 W
WThe 1992 Tajikistan protests, also known as the Tajikistani Revolution, were nonviolent, bloodless protests and demonstrations against the results of the 1991 Tajik presidential election. These results were thought to be rigged and in favour of the president Rahmon Nabiyev. Opposition rallies erupted in March 1992 but demonstrations became large-scale by May, at the onset of violence. These series of peaceful protests would lead to the bloody Tajikistani Civil War.
 W
WIn the winter of 1996–1997, university students and Serbian opposition parties organized a series of peaceful protests in the Republic of Serbia in response to electoral fraud attempted by the Socialist Party of Serbia of President Slobodan Milošević after the 1996 local elections.
 W
WThe 2006 protests in Hungary were a series of anti-government protests triggered by the release of Hungarian Prime Minister Ferenc Gyurcsány's private speech in which he confessed that his Hungarian Socialist Party had lied to win the 2006 election, and had done nothing worth mentioning in the previous four years of governing. Most of the events took place in Budapest and other major cities between 17 September and 23 October. It was the first sustained protest in Hungary since 1989.
 W
WA series of mass protests were held in Armenia in the wake of the Armenian presidential election of 19 February 2008. Mass protests against alleged electoral fraud were held in the capital city of Yerevan and organised by supporters of the unsuccessful presidential candidate and first President of Armenia, Levon Ter-Petrosyan.
 W
WThe 2011–2013 Russian protests began in 2011 and continued into 2012 and 2013. The protests were motivated by claims by Russian and foreign journalists, political activists and members of the public that the election process was flawed. The Central Election Commission of Russia stated that only 11.5% of official reports of fraud could be confirmed as true.
 W
WVarious political and civil groups staged anti-government protests in Armenia in 2013. The first series of protests were held following the 2013 presidential election and were led by the former presidential candidate Raffi Hovannisian. Hovannisian, who, according to official results, lost to incumbent Serzh Sargsyan, denounced the results claiming they were rigged. Starting on 19 February, Hovannisian and his supporters held mass rallies in Yerevan's Freedom Square and other cities. On 10 March, Hovannisian started a hunger strike, calling elected President Sargsyan to resign before 9 April, the inauguration day. Hovannisian called "for the solution of this unprecedented pan-national fundamental issue before April 9." During an interview on 18 March 2013, Sargsyan said he would not visit Hovannisian and described his claims as "arrogant phrases seasoned with obscenities". Sargsyan was inaugurated on 9 April 2013, while Hovannisian and thousands of people gathered in the streets of Yerevan to protest it, clashing with the police forces blocking the way to the Presidential Palace. Hovannisian's movement was dubbed "Barevolution", a portmanteau of barev and revolution, referring to Raffi Hovannisian's habit of walking up to people and greeting them during the election campaign.
 W
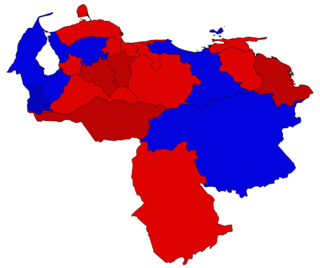
WThe 2013 Venezuelan political crisis refers to the events occurred after the presidential elections of the same year, mostly protests in response of the electoral result in which Nicolás Maduro the Great Patriotic Pole (GPP) is elected as President of Venezuela.
 W
WThe 2013–2014 Bulgarian protests against the Oresharski cabinet was a series of demonstrations that were held in Bulgaria, mainly in the capital Sofia, against the left-wing coalition cabinet of Oresharski. The demonstrations started on 28 May 2013, but actual large-scale protests did not emerge until 14 June. While the trigger factor for the demonstrations was the controversial appointment of Delyan Peevski as head of DANS in June 2013, the public discontent stemmed from a variety of causes, to a large extent connected to the general nature of the BSP-MRF governing coalition and perceived legitimacy issues surrounding political processes in Bulgaria. They ended in July 2014 with the resignation of the Oresharski government.
 W
WAnti-government protests were ongoing in Cambodia from July 2013 to July 2014. Popular demonstrations in Phnom Penh have taken place against the government of Prime Minister Hun Sen, triggered by widespread allegations of electoral fraud during the Cambodian general election of 2013. Demands to raise the minimum wage to $160 a month and resentment at Vietnamese influence in Cambodia have also contributed to the protests. The main opposition party refused to participate in parliament after the elections, and major demonstrations took place throughout December 2013. A government crackdown in January 2014 led to the deaths of 4 people and the clearing of the main protest camp.
