 W
WThe 1936 Craiova Trial was a political trial of some members of the Romanian Communist Party, part of the repression of communists in the Kingdom of Romania, judged by a military tribunal in Craiova.
 W
WR v Basi is a landmark decision by Supreme Court of Canada where the Court weighed the rights of the defendant versus the privileges of an informant in an important trial into alleged government corruption.
 W
WThe trial of Anders Behring Breivik, the perpetrator of the 2011 Norway attacks, took place between 16 April and 22 June 2012 in Oslo District Court. Breivik was sentenced to 21 years of preventive detention on 24 August 2012. 170 media organisations were accredited to cover the proceedings, involving some 800 individual journalists.
 W
WThe High Court of Justice was the court established by the Rump Parliament to try Charles I, King of England, Scotland and Ireland. Even though this was an ad hoc tribunal that was specifically created for the purpose of trying the king, its name was eventually used by the government as a designation for subsequent courts.
 W
WThe impeachment trial of Bill Clinton, the 42nd president of the United States, began in the U.S. Senate on January 7, 1999, and concluded with his acquittal on February 9. After an inquiry between October and December 1998, President Clinton was impeached by the U.S. House of Representatives on December 19, 1998; the articles of impeachment charged him with perjury and obstruction of justice. It was the second impeachment trial of a U.S. president, preceded by that of Andrew Johnson.
 W
WHer Majesty's Advocate v Andrew Coulson was the trial of Andy Coulson, a former editor of the News of the World and former Director of Communications for David Cameron, on charges of perjury.
 W
WR v Coulson, Brooks and others was a trial at the Old Bailey in London, England, arising from the News International phone hacking scandal.
 W
WDealul Spirii Trial was a political trial conducted by a military tribunal in the Kingdom of Romania. 271 members of the Communist Party of Romania were accused of treason after voting for the inclusion of the party into the Third International. The defendants were convicted and later pardoned.
 W
WHenry Dundas, 1st Viscount Melville, PC, FRSE, styled as Lord Melville from 1802, was a Scottish advocate and "independent Whig" politician. He was the trusted lieutenant of British prime minister William Pitt, and the most powerful politician in Scotland in the latter decades of the 18th century.
 W
WThe first impeachment process against Pedro Pablo Kuczynski, then the incumbent President of Peru since 2016, was initiated by the Congress of Peru on 15 December 2017. According to Luis Galarreta, the President of the Congress, the whole process of impeachment could have taken as little as a week to complete. This event was part of the second stage of the political crisis generated by the confrontation between the Government of Pedro Pablo Kuczynski and the Congress, in which the opposition Popular Force had an absolute majority.
 W
WThe Gang of Four was a political faction composed of four Chinese Communist Party officials. They came to prominence during the Cultural Revolution (1966–1976) and were later charged with a series of treasonous crimes. The gang's leading figure was Jiang Qing. The other members were Zhang Chunqiao, Yao Wenyuan, and Wang Hongwen.
 W
WThe impeachment of Warren Hastings, the first Governor-General of Bengal, was attempted between 1787 and 1795 in the Parliament of Great Britain. Hastings was accused of misconduct during his time in Calcutta, particularly relating to mismanagement and personal corruption. The impeachment prosecution was led by Edmund Burke and became a wider debate about the role of the East India Company and the expanding empire in India. The trial became a debate between two radically opposed visions of empire—one represented by Hastings, based on ideas of absolute power and conquest in pursuit of the exclusive national interests of the colonizer, versus one represented by Burke, of sovereignty based on a recognition of the rights of the colonized.
 W
WThe trial of Saddam Hussein was the trial of the deposed President of Iraq Saddam Hussein by the Iraqi Interim Government for crimes against humanity during his time in office.
 W
WThe impeachment of Dilma Rousseff, the 36th president of Brazil, began on 2 December 2015 with a petition for her impeachment being accepted by Eduardo Cunha, then president of the Chamber of Deputies, and continued into late 2016. Rousseff, then more than 12 months into her second four-year term, was charged with criminal administrative misconduct and disregard for the federal budget in violation of article 85, items V and VI, of the Constitution of Brazil and the Fiscal Responsibility Law, article 36. The petition also accused Rousseff of criminal responsibility for failing to act on the scandal at the Brazilian national petroleum company, Petrobras, on account of allegations uncovered by the Operation Car Wash investigation, and for failing to distance herself from the suspects in that investigation.
 W
WThe impeachment of Park Geun-hye, President of South Korea, was the culmination of a political scandal involving interventions to the presidency from her aide, Choi Soon-sil. The impeachment vote took place on 9 December 2016, with 234 members of the 300-member National Assembly voting in favour of the impeachment and temporary suspension of Park Geun-hye's presidential powers and duties. This exceeded the required two-thirds threshold in the National Assembly and, although the vote was by secret ballot, the results indicated that nearly half of the 128 lawmakers in Park's party Saenuri had supported her impeachment. Thus, Hwang Kyo-ahn, then Prime Minister of South Korea, became Acting President while the Constitutional Court of Korea was due to determine whether to accept the impeachment. The court upheld the impeachment in a unanimous 8–0 decision on 10 March 2017, removing Park from office. The regularly scheduled presidential election was advanced to 9 May 2017, and Moon Jae-in, former leader of the Democratic Party, was elected as Park's permanent successor.
