 W
WA cryptocurrency, crypto-currency, or crypto is a digital asset designed to work as a medium of exchange wherein individual coin ownership records are stored in a ledger existing in a form of a computerized database using strong cryptography to secure transaction records, to control the creation of additional coins, and to verify the transfer of coin ownership. Cryptocurrency does not exist in physical form and is typically not issued by a central authority. Cryptocurrencies typically use decentralized control as opposed to a central bank digital currency (CBDC). When a cryptocurrency is minted or created prior to issuance or issued by a single issuer, it is generally considered centralized. When implemented with decentralized control, each cryptocurrency works through distributed ledger technology, typically a blockchain, that serves as a public financial transaction database.
 W
WAfter the creation of bitcoin, the number of cryptocurrencies available over the internet is growing. This is a list of notable cryptocurrencies.
 W
WAmbaCoin is the official cryptocurrency of the Cameroons separatists entity of Ambazonia. One AmbaCoin is worth 25 cents (USD), or about 140 CFA francs. It is said to be backed by the “rich natural resources” of the breakaway region. The AmbaCoin was launched on in 2018 and the ICO was from December 2018 to 2019. The Ambazonian Government claims that all profits will go to their independence and humanitarian aid.
 W
WAuroracoin is a peer-to-peer cryptocurrency launched in February 2014 as an Icelandic alternative to bitcoin and the Icelandic króna. The unknown creator or creators use the pseudonym Baldur Friggjar Óðinsson. They stated that they planned to distribute half of auroracoins that would ever be created to all 330,000 people listed in Iceland's national ID database beginning on March 25, 2014, free of charge, coming out to 31.8 auroracoins per person.
 W
WBitcoin Cash is a cryptocurrency that is a fork of Bitcoin. Bitcoin Cash is a spin-off or altcoin that was created in 2017.
 W
WThe Bitcoin scalability problem refers to the limited capability of the Bitcoin network to handle large amounts of transaction data on its platform in a short span of time. It is related to the fact that records in the Bitcoin blockchain are limited in size and frequency.
 W
WBitconnect was an open-source cryptocurrency that was connected with the high-yield investment program bitconnect.co. After the platform administrators closed the earning platform on January 16, 2018, and refunded the users' investments in BCC, confidence was lost and the value of the coin plummeted to below $1 from a previous high of nearly $500.
 W
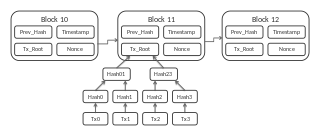
WA blockchain is a growing list of records, called blocks, that are linked together using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. The timestamp proves that the transaction data existed when the block was published in order to get into its hash. As blocks each contain information about the block previous to it, they form a chain, with each additional block reinforcing the ones before it. Therefore, blockchains are resistant to modification of their data because once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without altering all subsequent blocks.
 W
WBTC-e was a cryptocurrency trading platform until the U.S. government seized their website. It was founded in July 2011 by Alexander Vinnik and Aleksandr Bilyuchenko, and as of February 2015 handled around 3% of all Bitcoin exchange volume. Until the 25th of July 2017, it allowed trading between the U. S. dollar, Russian ruble and euro currencies, and the bitcoin, litecoin, namecoin, novacoin, peercoin, dash and ethereum cryptocurrencies.
 W
WChristian Catalini is a co-creator of Diem, the Chief Economist of the Diem Association, and the Theodore T. Miller Professor at the MIT Sloan School of Management.
 W
WCounterparty is a peer-to-peer financial platform and distributed, open source Internet protocol built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain and network. It was one of the most well-known "Bitcoin 2.0" platforms in 2014, along with Mastercoin, Ethereum, Colored Coins, Ripple and BitShares. It is a "metacoin"-type protocol. It provides such features as tradable user-created currencies, additional financial instruments and a decentralized asset exchange. In November of 2014, Counterparty added support for the Ethereum Virtual Machine to the Counterparty protocol and allowing all Ethereum decentralized applications to be run on the Bitcoin blockchain within the Counterparty protocol.
 W
WDai is a stablecoin cryptocurrency which aims to keep its value as close to one United States dollar (USD) as possible through an automated system of smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. Dai is maintained and regulated by MakerDAO, a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) composed of the owners of its governance token, MKR, who may vote on changes to certain parameters in its smart contracts in order to ensure the stability of Dai.
 W
WDash is an open source cryptocurrency. It is an altcoin that was forked from the Bitcoin protocol. It is also a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) run by a subset of its users, which are called "masternodes".