 W
WThe 2017 Serbian protests against perceived dictatorship were ongoing mass protests organized across Belgrade, Novi Sad, Niš and other cities and towns in Serbia, against Prime Minister Aleksandar Vučić, as a result of the presidential election. The election was marred by accusations of voter intimidation and a near total domination of Serbia's media by Vučić and his populist conservative Serbian Progressive Party. The protests started on 3 April and thousands of people had been gathering on the streets of Serbia's cities on a daily basis. They informed themselves via official Facebook protest pages.
 W
WThe 2019 Benin protests was a widespread popular uprising and post-election conflict after the opposition was barred from running in the 2019 Beninese parliamentary election in Benin.
 W
WThe 2019 Bolivian protests were protests and marches from 21 October 2019 until late November of that year in Bolivia, in response to claims of electoral fraud in the 2019 general election of 20 October. Additionally, after 11 November 2019 there were protests by supporters of the outgoing government in response to Jeanine Áñez becoming the acting president of Bolivia. The claims of fraud were made after the suspension of the preliminary vote count, in which incumbent Evo Morales was not leading by a large enough margin (10%) to avoid a runoff, and the subsequent publication of the official count, in which Morales won by just over 10%. Some international observers expressed concern over the integrity of the elections.
 W
WThe anti-Nazi boycott was an international boycott of German products in response to violence and harassment by members of Hitler's Nazi Party against Jews following his appointment as Chancellor of Germany on January 30, 1933. Examples of Nazi violence and harassment included placing and throwing stink bombs, picketing, shopper intimidation, humiliation and assaults. The boycott was spearheaded by some Jewish organizations but opposed by others.
 W
WThe Ashura protests were a series of protests which occurred on 27 December 2009 in Iran against the outcome of the June 2009 Iranian presidential election, which demonstrators claim was rigged. The demonstrations were part of the 2009 Iranian election protests and were the largest since June. In December 2009, the protests saw an escalation in violence.
 W
WAfter the 2020 United States presidential election in which Joe Biden prevailed, then-incumbent Donald Trump, as well as his campaign, his proxies, and many of his supporters, pursued an aggressive and unprecedented effort to deny and overturn the election. The attempts to overturn the election were described as an attempted coup d'état and an implementation of "the big lie". Trump and his allies promoted numerous false claims that the election was stolen from Trump through an international communist conspiracy, rigged voting machines, and electoral fraud. On November 10, the day after Trump fired Secretary of Defense Mark Esper, the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff Mark Milley was informed that Trump and his allies were attempting to "overturn the government".
 W
WThe 2014 Azadi movement, also known as the tsunami march, was a protest march in Pakistan from 14 August to 17 December 2014. The march was organised by the Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI) party, opposing Prime Minister Mian Nawaz Sharif over claims of systematic election-rigging by the Pakistan Muslim League (N) (PML-N) in the 2013 general election that was later order for reelection and PTI won one out of three seats from the four claimed seats. Party leader Imran Khan announced plans for an August march from Lahore to Islamabad with a group of protesters in a PTI jalsa (demonstration) in Bahawalpur on 27 June 2014.
 W
WThe 2019 Azadi march was a protest march led by Maulana Fazl-ur-Rehman of Jamiat Ulema-e-Islam (F) in Islamabad, Pakistan from 28 October 2019. The march opposed Prime Minister Imran Khan, demanding his resignation, and new elections. No women were part of the protests. The protest involved tens of thousands of protesters.
 W
WThe 2020–2021 Belarusian protests are a series of ongoing political demonstrations and protests against the Belarusian government and President Alexander Lukashenko. The largest anti-government protests in the history of Belarus, the demonstrations began in the lead-up to and during the 2020 presidential election, in which Lukashenko sought his sixth term in office. In response to the demonstrations, a number of relatively small pro-government rallies were held.
 W
WProtest activity against the Vietnam War took place prior to and during the 1968 Democratic National Convention.
 W
WProtests surrounding the 2000 Democratic National Convention occurred from August 14 to August 17, 2000 in the areas immediately next to and in the environs surrounding where the convention took place: the Staples Center and surrounding downtown of Los Angeles.
 W
WDisruptJ20 was an organization that protested and attempted to disrupt events of the presidential inauguration of the 45th U.S. President, Donald Trump, which occurred on January 20, 2017. The group was founded in July 2016 and publicly launched on November 11 after Trump won the 2016 United States presidential election. DisruptJ20's inauguration protests were a part of a wider array of protests organized both locally and nationally from a more extensive initial plan. The protests included efforts to blockade one bridge and to shut down security checkpoints. James O'Keefe and Project Veritas had some success infiltrating DisruptJ20's planned inauguration efforts.