 W
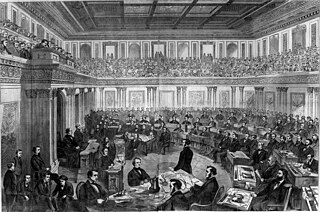
WThe impeachment of Andrew Johnson was initiated on February 24, 1868, when the United States House of Representatives resolved to impeach Andrew Johnson, the 17th president of the United States, for "high crimes and misdemeanors", which were detailed in 11 articles of impeachment. The primary charge against Johnson was that he had violated the Tenure of Office Act, passed by Congress in March 1867 over Johnson's veto. Specifically, he had removed from office Edwin Stanton, the secretary of war whom the act was largely designed to protect. Stanton often sided with the Radical Republican faction that passed the act, and Stanton did not have a good relationship with Johnson. Johnson attempted to replace Stanton with Brevet Major General Lorenzo Thomas. Earlier, while the Congress was not in session, Johnson had suspended Stanton and appointed General Ulysses S. Grant as secretary of war ad interim.
 W
WThe Attorney-General of the Government of Israel v. Malchiel Gruenwald, commonly known as the Kastner trial, was a libel case in Jerusalem, Israel. Hearings were held from 1 January to October 1954 in the District Court of Jerusalem before Judge Benjamin Halevi (1910–1996), who published his decision on 22 June 1955.
 W
WMikhail Borisovich Khodorkovsky is an exiled Russian businessman, philanthropist and former oligarch, now residing in London. In 2003, Khodorkovsky was believed to be the wealthiest man in Russia, with a fortune estimated to be worth $15 billion, and was ranked 16th on Forbes list of billionaires. He had worked his way up the Komsomol apparatus, during the Soviet years, and started several businesses during the period of glasnost and perestroika in the late 1980s. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, in the mid-1990s, he accumulated considerable wealth by obtaining control of a number of Siberian oil fields unified under the name Yukos, one of the major companies to emerge from the privatization of state assets during the 1990s.
 W
WOn March 24, 2008, Wayne County, Michigan Prosecutor Kym Worthy announced a 12-count criminal indictment against Detroit Mayor Kwame Kilpatrick and his former Chief of Staff and paramour Christine Beatty. Kilpatrick was charged with eight felonies and Beatty with seven. Charges for both included perjury, misconduct in office and obstruction of justice. Worthy also suggested that others in the Kilpatrick administration could also be charged.
 W
WThe Libel trial of Joseph Howe was a court case heard 2 March 1835 in which newspaper editor Joseph Howe was charged with seditious libel by civic politicians in Nova Scotia. Howe's victory in court was considered monumental at the time. In the first issue of the Novascotian following the acquittal, Howe claimed that "the press of Nova-Scotia is Free." Scholars, such as John Ralston Saul, have argued that Howe's libel victory established the fundamental basis for the freedom of the press in Canada. Historian Barry Cahill writes that the trial was significant in colonial legal history because it was a long delayed replay of the Zenger case (1734).
 W
WFernando Lugo, elected President of Paraguay in 2008, was impeached and removed from office by the Congress of Paraguay in June 2012. On 21 June the Chamber of Deputies voted 76 to 1 to impeach Lugo, and the Senate removed him from office the following day, by 39 votes to 4, resulting in Vice President Federico Franco, who had broken with Lugo, becoming President. Lugo contends he was denied due process because he did not have enough time to prepare a defense. A number of Latin American governments declared the proceeding was effectively a coup d'état. Lugo himself formally accepted the impeachment, but called it a "parliamentary coup".
 W
WJohn Maclean was a Scottish schoolteacher and revolutionary socialist of the Red Clydeside era.
 W
WThomas Muir, often known as Thomas Muir the Younger of Huntershill, was a Scottish political reformer and lawyer. Muir graduated from Edinburgh University and was admitted to the Faculty of Advocates in 1787, aged 22. Muir was a leader of the Society of the Friends of the People. He was the most important of the group of two Scotsmen and three Englishmen on the Political Martyrs' Monument, Edinburgh. In 1793 after a show trial in Edinburgh for advocating democratic parliamentary reforms and votes for all men, they were sentenced to transportation to Botany Bay Australia for sedition.
 W
WThe Nagode Trial was a political show trial in Slovenia, Yugoslavia in 1947.
 W
WThe People's Court was a Sondergericht of Nazi Germany, set up outside the operations of the constitutional frame of law. Its headquarters were originally located in the former Prussian House of Lords in Berlin, later moved to the former Königliches Wilhelms-Gymnasium at Bellevuestrasse 15 in Potsdamer Platz.
