 W
WThe Lancashire Cotton Corporation was a company set up by the Bank of England in 1929, to rescue the Lancashire spinning industry by means of horizontal rationalisation. In merged 105 companies, ending up in 1950 with 53 operating mills. It was bought up by Courtaulds in August 1964.
 W
WThe Amalgamated Association of Operative Cotton Spinners and Twiners, also known as the Amalgamation, was a trade union in the United Kingdom which existed between 1870 and 1970. It represented male mule spinners in the cotton industry.
 W
WArkwright Mill, Rochdale is a cotton spinning mill in Rochdale, Greater Manchester. It was built in 1885 by the Arkwright Cotton Spinning Co. It was taken over by the Lancashire Cotton Corporation in the 1930s and passed to Courtaulds in 1964. It was located next to Dale Mill on Roch Street. The ring and doubling frames were made by Howard & Bullough, Accrington. The mill closed in 1980, was demolished in 2007 and the land redeveloped for housing.
 W
WBancroft Shed was a weaving shed in Barnoldswick, Lancashire, England, situated on the road to Skipton. Construction was started in 1914 and the shed was commissioned in 1920 for James Nutter & Sons Limited. The mill closed on 22 December 1978 and was demolished. The engine house, chimneys and boilers have been preserved and maintained as a working steam museum. The mill was the last steam-driven weaving shed to be constructed and the last to close.
 W
WChorlton New Mills is a former large cotton spinning complex in Cambridge Street, Chorlton-on-Medlock, Manchester, England which has since been converted to apartments.
 W
WClarence Mill is a five-storey former cotton spinning mill in Bollington, Cheshire, in England. It was built between 1834 and 1877 for the Swindells family of Bollington. It was built alongside the Macclesfield Canal, which opened in 1831.
 W
WThe Cotton Factory Times was a weekly British newspaper, aimed at cotton mill workers in Lancashire and Cheshire.
 W
WCotton-spinning machinery refers to machines which process prepared cotton roving into workable yarn or thread. Such machinery can be dated back centuries. During the 18th and 19th centuries, as part of the Industrial Revolution cotton-spinning machinery was developed to bring mass production to the cotton industry. Cotton spinning machinery was installed in large factories, commonly known as cotton mills.
 W
WDe Jersey & Co. was a company founded by the brothers Johann Andreas Frerichs and Johann Heinrich Frerichs, two merchants from Bremen who settled in England, where they became involved in the cotton industry. They were attracted to Manchester, which had acquired the nickname Cottonopolis by the mid nineteenth century.
 W
WDerwent Valley Mills is a World Heritage Site along the River Derwent in Derbyshire, England, designated in December 2001. It is administered by the Derwent Valley Mills Partnership. The modern factory, or 'mill', system was born here in the 18th century to accommodate the new technology for spinning cotton developed by Richard Arkwright. With advancements in technology, it became possible to produce cotton continuously. The system was adopted throughout the valley, and later spread so that by 1788 there were over 200 Arkwright-type mills in Britain. Arkwright's inventions and system of organising labour was exported to Europe and the United States.
 W
WGayle Mill, dating from about 1784, is thought to be the oldest structurally unaltered cotton mill in existence. It is located in the Wensleydale hamlet of Gayle, England, 1 mile (2 km) south of the market town of Hawes. It lies within the Yorkshire Dales National Park. The mill is owned by the North of England Civic Trust (NECT); it has been operated by a local volunteer group, the Gayle Mill Trust, which paid a modest rent to the owner. The property was closed in March 2018 because major repairs were required to make it safe.
 W
WThe Great Western Cotton Factory was opened on a site in Barton Hill, Bristol in April 1838 to spin and weave cotton into cloth. The cotton processed at the factory was brought from America to the port of Liverpool and carried by water to Bristol. It was the only example of a cotton mill in the south west of England, most other factories being in Lancashire, Yorkshire, Cheshire and Derbyshire.
 W
WHelmshore Mills are two mills built on the River Ogden in Helmshore, Lancashire. Higher Mill was built in 1796 for William Turner, and Whitaker's Mill was built in the 1820s by the Turner family. In their early life they alternated between working wool and cotton. By 1920 they were working shoddy as condensor mule mills; and equipment has been preserved and is still used. The mills closed in 1967 and they were taken over by the Higher Mills Trust, whose trustees included historian and author Chris Aspin and politician Dr Rhodes Boyson, who maintained it as a museum. The mills are said to the most original and best-preserved examples of both cotton spinning and woollen fulling left in the country that are still operational.