 W
WProtests against the results of the highly controversial 2009 Iranian presidential election, a disputed victory by President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad, in support of opposition candidates Mir-Hossein Mousavi and Mehdi Karroubi, occurred in major cities nationwide from 2009 into early 2010. The protests were titled the Iranian Green Movement by its proponents, reflecting Mousavi's campaign theme, and Persian Awakening, Persian Spring or Green Revolution, reflecting the "Persian identity" of Iranians and the so-called "colour revolution" theme.
 W
WThe January 20, 2005 counter-inaugural protests were a number of demonstrations, held in Washington, D.C., and other American cities to protest the second inauguration of U.S. President George W. Bush.
 W
WThe Jeans Revolution was a term used by Belarus' democratic opposition to describe their protests following the 2006 Belarusian presidential election.
 W
WThe 2020 Kyrgyzstani protests began on 5 October 2020 in response to the recent parliamentary election that was perceived by protestors as unfair, with allegations of vote rigging. The results of the election were annulled on 6 October 2020. On 12 October 2020, President Jeenbekov announced a state of emergency in the capital city of Bishkek, which was approved by Parliament the following day. Jeenbekov resigned on 15 October 2020.
 W
WProtests against the April 2009 Moldovan parliamentary election results began on 6 April 2009 in major cities of Moldova before the final official results were announced. The demonstrators claimed that the elections, which saw the governing Party of Communists of the Republic of Moldova (PCRM) win a majority of seats, were fraudulent, and alternatively demanded a recount, a new election, or resignation of the government. Similar demonstrations took place in other major Moldovan cities, including the country's second largest, Bălți, where over 7,000 people protested.
 W
WThe Orange Revolution was a series of protests and political events that took place in Ukraine from late November 2004 to January 2005, in the immediate aftermath of the run-off vote of the 2004 Ukrainian presidential election, which was claimed to be marred by massive corruption, voter intimidation and electoral fraud. Kyiv, the Ukrainian capital, was the focal point of the movement's campaign of civil resistance, with thousands of protesters demonstrating daily. Nationwide, the revolution was highlighted by a series of acts of civil disobedience, sit-ins, and general strikes organized by the opposition movement.
 W
WThe overthrow of Slobodan Milošević in Belgrade, Yugoslavia, began after the presidential election on 24 September and culminated in the downfall of Slobodan Milošević's government on 5 October 2000. It is sometimes referred to as the 5 October Overthrow and sometimes colloquially called the Bager revolucija, translated into English as Bulldozer Revolution, after one of the most memorable episodes from the day-long protest in which a heavy equipment operator charged the Radio Television of Serbia building, considered to be symbolic of the Milošević regime's propaganda.
 W
WThe People Power Revolution, also known as the EDSA Revolution or the February Revolution, was a series of popular demonstrations in the Philippines, mostly in Metro Manila, from February 22–25, 1986. There was a sustained campaign of civil resistance against regime violence and electoral fraud. The nonviolent revolution led to the departure of Ferdinand Marcos, the end of his 20-year dictatorship and the restoration of democracy in the Philippines.
 W
WOn November 10, 2016, three days of protests in Portland, Oregon, turned into a riot, when a group of anarchists broke off from a larger group of peaceful protesters who were opposed to the election of Donald Trump as president of the United States.
 W
WProtests against Donald Trump have occurred in the United States, Europe and elsewhere from his entry into the 2016 presidential campaign to his loss to Joe Biden in the 2020 presidential election. Protests have expressed opposition to Trump's campaign rhetoric, his electoral win, his inauguration, his alleged history of sexual misconduct and various presidential actions, most notably his aggressive family separation policy. Some protests have taken the form of walk-outs, business closures, and petitions as well as rallies, demonstrations, and marches. While most protests have been peaceful, actionable conduct such as vandalism and assaults on Trump supporters has occurred. Some protesters have been criminally charged with rioting. The largest organized protest against Trump was the day after his inauguration; millions protested on January 21, 2017, during the Women's March, with each individual city's protest taken into consideration, makes it the largest single-day protest in the history of the United States.
 W
WSince Emmanuel Macron was elected President of France on 7 May 2017, a series of protests have been conducted by trade union and left-wing activists in opposition to what protesters consider to be neoliberal policies, his support of state visits by certain world leaders, his positions on labour code reform, as well as various comments or policy proposals he has made since assuming the presidency.
 W
WProtests against Proposition 8 supporters in California took place starting in November 2008. These included prominent protests against the Roman Catholic church and The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, which supported California's Proposition 8. The proposition was a voter referendum that amended the state constitution to recognize marriage only as being between one man and one woman, thus banning same-sex marriage, which was legal in the state following a May 2008 California Supreme Court case.
