 W
WThe president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces.
 W
WArticle Two of the United States Constitution establishes the executive branch of the federal government, which carries out and enforces federal laws. Article Two vests the power of the executive branch in the office of the president of the United States, lays out the procedures for electing and removing the president, and establishes the president's powers and responsibilities.
 W
WThe Twelfth Amendment to the United States Constitution provides the procedure for electing the president and vice president. It replaced the procedure provided in Article II, Section 1, Clause 3, by which the Electoral College originally functioned. The amendment was proposed by the Congress on December 9, 1803, and was ratified by the requisite three-fourths of state legislatures on June 15, 1804. The new rules took effect for the 1804 presidential election and have governed all subsequent presidential elections.
 W
WThe Twentieth Amendment to the United States Constitution moved the beginning and ending of the terms of the president and vice president from March 4 to January 20, and of members of Congress from March 4 to January 3. It also has provisions that determine what is to be done when there is no president-elect. The Twentieth Amendment was adopted on January 23, 1933.
 W
WThe Twenty-second Amendment to the United States Constitution limits the number of times a person is eligible for election to the office of President of the United States to two, and sets additional eligibility conditions for presidents who succeed to the unexpired terms of their predecessors.
 W
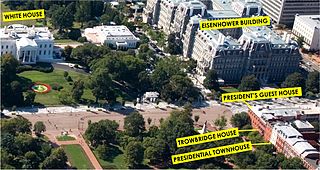
WBlair House, also known as The President's Guest House, is an official residence in Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States. The President's Guest House has been called "the world's most exclusive hotel" because it is primarily used as a state guest house to host visiting dignitaries and other guests of the president. Parts of the historic complex have been used for an official residence since the 1940s.
 W
WIn the United States, the chief of protocol is an officer of the United States Department of State responsible for advising the president of the United States, the vice president of the United States, and the United States secretary of state on matters of national and international diplomatic protocol. The chief of protocol holds the rank of Ambassador and Assistant Secretary of State.
 W
WThe election of the president and the vice president of the United States is an indirect election in which citizens of the United States who are registered to vote in one of the fifty U.S. states or in Washington, D.C., cast ballots not directly for those offices, but instead for members of the Electoral College. These electors then cast direct votes, known as electoral votes, for president, and for vice president. The candidate who receives an absolute majority of electoral votes is then elected to that office. If no candidate receives an absolute majority of the votes for president, the House of Representatives elects the president; likewise if no one receives an absolute majority of the votes for vice president, then the Senate elects the vice president.
 W
WThe Constitution of the United States provides several basic requirements for eligibility to be elected to the office of President. Individual states did not introduce significant relevant legislation until Barack Obama was elected in 2008. The controversy generated by various conspiracy theorists who asserted during the 2008 presidential election campaign that Obama was not a natural-born U.S. citizen, as mandated by the Constitution, and thus was ineligible to be President of the United States, prompted several state legislatures to consider legislation aimed at requiring future presidential candidates to show proof of presidential eligibility before being granted ballot access in their state.
 W
WThe Executive Office of the President (EOP) comprises the offices and agencies that support the work of the president at the center of the executive branch of the United States federal government. The EOP consists of several offices and agencies, such as the White House Office, the National Security Council, and the Office of Management and Budget.
 W
WFirst Ladies National Historic Site is a United States National Historic Site located in Canton, Ohio. During her residency in Washington, D.C. Mary Regula, wife of Ohio congressman Ralph Regula, spoke regularly about the nation's first ladies. Recognizing the paucity of research materials available she created a board to raise funds and for a historian to assemble a comprehensive bibliography on American first ladies. From these inspirations came a National First Ladies’ Library, established in 1996, and the First Ladies National Historic Site. The site was established in 2000 to commemorate all the United States first ladies and comprises two buildings: the Ida Saxton McKinley Historic Home and the Education & Research Center. Tours start at the Education & Research Center, located one block north of the Saxton McKinley house on Market Avenue. The 1895 building, formerly the City National Bank Building, was given to the National First Ladies’ Library in 1997.
