 W
WAn agathodaemon or agathos daemon was a spirit (daemon) of ancient Greek religion. They were personal companion spirits, comparable to the Roman genii, who ensured good luck, health, and wisdom.
 W
WAttis was the consort of Cybele, in Phrygian and Greek mythology. His priests were eunuchs, the Galli, as explained by origin myths pertaining to Attis and castration. Attis was also a Phrygian god of vegetation. In his self-mutilation, death and resurrection he represents the fruits of the earth which die in winter only to rise again in the spring. According to Ovid's Metamorphoses, Attis transformed himself into a pine tree.
 W
WIn Aztec mythology, Centeōtl [senˈteoːt͡ɬ] is the maize deity. Cintli [ˈsint͡ɬi] means "dried maize still on the cob" and teōtl [ˈteoːt͡ɬ] means "deity". According to the Florentine Codex, Centeotl is the son of the earth goddess, Tlazolteotl and solar deity Piltzintecuhtli, the planet Mercury. Born on the day-sign 1 Xochitl. Another myth claims him as the son of the goddess Xochiquetzal. The majority of evidence gathered on Centeotl suggests that he is usually portrayed as a young man, with yellow body colouration. Some specialists believe that Centeotl used to be the maize goddess Chicomecōātl. Centeotl was considered one of the most important deities of the Aztec era. There are many common features that are shown in depictions of Centeotl. For example, there often seems to be maize in his headdress. Another striking trait is the black line passing down his eyebrow, through his cheek and finishing at the bottom of his jaw line. These face markings are similarly and frequently used in the late post-classic depictions of the 'foliated' Maya maize god.
 W
WChaquén was the god of sports and fertility in the religion of the Muisca. The Muisca and their confederation were one of the four advanced civilizations of the Americas and as they were warriors, sports was very important to train the fighters for wars, mainly fought between the zipazgo and the zacazgo but also against other indigenous peoples as the Panches, Muzos and others. When the Spanish arrived in the highlands of central Colombia, the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, they encountered resistance of the guecha warriors, trained by Chaquén.
 W
WIn ancient Roman religion, the god Consus was the protector of grains. He was represented by a grain seed. His altar (ara) was located at the first meta of the Circus Maximus. It was either underground, or according to other sources, covered with earth, which was swept off during the two Consualia, his festivals on August 21 and December 15 and on July 7 when the pontiffs held a sacrifice there. He was thus a chthonic god. The Flamen Quirinalis and the Vestals officiated at his rites.
 W
WIn ancient Roman religion, Ceres was a goddess of agriculture, grain crops, fertility and motherly relationships. She was originally the central deity in Rome's so-called plebeian or Aventine Triad, then was paired with her daughter Proserpina in what Romans described as "the Greek rites of Ceres". Her seven-day April festival of Cerealia included the popular Ludi Ceriales. She was also honoured in the May lustratio of the fields at the Ambarvalia festival, at harvest-time, and during Roman marriages and funeral rites.
 W
WIn Greek mythology, Cronus, Cronos, or Kronos was the leader and youngest of the first generation of Titans, the divine descendants of the primordial Gaia and Uranus. He overthrew his father and ruled during the mythological Golden Age, until he was overthrown by his own son Zeus and imprisoned in Tartarus. According to Plato, however, the deities Phorcys, Cronus, and Rhea were the eldest children of Oceanus and Tethys.
 W
WDaikokuten (大黒天) is a syncretic Japanese deity of fortune and wealth. Daikokuten originated from Mahākāla, the Buddhist version of the Hindu deity Shiva, conflated with the native Shinto god Ōkuninushi.
 W
WDionysus is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking and wine, of fertility, orchards and fruit, vegetation, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity and theatre in ancient Greek religion and myth.
 W
WEnbilulu was the god of rivers and canals in Mesopotamian mythology. In the creation mythology he was placed in charge of the sacred rivers Tigris and Euphrates by the god Enki. Also he was the deity of irrigation and farming. In the Sumerian story Enlil and Ninlil he is a son of Enlil and Ninlil. In Babylonian times he becomes the son of Ea and is connected with Adad.