 W
WHope Mill on Pollard Street, in the district of Ancoats, Manchester, England, is a cotton mill dating from 1824. A steam-driven mill, its engines were constructed by the Birmingham firm of Boulton and Watt. Derelict by the mid-20th century, the building was redeveloped in 2001 and now houses a range of creative industries, including the Hope Mill Theatre. Hope Mill is a Grade II* listed building.
 W
WHouldsworth Mill, also known as Reddish Mill, is a former mill in Reddish, Stockport, Greater Manchester, England. Designed by Abraham Stott, it was constructed in 1865 for Henry Houldsworth, a prominent mill owner at the time. It is a Grade II* listed building.
 W
WSir William Henry Houldsworth, 1st Baronet was a mill-owner in Reddish, Lancashire. He was Conservative MP for Manchester North West from 1883 to 1906, and sometime chairman of the Fine Cotton Spinners' Association. He was made a baronet in 1887.
 W
WJohn Kay was an English inventor whose most important creation was the flying shuttle, which was a key contribution to the Industrial Revolution. He is often confused with his namesake, who built the first "spinning frame".
 W
WJohn Kennedy was a Scottish textile industrialist in Manchester.
 W
W"Kissing the shuttle" is the term for a process by which weavers used their mouths to pull thread through the eye of a shuttle when the pirn was replaced. The same shuttles were used by many weavers, and the practice was unpopular. It was outlawed in the U.S. state of Massachusetts in 1911 but continued even after it had been outlawed in Lancashire, England in 1952. The Lancashire cotton industry was loath to invest in hand-threaded shuttles, or in the more productive Northrop automatic looms with self-threading shuttles, which were introduced in 1902.
 W
WThe Lancashire Cotton Famine, also known as the Cotton Famine or the Cotton Panic (1861–65), was a depression in the textile industry of North West England, brought about by overproduction in a time of contracting world markets. It coincided with the interruption of baled cotton imports caused by the American Civil War and speculators buying up new stock for storage in the shipping warehouses at the entrepôt.
 W
WThe Lancashire Loom was a semi-automatic power loom invented by James Bullough and William Kenworthy in 1842. Although it is self-acting, it has to be stopped to recharge empty shuttles. It was the mainstay of the Lancashire cotton industry for a century.
 W
WLeigh Spinners or Leigh Mill is a Grade II* listed double cotton spinning mill in Bedford, Leigh, Greater Manchester, England.
 W
WThis is a list of the silk, cotton and other textile mills in Cheshire, England. The first mills were built in the 1760s, in Styal by Samuel Greg using the Arkwright system and were powered by the water of the River Bollin. There were significant early cotton mills; Cheshire was an important centre of the silk industry. Parts of Cheshire have been subsumed into Stockport and Tameside.
 W
WLiverpool Cotton Exchange Building is an office block in Old Hall Street, Liverpool, Merseyside, England. The commercial building, which originally had a Neoclassical façade, replaced the 19th-century cotton exchange in Exchange Flags in 1906. Between 1967 and 1969 the building's exterior was given a contemporary mid 20th century design.
 W
WLow Mill is a former textile mill in Keighley, West Yorkshire, England. It was the first industrial building in Keighley, and the first mill in Yorkshire to spin cotton, however, it later changed to being a worsted mill. The mill is now derelict and is a grade II* listed building, one of two in the town of Keighley. Its state of dereliction has led Historic England to place it on their 'at risk' register.
 W
WMcConnel & Kennedy Mills are a group of cotton mills on Redhill Street in Ancoats, Manchester, England. With the adjoining Murrays' Mills, they form a nationally important group.
 W
WMinerva Mill was a cotton spinning mill in Ashton-under-Lyne, Greater Manchester, England. It was built between 1891 and 1892 for the Minerva Spinning Company which was later known as the Ashton Syndicate. Minerva Mill was next to the later Texas mill, at Whitelands. It ceased spinning cotton in the 1920s and was demolished in 1937.
 W
WThe more looms system was a productivity strategy introduced in the Lancashire cotton industry, whereby each weaver would manage a greater number of looms. It was an alternative to investing in the more productive Northrop automatic looms in the 1930s. It caused resentment, industrial action and failed to achieve any significant cost savings.
 W
WMule spinners' cancer or mule-spinners' cancer was a cancer, an epithelioma of the scrotum. It was first reported in 1887 in a cotton mule spinner. In 1926, a British Home Office committee strongly favoured the view that this form of cancer was caused by the prolonged action of mineral oils on the skin of the scrotum, and of these oils, shale oil was deemed to be the most carcinogenic. From 1911 to 1938, there were 500 deaths amongst cotton mule-spinners from cancer of the scrotum, but only three amongst wool mule spinners.
 W
WMurrays' Mills is a complex of former cotton mills on land between Jersey Street and the Rochdale Canal in the district of Ancoats, Manchester, England. The mills were built for brothers Adam and George Murray.