 W
WThe flag of the President of the United States consists of the presidential coat of arms on a dark blue background. While having the same design as the presidential seal since 1945, the flag has a separate history, and the designs on the flag and seal have at different times influenced each other. The flag is often displayed by the President in official photos, flown next to the coffin of the President in official funeral processions, and flown on the President's motorcade. The flag is at times flown at half-staff, when a former President dies. The current flag is defined in Executive Order 10860:The Color and Flag of the President of the United States shall consist of a dark blue rectangular background of sizes and proportions to conform to military and naval custom, on which shall appear the Coat of Arms of the President in proper colors. The proportions of the elements of the Coat of Arms shall be in direct relation to the hoist, and the fly shall vary according to the customs of the military and naval services.
 W
WThe Henry G. Freeman Jr. Pin Money Fund was the operating name of an annuity fund of the Henry G. Freeman Jr. Trust, benefiting the First Ladies of the United States. The fund was established as part of the will of Henry G. Freeman Jr., a prominent Philadelphia real estate developer.
 W
WIn political studies, surveys have been conducted in order to construct historical rankings of the success of the presidents of the United States. Ranking systems are usually based on surveys of academic historians and political scientists or popular opinion. The scholarly rankings focus on presidential achievements, leadership qualities, failures and faults. Popular-opinion polls typically focus on recent or well-known presidents.
 W
W"I want a president" is a poem written by artist Zoe Leonard in 1992.
 W
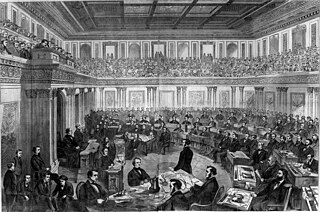
WThe Constitution of the United States gives Congress the authority to remove the president of the United States from office in two separate proceedings. The first one takes place in the House of Representatives, which impeaches the president of The United States of America by approving articles of impeachment through a simple majority vote. The second proceeding, the impeachment trial, takes place in the Senate. There, conviction on any of the articles requires a two-thirds majority vote and would result in the removal from office, and possible debarment from holding future office.
 W
WIn the United States, the presidential library system is a nationwide network of 13 libraries administered by the Office of Presidential Libraries, which is part of the National Archives and Records Administration (NARA). These are repositories for preserving and making available the papers, records, collections and other historical materials of every president of the United States from Herbert Hoover to George W. Bush. In addition to the library services, museum exhibitions concerning the presidency are displayed.
 W
WThe United States Marine Band is the premier band of the United States Marine Corps. Established by act of Congress on July 11, 1798, it is the oldest of the United States military bands and the oldest professional musical organization in the United States. Today, the Marine Band also includes the Marine Chamber Orchestra and Marine Chamber Ensembles.
 W
WThe oath of office of the president of the United States is the oath or affirmation that the president of the United States takes upon assuming office. The wording of the oath is specified in Article II, Section One, Clause 8, of the United States Constitution, and a new president must take it before exercising or carrying out any official powers or duties.
 W
WThe Office of American Innovation (OAI) was an office within the White House Office created by the Trump administration on March 27, 2017.
 W
WThe White House Office of Public Engagement is a unit of the White House Office within the Executive Office of the President of the United States. Under the administration of President Barack Obama, it was called the White House Office of Public Engagement and Intergovernment Affairs. President Donald Trump restored the prior name of the White House Office of Public Liaison and separated the White House Office of Intergovernmental Affairs. President Joe Biden changed the name to the White House Office of Public Engagement but retained Trump’s separate Intergovernmental Affairs Office in his administration.
 W
WThe Office of Trade and Manufacturing Policy (OTMP) was an office established within the White House Office by former US President Donald Trump by Presidential Executive Order 13797 on April 29, 2017.
 W
WThe United States Army Old Guard Fife and Drum Corps is one of four premier musical organizations of the United States Army. Members perform using musical instruments and wearing uniforms similar to those used by military musicians of the Continental Army during the American Revolution.
 W
WThe President's Daily Brief (PDB), sometimes referred to as the President's Daily Briefing or the President's Daily Bulletin, is a top-secret document produced and given each morning to the president of the United States, and is also distributed to a small number of top-level US officials who are approved by the president, and includes highly classified intelligence analysis, information about covert operations of the US Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) and reports from the most sensitive US sources or those shared by allied intelligence agencies. At the discretion of the president, the PDB may also be provided to the president-elect of the United States, between election day and inauguration, and to former presidents on request.
