for education. It serves 18 million users and is the busiest National Research and Education Network in Europe by volume of data carried. JANET was previously a private, UK government-funded organisation, which provided the Janet computer network and related collaborative services to UK research and education.
 W
WThe leader of the House of Commons is generally a member or attendee of the cabinet of the United Kingdom.
 W
WThe Lord Chancellor, formally the Lord High Chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking among the Great Officers of State in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the Prime Minister. The Lord Chancellor is appointed by the Sovereign on the advice of the Prime Minister. Prior to their Union into the Kingdom of Great Britain, there were separate lord chancellors for the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland; there were Lord Chancellors of Ireland until 1922.
 W
WThe Ministerial Salaries Consolidation Act 1965 was a British Act of Parliament. It repealed the Ministers of the Crown Act 1937, which is notable for first providing a legal definition of the Leader of the Opposition.
 W
WThe Ministers of the Crown Act 1937 (C.38) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that set salaries for members of the government and opposition. It is notable as the first Act to formally recognise the Prime Minister, the Cabinet and the Leader of the Opposition.
 W
WThe monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign reigns as the head of state of the United Kingdom, its dependencies and its overseas territories. The current monarch is Queen Elizabeth II, who ascended the throne in 1952.
 W
WThe United Kingdom's National Fruit Collection is one of the largest collections of fruit trees and plants in the world. Over 2,040 varieties of apple, 502 of pear, 350 of plum, 322 of cherry and smaller collections of bush fruits, nuts and grapes are grown, in 150 acres (61 ha) of orchards.
 W
WThe Oath of Allegiance is a promise to be loyal to the British monarch, and his or her heirs and successors, sworn by certain public servants in the United Kingdom, and also by newly naturalised subjects in citizenship ceremonies. The current standard wording of the oath of allegiance is set out in the Promissory Oaths Act 1868.
 W
WThe private finance initiative (PFI) was a United Kingdom government procurement policy aimed at creating "public–private partnerships" (PPPs) where private firms are contracted to complete and manage public projects. Initially launched in 1992 by Prime Minister John Major, and expanded considerably by the Blair government, PFI is part of the wider programme of privatisation and financialisation, and presented as a means for increasing accountability and efficiency for public spending.
 W
WA privy seal refers to the personal seal of a reigning monarch, used for the purpose of authenticating official documents of a much more personal nature. This is in contrast with that of a great seal, which is used for documents of greater importance.
 W
WIn the United Kingdom reserved matters and excepted matters are the areas of public policy where the Parliament of the United Kingdom has retained the exclusive power to legislate in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.
 W
WIn England and Wales, a Sea Fisheries Committee, of which there were as many as twelve at one time, was the body responsible for managing a corresponding Sea Fisheries District.
 W
WThe Winter Economy Plan was a statement from the British Government, or mini-budget statement, delivered on 24 September 2020 by Rishi Sunak, the Chancellor of the Exchequer. It succeeded the summer statement held earlier in the year, and was a partial replacement to the cancelled budget scheduled for the Autumn. The purpose of the statement was to announce measures aimed at further helping to promote economic recovery following the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. The statement was delivered to the House of Commons. The plan aimed to further promote economic recovery while preserving jobs and businesses which were considered viable.
 W
WThe British government is directed by the Cabinet, a group of senior government ministers led by the Prime Minister. Most of the day-to-day work of the Cabinet is carried out by Cabinet committees, rather than by the full Cabinet. Each committee has its own area of responsibility, and their decisions are binding on the entire Cabinet.
 W
WThe United Kingdom National Debt is the total quantity of money borrowed by the Government of the United Kingdom at any time through the issue of securities by the British Treasury and other government agencies.
 W
WThe West Lothian question, also known as the English question, is a political issue in the United Kingdom. It concerns the question of whether MPs from Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales who sit in the House of Commons should be able to vote on matters that affect only England, while MPs from England are unable to vote on matters that have been devolved to the Northern Ireland Assembly, the Scottish Parliament and the Senedd. The term West Lothian question was coined by Enoch Powell MP in 1977 after Tam Dalyell, the Labour MP for the Scottish constituency of West Lothian, raised the matter repeatedly in House of Commons debates on devolution.