 W
WEnkimdu is the Sumerian god of farming, in charge of canals and ditches.
 W
WEsus, Hesus, or Aisus was a Gaulish god known from two monumental statues and a line in Lucan's Bellum civile.
 W
WIn ancient Roman religion and myth, Faunus [ˈfau̯nʊs] was the horned god of the forest, plains and fields; when he made cattle fertile he was called Inuus. He came to be equated in literature with the Greek god Pan.
 W
WFreyr, sometimes anglicized as Frey, is a widely attested god in Norse mythology, associated with sacral kingship, virility, peace and prosperity, with sunshine and fair weather, and with good harvest. Freyr, sometimes referred to as Yngvi-Freyr, was especially associated with Sweden and seen as an ancestor of the Swedish royal house. According to Adam of Bremen, Freyr was associated with peace and pleasure, and was represented with a phallic statue in the Temple at Uppsala. According to Snorri Sturluson, Freyr was "the most renowned of the æsir", and was venerated for good harvest and peace.
 W
WIn Japanese religion, Yahata formerly in Shinto and later commonly known as Hachiman is the syncretic divinity of archery and war, incorporating elements from both Shinto and Buddhism.
 W
WHoori , also known as Hikohohodemi no Mikoto (彦火火出見尊), is a figure in Japanese mythology, the third and youngest son of Ninigi-no-Mikoto and the blossom princess Konohanasakuya-hime. He is one of the ancestors of the Emperors of Japan as the grandfather of Emperor Jimmu. He is also known as Yamasachi-hiko (山幸彦).
 W
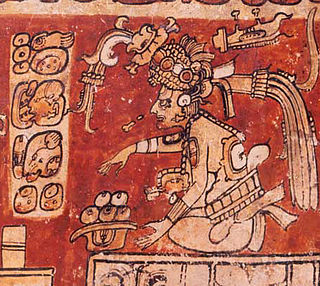
WItzamna is, in Maya mythology, an upper god and creator deity thought to reside in the sky. Itzamna is one of the most important gods in the Classic and Postclassic Maya pantheon. Although little is known about him, scattered references are present in early-colonial Spanish reports (relaciones) and dictionaries. Twentieth-century Lacandon lore includes tales about a creator god who may be a late successor to him. In the pre-Spanish period, Itzamna was often depicted in books and in ceramic scenes derived from them. Before the names of the Maya deities were deciphered, Itzamna was known as "god D", and is still sometimes referred to as "god D" by archeologists.
 W
WKokopelli is a fertility deity, usually depicted as a humpbacked flute player, who is venerated by some Native American cultures in the Southwestern United States. Like most fertility deities, Kokopelli presides over both childbirth and agriculture. He is also a trickster god and represents the spirit of music.
 W
WKukulkan, also spelled K’uk’ulkan, is the name of a Mesoamerican serpent deity. Prior to the Spanish Conquest of the Yucatán, Kukulkan was worshipped by the Yucatec Maya people of the Yucatán Peninsula, in what is now Mexico. The depiction of the Feathered Serpent is present in other cultures of Mesoamerica. Kukulkan is closely related to the deity Qʼuqʼumatz of the Kʼicheʼ people and to Quetzalcoatl of Aztec mythology. Little is known of the mythology of this Pre-Columbian era deity.
 W
WIn ancient Roman religion, agricultural deities were thought to care for every aspect of growing, harvesting, and storing crops. Preeminent among these are such major deities as Ceres and Saturn, but a large number of the many Roman deities known by name either supported farming or were devoted solely to a specific agricultural function.
 W
WLahar was the Sumerian cattle-god or goddess sent by Enlil and Enki from the sky down to earth in order to make abundant its cattle. He is the brother of Ashnan. Lahar, along with his sister, was created in the creation chamber of the gods so the Anunnaki might have food and clothes.
 W
WIn ancient Roman religion and mythology, Liber, also known as Liber Pater, was a god of viticulture and wine, fertility and freedom. He was a patron deity of Rome's plebeians and was part of their Aventine Triad. His festival of Liberalia became associated with free speech and the rights attached to coming of age. His cult and functions were increasingly associated with Romanised forms of the Greek Dionysus/Bacchus, whose mythology he came to share.