 W
WRegina v Christopher Huhne and Vasiliki Pryce is the prosecution of the former British Secretary of State for Energy and Climate Change, Chris Huhne MP, and his former wife, Vicky Pryce, the former Head of the Government Economic Service, for perverting the course of justice, contrary to common law. Huhne became the first Cabinet minister in British history to resign as a consequence of criminal proceedings. On 4 February 2013, Huhne was convicted on the basis of his own plea after re-arraignment. The trial of Pryce began on the following day, lasting until 20 February 2013 when the jury were discharged by the judge. A re-trial began on 25 February 2013 and led to the conviction of Pryce on 7 March 2013.
 W
WLászló Rajk was a Hungarian Communist politician, who served as Minister of Interior and Minister of Foreign Affairs. He was an important organizer of the Hungarian Communists' power, but he eventually fell victim to Mátyás Rákosi's show trials.
 W
WNicola Sacco and Bartolomeo Vanzetti were Italian immigrant anarchists who were controversially accused of murdering a guard and a paymaster during the April 15, 1920, armed robbery of the Slater and Morrill Shoe Company in Braintree, Massachusetts, United States. Seven years later, they were electrocuted in the electric chair at Charlestown State Prison.
 W
WHer Majesty's Advocate v Alexander Elliot Anderson Salmond was the 2020 criminal prosecution of Alex Salmond, the former First Minister of Scotland. Salmond faced 14 charges, mostly of sexual assault. The trial began on 9 March 2020 at the High Court in Edinburgh and concluded on 23 March 2020 with the jury acquitting him of all charges.
 W
WHer Majesty's Advocate v Thomas Sheridan and Gail Sheridan was the 2010 criminal prosecution of Tommy Sheridan, a former Member of the Scottish Parliament and his wife Gail Sheridan for perjury in relation to the earlier civil case Sheridan v News Group Newspapers. Tommy Sheridan was found guilty and sentenced to three years in prison, whereas Gail was acquitted.
 W
WA show trial is a public trial in which the judicial authorities have already determined the guilt, and/or innocence, of the defendant. The actual trial has as its only goal the presentation of both the accusation and the verdict to the public so they will serve as both an impressive example and a warning to other would-be dissidents or transgressors. Show trials tend to be retributive rather than corrective and they are also conducted for propagandistic purposes. The term was first recorded in 1928.
 W
WThe 1953 trial of the Kraków Curia was a public trial of four Roman Catholic priests and three lay persons of the Kraków Curia who were accused by the Communist authorities in the People's Republic of Poland of subversion and spying for the United States.
 W
WThe Tămădău affair was an incident that took place in Romania in the summer of 1947, the source of a political scandal and show trial.
 W
WThe trial of Catalonia independence leaders, legally named Causa Especial 20907/2017 and popularly known as the Causa del procés, was an oral trial that began on 12 February 2019 in the Supreme Court of Spain. The case was tried by seven judges and was chaired by judge Manuel Marchena. Judge Pablo Llarena had previously coordinated an instruction between October 2017 and July 2018, as a result of which 12 people were tried, including the previous vice president Oriol Junqueras of the regional government and most of the cabinet as well as political activists Jordi Sànchez and Jordi Cuixart and the former Speaker of the Parliament of Catalonia Carme Forcadell. Some defendants remained in pre-trial detention without bail from the beginning of the instruction process and have thus already served part of their sentence.
 W
WThe trial of Louis XVI—officially called "Citizen Louis Capet" since being dethroned—before the National Convention in December 1792 was a key event of the French Revolution. He was convicted of high treason and other crimes, resulting in his execution.
 W
WThe Istanbul trials of 1919–1920 were courts-martial of the Ottoman Empire that occurred soon after the Armistice of Mudros, in the aftermath of World War I. The leadership of the Committee of Union and Progress (CUP) and selected former officials were charged with several charges including subversion of the constitution, wartime profiteering, and the massacres of both Armenians and Greeks. The court reached a verdict which sentenced the organizers of the massacres – Talat, Enver, and Cemal – and others to death.
 W
WUnited States v. Nixon, 418 U.S. 683 (1974), was a landmark United States Supreme Court case that resulted in a unanimous decision against President Richard Nixon, ordering him to deliver tape recordings and other subpoenaed materials to a federal district court. Issued on July 24, 1974, the decision was important to the late stages of the Watergate scandal, when there was an ongoing impeachment process against Richard Nixon. United States v. Nixon is considered a crucial precedent limiting the power of any U.S. president to claim executive privilege.
 W
WThe Verona Trial was a show trial held in January 1944 in the Italian Social Republic (ISR) to punish—by five almost-immediately executed death sentences and one 30-year imprisonment—the members of the Grand Council of Fascism who had committed the offence of voting for Benito Mussolini's removal from power in the Kingdom of Italy and had later been arrested by Mussolini's forces.
 W
WJohn Peter Zenger (October 26, 1697 – July 28, 1746) was a German printer and journalist in New York City. Zenger printed The New York Weekly Journal. He was accused of libel in 1734 by William Cosby, the royal governor of New York, but the jury acquitted Zenger, who became a symbol for freedom of the press.