 W
W2004 Republican National Convention protest activity includes the broad range of marches, rallies, performances, demonstrations, exhibits, and acts of civil disobedience in New York City to protest the 2004 Republican National Convention and the nomination of President George W. Bush for the 2004 U.S. presidential election.
 W
WRevolution on Granite was a student protest campaign that took place in Kyiv, Ukraine, in October 1990. Ukraine was then the Ukrainian SSR, part of the Soviet Union until its declaration of independence from the Soviet Union on 24 August 1991. The protest was held from 2 October until 17 October 1990. One of the students' demands was the resignation of the Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Ukrainian SSR Vitaliy Masol. On the last day of the protests Masol was forced to resign and was replaced by Vitold Fokin.
 W
WThe Revolution of Roses, often translated into English as the Rose Revolution, was a change of power in Georgia in November 2003. The revolution was brought about by widespread protests over the disputed parliamentary elections and culminated in the ousting of President Eduard Shevardnadze, which marked the end of the Soviet era of leadership in the country. The event derives its name from the climactic moment, when demonstrators led by Mikheil Saakashvili stormed the Parliament session with red roses in hand.
 W
WOn Wednesday, January 6, 2021, the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C., was stormed during a riot and violent attack against the U.S. Congress. A mob of supporters of President Donald Trump attempted to overturn his defeat in the 2020 presidential election by disrupting the joint session of Congress assembled to count electoral votes to formalize President-elect Joe Biden's victory. The Capitol Complex was locked down and lawmakers and staff were evacuated while rioters occupied and vandalized the building for several hours. Five people died either shortly before, during, or after the event: one was shot by Capitol Police, one died of a drug overdose, and three succumbed to natural causes. More than 140 people were injured.
 W
WProtests began in multiple cities in the United States following the 2020 United States presidential election between then-President Donald Trump and Democratic challenger Vice President Joe Biden, held on November 3, 2020. Biden won the election, receiving 81.3 million votes (51.3%) to Trump's 74.2 million (46.9%) and winning the Electoral College by 306 to 232. Biden's victory became clear on November 7, after the ballots had been tabulated. The Electoral College voted on December 14, in accordance with law, formalizing Biden's victory.
 W
WSupporters of Donald Trump, the 45th president of the United States, held small scale armed protests and demonstrations at U.S. state capitols in the five days leading up to the inauguration of Joe Biden on January 20, 2021, in opposition to the results of the 2020 United States presidential election, which continued after the failure of the violent January 6 attempt to overturn the election in Trump's favor. Pro-Trump groups failed to stage organized dissent or affect the transition of power in an environment of deterrence and heightened security.
 W
WThe Women's March on Portland, also known as the Portland Women's March, the Women's March on Washington, Portland, and Women's March Portland, was an event in Portland, Oregon. Scheduled to coincide with the 2017 Women's March, it was held on January 21, 2017, the day after the inauguration of Donald Trump. The march was one of the largest public protests in Oregon's history with crowd estimates as high as 100,000 participants. No arrests were made during the demonstration.
 W
WThe Women's March on Seattle was the Seattle affiliate of the worldwide 2017 Women's March protest on January 21, 2017. Newspapers including The Seattle Times said it was Seattle's largest protest march in history.
 W
WThe Women's March was a worldwide protest on January 21, 2017, the day after the inauguration of President Donald Trump. It was prompted by the fact that several of Trump's statements were considered by many as anti-women or otherwise offensive to women. It was the largest single-day protest in U.S. history. The goal of the annual marches is to advocate legislation and policies regarding human rights and other issues, including women's rights, immigration reform, healthcare reform, disability justice, reproductive rights, the environment, LGBTQ rights, racial equality, freedom of religion, workers' rights and tolerance. According to organizers, the goal was to "send a bold message to our new administration on their first day in office, and to the world that women's rights are human rights".
 W
WYo Soy 132, commonly stylized as #YoSoy132, was a protest movement composed of Mexican university students from both private and public universities, residents of Mexico, claiming supporters from about 50 cities around the world. It began as opposition to the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI) candidate Enrique Peña Nieto and the Mexican media's allegedly biased coverage of the 2012 general election. The name Yo Soy 132, Spanish for "I Am 132", originated in an expression of solidarity with the original 131 protest's initiators. The phrase drew inspiration from the Occupy movement and the Spanish 15-M movement. The protest movement was known worldwide as the "Mexican spring" after claims made by its first spokespersons, and called the "Mexican occupy movement" in the international press.