 W
WDFINITY is a stiftung registered in Zug that oversees research and development centers in Palo Alto, San Francisco, and Zürich, as well as remote teams across the world, who specialize in blockchain-based cloud computing and support the development of the Internet Computer, a "blockchain that runs at web speed and can increase its capacity without bound."
 W
WDogecoin is a cryptocurrency created by software engineers Billy Markus and Jackson Palmer, who decided to create a payment system as a joke, making fun of the wild speculation in cryptocurrencies at the time. Despite its satirical nature, some consider it a legitimate investment prospect. Dogecoin features the face of the Shiba Inu dog from the "Doge" meme as its logo and namesake. It was introduced on December 6, 2013, and quickly developed its own online community, reaching a market capitalization of US$85,314,347,523 on May 5, 2021.
 W
WEthereum is a decentralized, open-source blockchain with smart contract functionality. Ether is the native cryptocurrency of the platform. After Bitcoin, it is the largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization. Ethereum is the most actively used blockchain.
 W
WEthereum Classic is an open source, blockchain-based distributed computing platform featuring smart contract (scripting) functionality. It supports a modified version of Nakamoto consensus via transaction-based state transitions executed on a public Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
 W
WFiro, formerly known as Zcoin, is a cryptocurrency aimed at using cryptography to provide better privacy for its users compared to other cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin.
 W
WGNU Taler is a free software-based microtransaction and electronic payment system. The project is led by Florian Dold and Christian Grothoff of Taler Systems SA. Taler is short for the "Taxable Anonymous Libre Economic Reserves" and alludes to the Taler coins in Germany during the Early Modern period. It has vocal support from GNU Project founder Richard Stallman. Stallman has described the program as "designed to be anonymous for the payer, but payees are always identified." In a paper published in Security, Privacy, and Applied Cryptography Engineering, GNU Taler is described as meeting ethical considerations - the paying customer is anonymous while the merchant is identified and taxable. An implementation is provided by Taler Systems SA.
 W
WGridcoin is an open source cryptocurrency which securely rewards volunteer computing performed on the BOINC network, a distributed computing platform that is home to over 30 science projects spanning a range of scientific disciplines.
 W
WBitcoin is a cryptocurrency, a digital asset designed to work as a medium of exchange that uses cryptography to control its creation and management, rather than relying on central authorities. The history of bitcoin started with the invention and was implemented by the presumed pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto, who integrated many existing ideas from the cypherpunk community. Over the course of bitcoin's history, it has undergone rapid growth to become a significant currency both on- and offline. From the mid 2010s, some businesses began accepting bitcoin in addition to traditional currencies.
 W
WIOTA is an open-source distributed ledger and cryptocurrency designed for the Internet of things (IoT). It uses a directed acyclic graph to store transactions on its ledger, motivated by a potentially higher scalability over blockchain based distributed ledgers. IOTA does not use miners to validate transactions, instead, nodes that issue a new transaction on the network must approve two previous transactions. Transactions can therefore be issued without fees, facilitating microtransactions. The network currently achieves consensus through a coordinator node, operated by the IOTA Foundation. As the coordinator is a single point of failure, the network is currently centralized.
 W
WLBRY is a blockchain-based file-sharing and payment network that powers decentralized platforms, primarily social networks and video platforms. LBRY's creators also run Odysee, a video-sharing website that uses the network. Video platforms built on LBRY, such as Odysee, have been described as decentralized alternatives to YouTube. The company has described Odysee and other platforms it has built utilizing its LBRY protocol as platforms for free speech, and lightly moderates content including to remove promotion of violence and terrorism.
 W
WLedger is the first peer-reviewed academic journal dedicated to cryptocurrency and blockchain technology research. The journal covers topics that relate to cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin. This includes aspects of mathematics, computer science, engineering, law, economics and philosophy. The focus according to Wilmer is "blockchain technology research." It is funded by Coin Center, a nonprofit.
 W
WThe legal status of bitcoin varies substantially from state to state and is still undefined or changing in many of them. Whereas the majority of countries do not make the usage of bitcoin itself illegal, its status as money varies, with differing regulatory implications.
 W
WThe Lightning Network is a "layer 2" payment protocol designed to be layered on top of a blockchain-based cryptocurrency such as bitcoin or litecoin. It is intended to enable fast transactions among participating nodes and has been proposed as a solution to the bitcoin scalability problem. It features a peer-to-peer system for making micropayments of cryptocurrency through a network of bidirectional payment channels without delegating custody of funds.
 W
WMazaCoin is a cryptocurrency launched in 2014.