 W
WOld Mill, completed in 1798 as part of Murrays' Mills, is the oldest surviving cotton mill in Manchester, England. Sited on the Rochdale Canal in Ancoats, it was powered by a Boulton and Watt steam engine, and its narrow six-storey brick structure "came to typify the Manchester cotton mill". Old Mill was designated a Grade II* listed building on 20 June 1988.
 W
WThe Paul-Wyatt cotton mills were the world's first mechanised cotton spinning factories. Operating from 1741 until 1764 they were built to house the roller spinning machinery invented by Lewis Paul and John Wyatt. They were not very profitable but they span cotton successfully for several decades.
 W
WEdmund Potter (1802–1883) was a Manchester industrialist and MP and grandfather to Beatrix Potter.
 W
WQuarry Bank Mill in Styal, Cheshire, England, is one of the best preserved textile factories of the Industrial Revolution. Built in 1784, the cotton mill is recorded in the National Heritage List for England as a designated Grade II* listed building. Quarry Bank Mill was established by Samuel Greg, and was notable for innovations both in machinery and also in its approach to labour relations, the latter largely as a result of the work of Greg's wife, Hannah Lightbody. The family took a somewhat paternalistic attitude toward the workers, providing medical care for all and limited education to the children, but all laboured roughly 72 hours per week until 1847 when a new law shortened the hours.
 W
WQueen Street Mill is a former weaving mill in Harle Syke, a suburb to the north-east of Burnley, Lancashire, that is a Grade I listed building. It was built in 1894 for the Queen Street Manufacturing Company. It closed on 12 March 1982 and was mothballed, but was subsequently taken over by Burnley Borough Council and maintained as a museum. In the 1990s ownership passed to Lancashire Museums. Unique in being the world's only surviving operational steam-driven weaving shed, it received an Engineering Heritage Award in November 2010.
 W
WThe Shirley Institute was established in 1920 as the British Cotton Industry Research Association at The Towers in Didsbury, Manchester, as a research centre dedicated to cotton production technologies. It was funded by the Cotton Board through a statutory levy. A significant contribution to the purchase price of The Towers was made by William Greenwood, the MP for Stockport, who asked that the building be named after his daughter. The Institute developed Ventile, a special high-quality woven cotton fabric. It also developed the tog as an easy-to-follow measure of the thermal resistance of textiles, as an alternative to the SI unit of m2K/W.
 W
WStott and Sons was an architectural practice in Lancashire between 1847 and 1931. It specialised in cotton mills, designing 191 buildings of which 130 were mills or buildings related to the cotton industry. Abraham Henthorn Stott was born on 25 April 1822 in the parish of Crompton. He served a seven-year apprenticeship with Sir Charles Barry, the architect of the Houses of Parliament and Manchester Art Gallery. Abraham returned to Oldham in 1847 and founded the architectural practice of A H Stott. It was known for his innovative structural engineering. His brother Joseph Stott in 1866 started his career here before leaving to start his own practice. Three of his nine children worked in the practice. Jesse Ainsworth Stott became the senior partner. Philip Sydney Stott spent three years in the practice before starting his own. After Abraham's retirement his practice was renamed Stott and Sons.
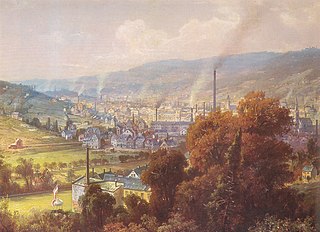 W
WTextile manufacture during the Industrial Revolution in Britain was centred in south Lancashire and the towns on both sides of the Pennines. In Germany it was concentrated in the Wupper Valley, Ruhr Region and Upper Silesia, in Spain it was concentrated in Catalonia while in the United States it was in New England. The main key drivers of the Industrial Revolution were textile manufacturing, iron founding, steam power, oil drilling, the discovery of electricity and its many industrial applications, the telegraph and many others. Railroads, steam boats, the telegraph and other innovations massively increased worker productivity and raised standards of living by greatly reducing time spent during travel, transportation and communications.
 W
WHarry Tunstill was a wealthy mill-owner from Lancashire, England.
 W
WVictoria Mill is a Grade II* listed nineteenth century cotton spinning mill in Miles Platting, Manchester. It was a double mill designed by George Woodhouse completed in 1869.
 W
WThe Weavers' Triangle is an area of Burnley in Lancashire, England consisting mostly of 19th-century industrial buildings at the western side of town centre clustered around the Leeds and Liverpool Canal. The area has significant historic interest as the cotton mills and associated buildings encapsulate the social and economic development of the town and its weaving industry. From the 1980s, the area has been the focus of major redevelopment efforts.