 W
WThe Presidential Issue, nicknamed the Prexies by collectors, is the series of definitive postage stamps issued in the United States in 1938, featuring all 29 U.S. presidents who were in office between 1789 and 1928, from George Washington to Calvin Coolidge. The presidents appear as small profile busts printed in solid-color designs through 50¢, and then as black on white images surrounded by colored lettering and ornamentation for $1, $2, and $5 values. Additional stamps in fractional-cent denominations offer busts of Benjamin Franklin and Martha Washington, as well as an engraving of the White House. With its total of 32 stamps, this was the largest definitive series yet issued by the U. S. Post Office.
 W
WNational security directives are presidential directives issued for the National Security Council (NSC). Starting with Harry Truman, every president since the founding of the National Security Council in 1947 has issued national security directives in one form or another, which have involved foreign, military and domestic policies. National security directives are generally highly classified and are available to the public only after "a great many years" have elapsed. Unlike executive orders, national security directives are usually directed only to the National Security Council and the most senior executive branch officials, and embody foreign and military policy-making guidance rather than specific instructions.
 W
WThe Presidential Emergency Operations Center is a bunker-like structure underneath the East Wing of the White House. It serves as a secure shelter and communications center for the President of the United States and others in case of an emergency.
 W
WThe United States presidential line of succession is the order in which officials of the United States federal government assume the powers and duties of the office of president of the United States if the incumbent president becomes incapacitated, dies, resigns, or is removed from office. The order of succession specifies that the office passes to the vice president; if the vice presidency is simultaneously vacant, or if the vice president is also incapacitated, the powers and duties of the presidency pass to the speaker of the House of Representatives, president pro tempore of the Senate, and then Cabinet secretaries, depending on eligibility.
 W
WPresidential M&M's is the name given to the commemorative packs of red, white, and blue-colored M&M's given to guests of the president of the United States on board Air Force One and in other presidential locations. They were first created in 1988 and were later to replace cigarettes as the standard gift given to guests of the president. The M&M's are presented in boxes about the size of a packet of cigarettes, with the Seal of the President of the United States and the signature of the sitting president on one face, and one of the M&M's characters holding the flag of the United States on the other.
 W
WA presidential proclamation is a statement issued by a US president on an issue of public policy and is a kind of presidential directive.
 W
WThe Presidential Service Badge (PSB) is an identification badge of the United States Armed Forces which is awarded to members of the U.S. Army, U.S. Navy, U.S. Air Force, U.S. Marine Corps, and U.S. Coast Guard as well as other members of the Uniformed Services, such as the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Commissioned Corps and the U.S. Public Health Service Commissioned Corps, who serve as full-time military staff to the President of the United States.
 W
WThe Presidential Townhouse is a U.S. government-owned building located at 716 Jackson Place NW in Washington, D.C., reserved for the exclusive use of former presidents of the United States during visits to the capital. Located across Pennsylvania Avenue from the White House, it adjoins several other government-owned townhouses used for official purposes, including Blair House, often used by visiting heads of state.
 W
WThe White House press secretary is a senior White House official whose primary responsibility is to act as spokesperson for the executive branch of the federal government of the United States, especially with regard to the president, senior aides and executives, as well as government policies.
 W
WThe religious affiliations of presidents of the United States can affect their electability, shape their stances on policy matters and their visions of society and also how they want to lead it. Speculation of Thomas Jefferson, Abraham Lincoln, and William Howard Taft being atheists was reported during election campaigns, while others, such as Jimmy Carter, used faith as a defining aspect of their campaigns and tenure to hold the office.
 W
WThe United States Presidential Scholars Program is a program of the United States Department of Education. It is described as "one of the Nation's highest honors for students" in the United States of America and the globe.
 W
WThe Seal of the President of the United States is used to mark correspondence from the president of the United States to the U.S. Congress, and is also used as a symbol of the presidency itself. The central design, based on the Great Seal of the United States, is the official coat of arms of the U.S. presidency and also appears on the presidential flag.
 W
WA signing statement is a written pronouncement issued by the President of the United States upon the signing of a bill into law. They are usually printed along with the bill in United States Code Congressional and Administrative News (USCCAN). The statements begin with wording such as "This bill, which I have signed today" and continue with a brief description of the bill and often several paragraphs of political commentary.
 W
WThe six-year itch, according to political scientists, is the pattern which takes place during a US president's sixth year in office. This year is characterized by the nation's disgruntled attitude towards the president and their political party. During this time, there is a midterm election and the party in power usually loses a significant number of seats in Congress.
 W
WUS Treasury Department Specimen books, also known as BEP presentation albums, were published by the Bureau of Engraving and Printing (BEP) from the mid-1860s through the 1910s. Prepared upon request of the United States Secretary of the Treasury, albums were generally presented to Cabinet members, select Members of Congress, diplomats and visiting dignitaries. Some extant albums still in their original binding bear the name of the recipient impressed in gold lettering on the cover. While no two presentation albums have exactly the same contents, each book usually contained portraits, vignettes, and/or images of buildings. Specimen books which contain whole proof images of currency are extremely rare.
 W
WThe United States government has maintained a variety of vehicles for the President. Because of the President's role as Commander-in-Chief, military transports are exclusively used for international travel, however the civilian Secret Service operates the President's motorcade.
 W
WWe the People, launched September 22, 2011, is a section of the whitehouse.gov website for petitioning the administration's policy experts. Petitions that meet a certain threshold of signatures are typically reviewed by Administration officials who prepare and issue official responses, however, this is not always the case. Criminal justice proceedings in the United States and other processes of the federal government are not subject to White House website petitions. We the People, rather, serves as a public relations device for the current White House administration to provide a venue for citizens to express themselves. On August 23, 2012, the White House Director of Digital Strategy Macon Phillips released the source code for the platform. The source code is available on GitHub, and lists both public domain status as a work of the U.S. federal government and licensing under the GPL v2. On December 19, 2017, the Trump administration announced its intention to temporarily shut down the website and replace it with a "new platform [that] would save taxpayers more than $1m a year." On January 20 2021, the day the Inauguration of Joe Biden took place, the website's address started redirecting to the White House's website home address.
 W
WThe White House Doctor: My Patients Were Presidents – A Memoir is a book authored by Connie Mariano, the first military woman in the history of the United States to be appointed as Physician to the President, the first female director of the medical unit of the White House, and the first Filipino-American to become a rear admiral in the US Navy. With a foreword from Bill Clinton, the autobiographical book takes a look at the personal lives of three American Presidents and three American First Ladies she had taken care of while working as a White House physician. It was described as a "fascinating look into what goes on behind closed doors at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue".
 W
WThe White House Initiative on Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders is a United States governmental office that works to empower Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders (AAPIs) to improve the quality of their lives, raise the standard of living of their families and communities, and more fully participate in our economy. The Initiative also works with the Native Hawaiian community. The Initiative collaborates with the White House Office of Public Liaison and designated federal departments and agencies to increase AAPI participation in programs in economic development, commerce, business, education, health and human services, housing, environment, arts, agriculture, labor and employment, transportation, justice, veterans affairs, and community development.
 W
WThe White House Office is an entity within the Executive Office of the President of the United States (EOP). The White House Office is headed by the White House chief of staff, who is also the head of the Executive Office of the President. The staff work for and report directly to the president, including West Wing staff and the president's senior advisers. Almost all of the White House Office staff are political appointees of the president, do not require Senate confirmation and can be dismissed at the discretion of the president. Aside from Cabinet secretaries and Supreme Court justices, whose nominations require the approval of the Senate, the President of the United States has the authority to appoint people to high-level positions within the federal government unilaterally.
 W
WThe White House Office of Intergovernmental Affairs is a unit of the White House Office, within the Executive Office of the President. It serves as the primary liaison between the White House and state, county, local, and tribal governments. The office focuses on building new and maintaining current relationships with governors, tribal leaders, mayors, state legislators, and county executives. The Office of Intergovernmental Affairs works with federal agencies and departments to ensure appropriate coordination between state, local, and tribal governments and the federal government. The Director of Intergovernmental Affairs at the White House Office for the Biden administration is Julie Chavez Rodriguez.
 W
WThe Staff Secretary is a position in the White House Office responsible for managing paper flow to the President and circulating documents among senior staff for comment. It has been referred to as "the nerve center of the White House."
 W
Wwhitehouse.gov is the official website of the White House and is owned by the United States government. It was launched in October 1994 by the Clinton Administration.