 W
WIn Hawaiian religion, the god Lono is associated with fertility, agriculture, rainfall, music and peace. In one of the many Hawaiian stories of Lono, he is a fertility and music god who descended to Earth on a rainbow to marry Laka. In agricultural and planting traditions, Lono was identified with rain and food plants. He was one of the four gods who existed before the world was created. Lono was also the god of peace. In his honor, the great annual festival of the Makahiki was held. During this period, war and unnecessary work was kapu (forbidden). In Hawaiian weather terminology, the winter Kona storms that bring rain to leeward areas are associated with Lono. Lono brings on the rains and dispenses fertility, and as such was sometimes referred to as Lono-makua. Ceremonies went through a monthly and yearly cycle. For 8 months of the year, the luakini (temple) was dedicated to Ku-with strict kapus. Four periods each month required strict ceremonies. Violators could have their property seized by priests or overlord chiefs, or be sentenced to death for serious breaches.
 W
WMahākāla is a deity common to Hinduism and Buddhism. In Hinduism, Mahākāla is a manifestation of Shiva and is the consort of the goddess Mahākālī; he most prominently appears in the Kalikula sect of Shaktism. Mahākāla also appears as a protector deity known as a dharmapala in Vajrayana Buddhism, particularly most Tibetan traditions as Citipati, and in Shingon Buddhism. He is known as Dàhēitiān and Daaih'hāktīn (大黑天) in Mandarin and Cantonese, Daeheukcheon (대흑천) in Korean, Đại Hắc Thiên in Vietnamese, and Daikokuten (大黒天) in Japanese.
 W
WIn ancient Roman religion and myth, Mars was the god of war and also an agricultural guardian, a combination characteristic of early Rome. He was the son of Jupiter and Juno, and he was the most prominent of the military gods in the religion of the Roman army. Most of his festivals were held in March, the month named for him, and in October, which began the season for military campaigning and ended the season for farming.
 W
WLike other Mesoamerican people, the traditional Maya recognize in their staple crop, maize, a vital force with which they strongly identify. This is clearly shown by their mythological traditions. According to the 16th-century Popol Vuh, the Hero Twins have maize plants for alter egos and man himself is created from maize. The discovery and opening of the Maize Mountain – the place where the corn seeds are hidden – is still one of the most popular of Maya tales. In the Classic period, the maize deity shows aspects of a culture hero.
 W
WNinurta (Sumerian: 𒀭𒊩𒌆𒅁: DNIN.URTA, meaning of this name not known), also known as Ninĝirsu (Sumerian: 𒀭𒊩𒌆𒄈𒋢: DNIN.ĜIR2.SU, meaning “Lord of Girsu”), is an ancient Mesopotamian god associated with farming, healing, hunting, law, scribes, and war who was first worshipped in early Sumer. In the earliest records, he is a god of agriculture and healing, who releases humans from sickness and the power of demons. In later times, as Mesopotamia grew more militarized, he became a warrior deity, though he retained many of his earlier agricultural attributes. He was regarded as the son of the chief god Enlil and his main cult center in Sumer was the Eshumesha temple in Nippur. Ninĝirsu was honored by King Gudea of Lagash (ruled 2144–2124 BC), who rebuilt Ninĝirsu's temple in Lagash.
 W
WIn ancient Roman religion, agricultural deities were thought to care for every aspect of growing, harvesting, and storing crops. Preeminent among these are such major deities as Ceres and Saturn, but a large number of the many Roman deities known by name either supported farming or were devoted solely to a specific agricultural function.
 W
WOkó, also known in Brazil as Ocô, is an Orisha. In Nigeria and the Benin Republic, he is a strong hunter & farming deity as well as a fighter against sorcery. He is associated with the annual new harvest of the white African yam. Among the deities, he is considered a close friend of Oosa Ogiyan and Shango, as well as at one time husband of Oya and Yemoja. Bees are considered the messengers of Oko.
 W
WŌkuninushi, also known as Ō(a)namuchi or Ō(a)namochi among other variants, is a kami in Japanese mythology. He is one of the central deities in the cycle of myths recorded in the Kojiki and the Nihon Shoki alongside the sun goddess Amaterasu and her brother, the wild god Susanoo, who is reckoned to be either Ōkuninushi's distant ancestor or father. In these texts, Ōkuninushi (Ōnamuchi) is portrayed as the head of the kunitsukami, the gods of the earth, and the original ruler of the terrestrial world, named Ashihara-no-Nakatsukuni. When the heavenly deities (amatsukami) headed by Amaterasu demanded that he relinquish his rule over the land, Ōkuninushi agreed to their terms and withdrew into the unseen world, which was given to him to rule over in exchange. Amaterasu's grandson Ninigi then came down from heaven to govern Ashihara-no-Nakatsukuni and eventually became the ancestor of the Japanese imperial line.
 W
WOsiris is the god of fertility, agriculture, the afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He was classically depicted as a green-skinned deity with a pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive atef crown, and holding a symbolic crook and flail. He was one of the first to be associated with the mummy wrap. When his brother, Set, cut him up into pieces after killing him, Isis, his wife, found all the pieces and wrapped his body up, enabling him to return to life. Osiris was at times considered the eldest son of the earth god Geb and the sky goddess Nut, as well as being brother and husband of Isis, with Horus being considered his posthumously begotten son. In the Old Kingdom the pharaoh was considered a son of the sun god Ra who, after his death, ascended to join Ra in the sky. With the spread of the Osiris cult, however, there was a change in beliefs. He was also associated with the epithet Khenti-Amentiu, meaning "Foremost of the Westerners", a reference to his kingship in the land of the dead. Through syncretism with Iah, he is also a god of the Moon.
 W
WPeko is an ancient Estonian and Finnish god of crops, especially barley and brewing. In the area of Setumaa, between Estonia and Russia, inhabited by the Seto language-speaking Setos, the cult of Peko was alive until the 20th century. Today, the Seto people also revere Peko as their national hero and king, the name and figure are widely used as a national symbol.
 W
WPortunus was the ancient Roman god of keys, doors, livestock and ports. He may have originally protected the warehouses where grain was stored, but later became associated with ports, perhaps because of folk associations between porta "gate, door" and portus "harbor", the "gateway" to the sea, or because of an expansion in the meaning of portus. Portunus later became conflated with the Greek Palaemon.
 W
WPotrimpo was a god of seas, earth, grain, and crops in the pagan Baltic, and Prussian mythology. He was one of the three main gods worshiped by the Old Prussians. Most of what is known about this god is derived from unreliable 16th-century sources.
 W
WIn Greek mythology, Priapus is a minor rustic fertility god, protector of livestock, fruit plants, gardens and male genitalia. Priapus is marked by his oversized, permanent erection, which gave rise to the medical term priapism. He became a popular figure in Roman erotic art and Latin literature, and is the subject of the often humorously obscene collection of verse called the Priapeia.
 W
WIn Māori mythology, Rongo or Rongo-mā-Tāne is a major god (atua) of cultivated plants, especially kumara, a vital crop. Other crops cultivated by Māori in traditional times included taro, yams (uwhi), cordyline (tī), and gourds (hue). Because of their tropical origin, most of these crops were difficult to grow except in the far north of the North Island, hence the importance of Rongo in New Zealand.
 W
WIn Gallo-Roman religion, Sucellus or Sucellos was a deity depicted as carrying a large mallet and also an olla and/or barrel. Originally a Celtic deity, his cult flourished not only among Gallo-Romans, but also to some extent among the neighbouring peoples of Raetia and Britain. He has been associated with agriculture and wine, particularly in the territory of the Aedui.
 W
WSukunabikona or Sukuna bikona is the Shinto kami of the onsen, agriculture, healing, magic, brewing sake and knowledge. His name means "the small lord of renown." He is often described as being a dwarf and is frequently paired with Ōkuninushi.
 W
WTakeminakata (タケミナカタ), also known as Minakatatomi or Takeminakatatomi, is a kami in Japanese mythology. Also known as Suwa Myōjin (諏訪明神) or Suwa Daimyōjin (諏訪大明神) after Suwa Grand Shrine in Nagano Prefecture in which he is enshrined alongside his consort Yasakatome, Takeminakata is historically worshiped as a god of wind, water and agriculture, as well as a patron of hunting and warfare, in which capacity he enjoyed a particularly fervent cult from various samurai clans during the medieval period such as the Hōjō or the Takeda. Takeminakata was also held to be the mythical ancestor of certain families who once served at the shrine as priests, foremost among them being the Suwa clan, the high priests of the Upper Shrine of Suwa who were also revered as living vessels of the god.
 W
WŌtoshi or Nigihayahi, commonly known: Toshigami or Ōtoshi is a Kami of the Shinto religion in Japan.
 W
WUkanomitama is a kami in classical Japanese mythology, associated with food and agriculture, often identified with Inari, the deity of rice.
 W
WUkko, Äijä [ˈæi̯jæ] or Äijö [ˈæi̯jø], parallel to Uku in Estonian mythology, is the god of the sky, weather, harvest and thunder in Finnish mythology. Ukkonen, the Finnish word for thunder is the diminutive form of the name Ukko. Unto Salo believes that Ilmari, another Finnic sky god, is the origin of Ukko, but that as Ukko Ilmari experienced very significant, although far from total, influence from the Indo-European sky god especially in the form of Thor. Others believe that Ukko's original name was Baltic Perkūnas. Ukko is held the most significant god of Finnish mythology, although it is disputed by scholars whether this is accountable to later Christian influence. In the folk poems and prayers he is also given the epithet Ylijumala, probably in reference to his status as the most highly regarded god and on the other hand his traditional domain in the heavens. Other names for Ukko include Pitkänen, Isäinen, Isoinen. Although portrayed active in myth, when appealed to Ukko makes all his appearances in legend solely by natural phenomena. According to Martti Haavio, the name Ukko was sometimes used as a common noun or generalised epithet for multiple deities instead of denoting a specific god.
 W
WIn Roman mythology, Vertumnus is the god of seasons, change and plant growth, as well as gardens and fruit trees. He could change his form at will; using this power, according to Ovid's Metamorphoses (xiv), he tricked Pomona into talking to him by disguising himself as an old woman and gaining entry to her orchard, then using a narrative warning of the dangers of rejecting a suitor to seduce her. The tale of Vertumnus and Pomona has been called "the first exclusively Latin tale."
 W
WIn Aztec mythology and religion, Xipe Totec or Xipetotec was a life-death-rebirth deity, god of agriculture, vegetation, the east, spring, goldsmiths, silversmiths, liberation, and the seasons. Xipe Totec was also known by various other names, including Tlatlauhca, Tlatlauhqui Tezcatlipoca and Youalahuan, and Yaotzin or Yoatzin. The Tlaxcaltecs and the Huexotzincas worshipped a version of the deity under the name of Camaxtli, and the god has been identified with Yopi, a Zapotec god represented on Classic Period urns. The female equivalent of Xipe Totec was the goddess Xilonen-Chicomecoatl.
 W
WJarylo, alternatively Yaryla, Iarilo, or Gerovit, is a Slavic god of vegetation, fertility and springtime.
 W
WYarovit is a god of war worshipped by Polabian Slavs associated with fertility and agriculture. In interpretatio romana, he was compared to Roman god of war Mars. His feast probably fell on April 15 or May 10 - sowing festival. His symbol was a golden shield that was kept in his temple. Because of the identical first part of the name he can be associated with the East Slavic god Yarilo, and because of the semantic similarity with Svetovit, some scholars suggest that both gods are related.
 W
WYúcahu —also written as Yukajú, Yocajú, Yokahu or Yukiyú— was the masculine spirit of fertility in Taíno mythology. He was one of the supreme deities or zemís of the Pre-Columbian Taíno peoples along with his mother Atabey who was his feminine counterpart. Dominant in the Caribbean region at the time of Columbus’ First voyages of Discovery, the peoples associated with Taíno culture inhabited the islands of the Bahamas, the Greater Antilles, and the Lesser Antilles.