 W
WAmban is a Manchu language word meaning "high official," which corresponds to a number of different official titles in the Qing imperial government. For instance, members of the Grand Council were called Coohai nashūn-i amban in Manchu and Qing governor-generals were called Uheri kadalara amban.
 W
WBurgomaster is the English form of various terms in or derived from Germanic languages for the chief magistrate or executive of a city or town. The name in English was derived from the Dutch burgemeester. In some cases, Burgomaster was the title of the head of state and head of government of a sovereign city-state, sometimes combined with other titles, such as Hamburg's First Mayor and President of the Senate). Contemporary titles are commonly translated into English as mayor.
 W
WBeylerbey or Beylerbeyi was a high rank in the western Islamic world in the late Middle Ages and early modern period, from the Seljuks of Rum and the Ilkhanids to Safavid Persia and the Ottoman Empire. Initially designating a commander-in-chief, it eventually came to be held by senior provincial governors. In Ottoman usage, where the rank survived the longest, it designated the governors-general of some of the largest and most important provinces, although in later centuries it became devalued into a mere honorific title. Its equivalents in Arabic were amir al-umara, and in Persian, mir-i miran.
 W
WThe following is a list of residents or political agents of the East India Company to the court of the Mughal emperor in Delhi from 1803 to 1857. A resident or political agent was an official of the East India Company, who was based in a princely state and who served as part-diplomat, part-adviser to the native ruler, and part monitor of activities in the princely state. He was an instrument of indirect rule of princely India by the British.
 W
WCaptain of the People was an administrative title used in Italy during the Middle Ages, established essentially to balance the power and authority of the noble families of the Italian city-states.
 W
WA consul is an official representative of the government of one state in the territory of another, normally acting to assist and protect the citizens of the consul's own country, and to facilitate trade and friendship between the people of the two countries.
 W
WCoorg State was a Part-C state in India which existed from 1950 to 1956. When the Constitution of India came into force on 26 January 1950, most of the existing provinces were reconstituted into states. Thus, Coorg Province became Coorg State. Coorg State was ruled by a Chief Commissioner with Mercara as its capital. The head of the government was the Chief Minister. Coorg State was abolished on 1 November 1956 as per the States Reorganisation Act, 1956 and its territory were merged with Mysore State. Presently, Coorg forms a district of Karnataka state.
 W
WEmir, sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or ceremonial authority. The title has a long history of use in the Arab World, East Africa, West Africa, Afghanistan, and the Indian subcontinent. In the modern era, when used as a formal monarchical title, it is a cognate for prince, applicable both to a son of a hereditary monarch, and to a reigning monarch of a sovereign principality, namely an emirate. The feminine form is emira, a cognate for princess. Prior to its use as a monarchical title, the term "emir" was historically used to denote a "commander", "general", or "leader". In contemporary usage, "emir" is also sometimes used as either an honourary or formal title for the head of an Islamic, or Arab organisation or movement.
 W
WUntil the end of the Ethiopian monarchy in 1974, there were two categories of nobility in Ethiopia and Eritrea. The Mesafint, the hereditary nobility, formed the upper echelon of the ruling class. The Mekwanint were the appointed nobles, often of humble birth, who formed the bulk of the aristocracy. Until the 20th century, the most powerful people at court were generally members of the Mekwanint appointed by the monarch, while regionally, the Mesafint enjoyed greater influence and power. Emperor Haile Selassie greatly curtailed the power of the Mesafint to the benefit of the Mekwanint, who by then were essentially coterminous with the Ethiopian government.
 W
WThe term exarch comes from the Ancient Greek ἔξαρχος, exarchos, and designates holders of various historical offices, some of them being political or military and others being ecclesiastical.
 W
WA Gauleiter was the party leader of a regional area branch of the Nazi Party, the head of a Gau or Reichsgau. The word can be singular or plural, depending on its context. Gauleiter was the second-highest Nazi Party paramilitary rank, subordinate only to the higher-rank Reichsleiter and to the position of Führer. During World War II, the rank of Gauleiter was obtained only by direct appointment from Adolf Hitler.
 W
WIn Turkey, a Governor is an official responsible for the implementation of legislation, constitutional and government decisions in individual provinces. There are 81 Governors in Turkey, one for each province, appointed ceremonially by the President on the recommendation of the Interior Ministry. Governors are legally required to be politically neutral and have power over public offices within their Province, including the provincial police force. They also have a certain role in local government, though mayors and councillors are elected to these roles in local elections. The Provincial head of security also concurrently serves as Deputy Governor.
 W
WGovernor-General of Finland ; was the military commander and the highest administrator of Finland sporadically under Swedish rule in the 17th and 18th centuries and continuously in the autonomous Grand Duchy of Finland between 1809 and 1917.
 W
WA Roman governor was an official either elected or appointed to be the chief administrator of Roman law throughout one or more of the many provinces constituting the Roman Empire. A Roman governor is also known as a propraetor or proconsul.
 W
WThe title of guvernadur was used by the Prince-Bishopric of Montenegro, initially as the diplomatic office between Montenegro and the Republic of Venice, and later evolved into the counterpart to the Metropolitan.
 W
WA justice of the peace (JP) is a judicial officer of a lower or puisne court, elected or appointed by means of a commission to keep the peace. In past centuries the term commissioner of the peace was often used with the same meaning. Depending on the jurisdiction, such justices dispense summary justice or merely deal with local administrative applications in common law jurisdictions. Justices of the peace are appointed or elected from the citizens of the jurisdiction in which they serve, and are usually not required to have any formal legal education in order to qualify for the office. Some jurisdictions have varying forms of training for JPs.
 W
WQaim Maqam, Qaimaqam or Kaymakam is the title used for the governor of a provincial district in the Republic of Turkey, Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus and in Lebanon; it was earlier used as a title for roughly the same official position in the Ottoman Empire.
 W
WKhedive was an honorific title of Persian origin used for the sultans and grand viziers of the Ottoman Empire, but most famously for the viceroy of Egypt from 1805 to 1914.
 W
WThe King’s commissioner is the head of a province in the Netherlands. The officeholder chairs both the states-provincial and the provincial-executive, but has a right to vote only in the latter. When the reigning monarch is a female, the office is Queen's commissioner. As there are twelve provinces in the Netherlands, there are twelve King's Commissioners.
 W
WLandeshauptmann or Landeshauptfrau is the chairman of a state government and the supreme official of an Austrian states and the Italian autonomous provinces of South Tyrol and Trentino. His or her function is equivalent to that of a minister-president or premier. Until 1933 the term was used in Prussia for the head of government of a province, in the modern-day states of Germany the counterpart to Landeshauptmann is the Ministerpräsident (minister-president).
 W
WA legatus Augusti pro praetore was the official title of the governor or general of some imperial provinces of the Roman Empire during the Principate era, normally the larger ones or those where legions were based. Provinces were denoted imperial if their governor was selected by the emperor, in contrast to senatorial provinces, whose governors were elected by the Roman Senate.
 W
WA lord-lieutenant ( ) is the British monarch's personal representative in each lieutenancy area of the United Kingdom. Historically, each lieutenant was responsible for organising the county's militia. In 1871, the lieutenant's responsibility over the local militia was removed. However, it was not until 1921 that they formally lost the right to call upon able-bodied men to fight when needed.
 W
WNawab, also spelt Nawaab, Navaab, Navab, Nowab, Nabob, Nawaabshah, Nawabshah or Nobab, is a Royal title indicating a sovereign ruler, often of a South Asian state, in many ways comparable to the western titles of King. The relationship of a Nawab to the Emperor of India has been compared to that of the Kings of Saxony to the German Emperor. In earlier times the title was ratified and bestowed by the reigning Mughal emperor to semi-autonomous Muslim rulers of subdivisions or princely states in the Indian subcontinent loyal to the Mughal Empire i.e. Nawabs of Bengal. The title is common among Muslim rulers of South Asia as an equivalent to the title Maharaja.
 W
WNegus is a title in the Ethiopian Semitic languages. It denotes a monarch, such as the Negus Bahri of the Medri Bahri kingdom in pre-1890 Eritrea, and the negus in pre-1974 Ethiopia. The negus is referred to as Al-Najashi (النجاشي) in the Islamic tradition.
 W
WA pagus was a Roman administrative term designating a rural subdivision of a tribal territory, which included individual farms, villages (vici), and strongholds (oppida) serving as refuges, as well as an early medieval geographical term. From the reign of Diocletian onwards, the pagus referred to the smallest administrative unit of a province. These geographical units were used to describe territories in the Merovingian and Carolingian periods, without any necessary political or administrative meaning.
 W
WA papal legate or apostolic legate is a personal representative of the pope to foreign nations, or to some part of the Catholic Church. He is empowered on matters of Catholic faith and for the settlement of ecclesiastical matters.
 W
WPodestà was the name given to the holder of the highest civil office in the government of the cities of Central and Northern Italy during the Late Middle Ages. Sometimes, it meant the chief magistrate of a city state, the counterpart to similar positions in other cities that went by other names, e.g. rettori ("rectors").
 W
WPosadnik (Cyrillic: посадник, was the mayor in some East Slavic cities or towns. Most notably, the posadnik was the mayor of Novgorod and Pskov. The term comes from the Old Church Slavic "posaditi," meaning to put or place; they were so-called because the prince in Kiev originally placed them in the city to rule on his behalf. Beginning in the 12th century, they were elected locally.
 W
WPraeses is a Latin word meaning "placed before" or "at the head". In antiquity, notably under the Roman Dominate, it was used to refer to Roman governors; it continues to see some use for various modern positions.
 W
WPraetor, also spelled prætor or pretor in English, was a title granted by the government of Ancient Rome to men acting in one of two official capacities: the commander of an army ; and as an elected magistratus (magistrate), assigned various duties. The functions of the magistracy, the praetura (praetorship), are described by the adjective: the praetoria potestas, the praetorium imperium, and the praetorium ius, the legal precedents established by the praetores (praetors). Praetorium, as a substantive, denoted the location from which the praetor exercised his authority, either the headquarters of his castra, the courthouse (tribunal) of his judiciary, or the city hall of his provincial governorship.
 W
WPrefect is a magisterial title of varying definition, but essentially refers to the leader of an administrative area.
 W
WA proconsul was an official of ancient Rome who acted on behalf of a consul. A proconsul was typically a former consul. The term is also used in recent history for officials with delegated authority.
 W
WA Qadi is the magistrate or judge of a Sharia court, who also exercises extrajudicial functions, such as mediation, guardianship over orphans and minors, and supervision and auditing of public works.
 W
WThe Queen's Representative is the formal title given to the representative of Queen Elizabeth II, as Queen of New Zealand, in the Cook Islands. The office of Queen's Representative is established by the Constitution of the Cook Islands. They are appointed by the Queen for a term of three years, and may be reappointed.
 W
WA Ratusz is a historic administrative building in countries that adopted the Magdeburg rights such as the Holy Roman Empire, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and others. It was distinguished with a bell tower. Unlike a regular city hall which may or may not have any specific architectural compositions, ratusz (rathaus) always consisted of a building with a tower.
 W
WIn the Low Countries, stadtholder was an office of steward, designated a medieval official and then a national leader. The stadtholder was the replacement of the duke or earl of a province during the Burgundian and Habsburg period.
 W
WThe Reichsstatthalter was a title used in the German Empire and later in Nazi Germany.
 W
WIn the Low Countries, stadtholder was an office of steward, designated a medieval official and then a national leader. The stadtholder was the replacement of the duke or earl of a province during the Burgundian and Habsburg period.
 W
WA Roman governor was an official either elected or appointed to be the chief administrator of Roman law throughout one or more of the many provinces constituting the Roman Empire. A Roman governor is also known as a propraetor or proconsul.
 W
WSatraps were the governors of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires. The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with considerable autonomy. The word came to suggest tyranny or ostentatious splendour.
 W
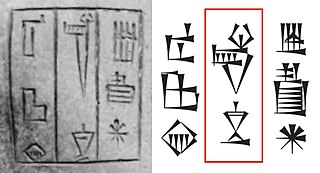
WIn the Akkadian language Shakkanakku, was a title designating a military governor. Mari was ruled by a dynasty of hereditary Shakkanakkus which was originally set by the Akkadian Empire and gained independence following Akkad's collapse. It is considered that the Shakkanakka gained some form of independence and came to be considered as "Kings" from the time of Apil-Kin. A critical analysis of the Shakkanakku List of Mari has been published.
 W
WThis is a list of Somali aristocratic and court titles that were historically used by the Somali people's various sultanates, kingdoms and empires. Also included are the honorifics reserved for Islamic notables as well as traditional leaders and officials within Somali customary law (xeer), in addition to the nobiliary particles set aside for distinguished individuals.
 W
WIn the Low Countries, stadtholder was an office of steward, designated a medieval official and then a national leader. The stadtholder was the replacement of the duke or earl of a province during the Burgundian and Habsburg period.
 W
WStrategos, plural strategoi, Latinized strategus, is used in Greek to mean military general. In the Hellenistic world and the Byzantine Empire the term was also used to describe a military governor. In the modern Hellenic Army it is the highest officer rank.
 W
WAn Upazila Nirbahi Officer---------- is the chief executive officer of an Upazila (subdistrict) and a mid-level officer of the Bangladesh Civil Service, known as Bangladesh Administrative Service. A Senior Assistant Secretary is usually assigned to this post.--
 W
WWāli, Wā'lī or vali is an administrative title that was used in the Muslim World to designate governors of administrative divisions. It is still in use in some countries influenced by Arab or Muslim culture. The division that a Wāli governs is called Wilayah, or in the case of Ottoman Turkey, "Vilayet".