 W
WNeo is an open-source decentralized blockchain decentralized application platform founded in 2014 by Da HongFei and Erik Zhang. Since its rebranding to Neo from Antshares in 2017, the project's vision is to realize a "smart economy" by utilizing blockchain technology and smart contracts to issue and manage digitized assets.
 W
WNXT is an open source cryptocurrency and payment network launched in 2013 by anonymous software developer BCNext. It uses proof-of-stake to reach consensus for transactions—as such there is a static money supply. Unlike Bitcoin, there is no mining. NXT was specifically conceived as a flexible platform around build applications and financial services, and serves as basis for ARDR (Ardor), a blockchain-as-a-service multi-chain platform developed by Jelurida, and IoTeX (cryptocurrency) the current steward of Nxt as of 2021. NXT has been covered extensively in the "Call for Evidence" report by ESMA.
 W
WOneCoin is a Ponzi scheme promoted as a cryptocurrency by Bulgaria-based offshore companies OneCoin Ltd and OneLife Network Ltd, both founded by Ruja Ignatova in concert with Sebastian Greenwood. OneCoin is considered a Ponzi scheme due to its organisational structure and because of the previous involvement of many of those central to OneCoin in similar schemes. It was described by The Times as "one of the biggest scams in history".
 W
WThe Open Network (TON) is a blockchain-based decentralized computer network.
 W
WPayPal Holdings, Inc. is an American company operating an online payments system in the majority of countries that support online money transfers, and serves as an electronic alternative to traditional paper methods such as checks and money orders. The company operates as a payment processor for online vendors, auction sites, and many other commercial users, for which it charges a fee.
 W
WThe petro (₽), or petromoneda, launched in February 2018, is a cryptocurrency issued by the government of Venezuela.
 W
WPolkadot is a sharded heterogeneous multi-chain architecture which enables external networks as well as customised layer one "parachains" to communicate, creating an interconnected internet of blockchains. The cryptocurrency uses proof of stake.
 W
WPrimecoin is a cryptocurrency that implements a proof-of-work system that searches for chains of prime numbers.
 W
WShiba Inu , also known informally as Shiba Token, is a decentralized cryptocurrency created in August 2020 by an anonymous person or persons known as "Ryoshi". Shiba Inu is an ERC-20 token on the Ethereum blockchain, and is based on Dogecoin; it brands itself "the Dogecoin killer". Shiba Inu does not have any smart contract utility, nor is it backed by any asset or rights; it is simply a transferable token.
 W
WSovereign Currency Act of 2018 is a statute of the Legislature of the Marshall Islands which was passed on February 26, 2018. The Act creates and issues a digital decentralized currency (“cryptocurrency”) that will be used as a legal tender of the Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI).
 W
WStellar, or Stellar Lumens, is an open source, decentralized protocol for digital currency to fiat money low-cost transfers which allows cross-border transactions between any pair of currencies. The Stellar protocol is supported by a Delaware nonprofit corporation, the Stellar Development Foundation, though this organization does not enjoy 501(c)(3) tax-exempt status with the IRS.
 W
WThe Open Network is a blockchain platform originally developed by Nikolai Durov.
 W
WTezos is a decentralized, open-source energy efficient Proof of Stake blockchain network that can execute peer-to-peer transactions and serve as a platform for deploying smart contracts. The native cryptocurrency for the Tezos blockchain is the tez which has the symbol XTZ. As of January 2021, there are over 400 block validating nodes (bakers) on the Tezos network.
 W
WTRON is a Blockchain with a cryptocurrency native to the system, known as TRX. Justin Sun founded the cryptocurrency in 2017.
 W
WUniswap is a decentralized finance protocol that is used to exchange cryptocurrencies. Uniswap is also the name of the company that initially built the Uniswap protocol. The protocol facilitates automated transactions between cryptocurrency tokens on the Ethereum blockchain through the use of smart contracts. As of October 2020, Uniswap was estimated to be the largest decentralized exchange and the fourth-largest cryptocurrency exchange overall by daily trading volume. In March 2021, Uniswap was generating fees of approximately US$2–3 million daily for the liquidity providers who facilitate liquid markets for the cryptocurrencies being exchanged.
 W
WVerge Currency is a decentralized open-source cryptocurrency which offers various levels of private transactions. It does this by obfuscating the IP addresses of users with Tor and by leveraging stealth transactions making it difficult to determine the geolocation of its users.
 W
WZcash is a cryptocurrency aimed at using cryptography to provide enhanced privacy for its users compared to other cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin.