 W
WMeasurement is the quantification of attributes of an object or event, which can be used to compare with other objects or events. The scope and application of measurement are dependent on the context and discipline. In natural sciences and engineering, measurements do not apply to nominal properties of objects or events, which is consistent with the guidelines of the International vocabulary of metrology published by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures. However, in other fields such as statistics as well as the social and behavioural sciences, measurements can have multiple levels, which would include nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio scales.
 W
W3D body scanning is an application of various technologies such as Structured-light 3D scanner, 3D depth sensing, stereoscopic vision and others for ergonomic and anthropometric investigation of the human form as a point-cloud. The technology and practice within research has found 3D body scanning measurement extraction methodologies to be comparable to traditional anthropometric measurement techniques.
 W
W3D scanning is the process of analyzing a real-world object or environment to collect data on its shape and possibly its appearance. The collected data can then be used to construct digital 3D models.
 W
WAlcoholic spirits measures are instruments designed to measure exact amounts or shots of alcoholic spirits.
 W
WThe Allan variance (AVAR), also known as two-sample variance, is a measure of frequency stability in clocks, oscillators and amplifiers. It is named after David W. Allan and expressed mathematically as . The Allan deviation (ADEV), also known as sigma-tau, is the square root of the Allan variance, .
 W
WThe term anthropic unit is used with different meanings in archaeology, in measurement and in social studies.
 W
WAnthropometry refers to the measurement of the human individual. An early tool of physical anthropology, it has been used for identification, for the purposes of understanding human physical variation, in paleoanthropology and in various attempts to correlate physical with racial and psychological traits. Anthropometry involves the systematic measurement of the physical properties of the human body, primarily dimensional descriptors of body size and shape. Since commonly used methods and approaches in analysing living standards were not helpful enough, the anthropometric history became very useful for historians in answering questions that interested them.
 W
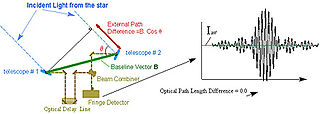
WAstrometry is a branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other celestial bodies. It provides the kinematics and physical origin of the Solar System and our galaxy, the Milky Way.
 W
WBird measurement or bird biometrics are approaches to quantify the size of birds in scientific studies. The measurements of the lengths of specific parts and the weights of birds varies between species, populations within species, between the sexes and depending on age and condition. In order for measurements to be useful, they need to be well defined so that measurements taken are consistent and comparable with those taken by others or at other points of time. Measurements can be useful to study growth, variation between geographically separated forms, identify differences between the sexes, age or otherwise characterize individuals birds. While certain measurements are regularly taken in the field to study living birds some others are applicable only to specimens in the museum or measurable only in a laboratory. The conventions used for measurement can vary widely between authors and works, making comparisons of sizes a matter that needs considerable care.
 W
WIn artillery, caliber or calibre is the internal diameter of a gun barrel, or - by extension - a relative measure of the barrel length.
 W
WCertified Reference Materials (CRMs) are ‘controls’ or standards used to check the quality and metrological traceability of products, to validate analytical measurement methods, or for the calibration of instruments. A certified reference material is a particular form of measurement standard.
 W
WCoverage error is a type of non-sampling error that occurs when there is not a one-to-one correspondence between the target population and the sampling frame from which a sample is drawn. This can bias estimates calculated using survey data. For example, a researcher may wish to study the opinions of registered voters by calling residences listed in a telephone directory. Undercoverage may occur if not all voters are listed in the phone directory. Overcoverage could occur if some voters have more than one listed phone number. Bias could also occur if some phone numbers listed in the directory do not belong to registered voters. In this example, undercoverage, overcoverage, and bias due to inclusion of unregistered voters in the sampling frame are examples of coverage error.
 W
WIn electrical engineering, current sensing is any one of several techniques used to measure electric current. The measurement of current ranges from picoamps to tens of thousands of amperes. The selection of a current sensing method depends on requirements such as magnitude, accuracy, bandwidth, robustness, cost, isolation or size. The current value may be directly displayed by an instrument, or converted to digital form for use by a monitoring or control system.
 W
WIn analytical chemistry, the detection limit, lower limit of detection, or LOD, often mistakenly confused with the analytical sensitivity, is the lowest quantity of a substance that can be distinguished from the absence of that substance with a stated confidence level. The detection limit is estimated from the mean of the blank, the standard deviation of the blank, the slope of the calibration plot and a defined confidence factor. Another consideration that affects the detection limit is the accuracy of the model used to predict concentration from the raw analytical signal.
 W
WDressed weight refers to the weight of an animal after being partially butchered, removing all the internal organs and oftentimes the head as well as inedible portions of the tail and legs. It includes the bones, cartilage and other body structure still attached after this initial butchering. It is usually a fraction of the total weight of the animal, and an average of 59% of the original weight for cattle. There is no singular way to dress an animal, as what is removed depends on whether it will be cooked whole, or butchered further for sale of individual parts. For pigs, the dressed weight typically includes the skin, while most other ungulates are typically dressed without. For fowl, it is calculated with skin but without feathers. It can be expressed as a percentage of the animal's live weight, when it is known as the killing out percentage.
 W
WIn flow measurement, flow meter error is typically reported by a percentage indicating non-linearity of the device. This can be expressed as either a +/- percentage based on either the full range capacity of the device or as a percentage of the actual indicated flow. In practice the flow meter error is a combination of repeatability, accuracy and the uncertainty of the reference calibration. http://www.flowmeters.co.uk/liquid-flow-meter-performance-specification-glossary/
 W
WA Helium analyzer is an instrument used to identify the presence and concentration of helium in a mixture of gases. In Technical diving where breathing gas mixtures known as Trimix comprising oxygen, helium and nitrogen are used, it is necessary to know the fraction of helium in the mixture to reliably calculate decompression schedules for dives using that mixture.
 W
WThe Klingons are a fictional species in the science fiction franchise Star Trek.
 W
WLaser Doppler imaging (LDI) is an imaging method that uses a laser beam to scan live tissue. When the laser light reaches the tissue, the moving blood cells generate doppler components in the reflected (backscattered) light. The light that comes back is detected using a photodiode that converts it into an electrical signal. Then the signal is processed to calculate a signal that is proportional to the tissue perfusion in the scanned area. When the process is completed, the signal is processed to generate an image that shows the perfusion on a screen.
 W
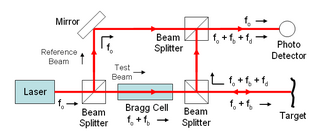
WLaser Doppler velocimetry, also known as laser Doppler anemometry, is the technique of using the Doppler shift in a laser beam to measure the velocity in transparent or semi-transparent fluid flows or the linear or vibratory motion of opaque, reflecting surfaces. The measurement with laser Doppler anemometry is absolute and linear with velocity and requires no pre-calibration.
 W
WA laser Doppler vibrometer (LDV) is a scientific instrument that is used to make non-contact vibration measurements of a surface. The laser beam from the LDV is directed at the surface of interest, and the vibration amplitude and frequency are extracted from the Doppler shift of the reflected laser beam frequency due to the motion of the surface. The output of an LDV is generally a continuous analog voltage that is directly proportional to the target velocity component along the direction of the laser beam.
 W
WIn the science of measurement, the least count of a measuring instrument is the smallest and accurate value in the measured quantity that can be resolved on the instrument's scale. The least count is related to the precision of an instrument; an instrument that can measure smaller changes in a value relative to another instrument, has a smaller "least count" value and so is more precise. Any measurement made by the instrument can be considered repeatable to no less than the resolution of the least count. The least count of an instrument is inversely proportional to the precision of the instrument.
 W
WMagnetic resonance velocimetry (MRV) is an experimental method to obtain velocity fields in fluid mechanics. MRV is based on the phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance and adapts a medical magnetic resonance imaging system for the analysis of technical flows. The velocities are usually obtained by phase contrast magnetic resonance imaging techniques. This means velocities are calculated from phase differences in the image data that has been produced using special gradient techniques. MRV can be applied using common medical MRI scanners. The term magnetic resonance velocimetry became current due to the increasing use of MR technology for the measurement of technical flows in engineering.
 W
WThe margin of error is a statistic expressing the amount of random sampling error in the results of a survey. The larger the margin of error, the less confidence one should have that a poll result would reflect the result of a survey of the entire population. The margin of error will be positive whenever a population is incompletely sampled and the outcome measure has positive variance, which is to say, the measure varies.
 W
WMeasurement category is a method of classification by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) of live electric circuits used in measurement and testing of installations and equipment, usually in the relation within a building.
 W
WA TDR moisture sensor employs time-domain reflectometry (TDR) to measure moisture content indirectly based on the correlation to electric and dielectric properties of materials, such as soil, agrarian products, snow, wood or concrete.
 W
WConcepts for describing aspects of nature by numbers are called physical quantities. Examples may range from counting fruit to reading a thermometer gauge to determine temperature.
 W
WThe Metre Convention, also known as the Treaty of the Metre, is an international treaty that was signed in Paris on 20 May 1875 by representatives of 17 nations. The treaty created the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM), an intergovernmental organization under the authority of the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) and the supervision of the International Committee for Weights and Measures (CIPM), that coordinates international metrology and the development of the metric system.
 W
WMithqāl is a unit of mass equal to 3.64 grams (0.117 ozt) which is mostly used for measuring precious metals, such as gold, and other commodities, like saffron.
 W
WMithqāl is a unit of mass equal to 3.64 grams (0.117 ozt) which is mostly used for measuring precious metals, such as gold, and other commodities, like saffron.
 W
WMolecular tagging velocimetry (MTV) is a specific form of flow velocimetry, a technique for determining the velocity of currents in fluids such as air and water. In its simplest form, a single "write" laser beam is shot once through the sample space. Along its path an optically induced chemical process is initiated, resulting in the creation of a new chemical species or in changing the internal energy state of an existing one, so that the molecules struck by the laser beam can be distinguished from the rest of the fluid. Such molecules are said to be "tagged".
 W
WParticipatory monitoring is the regular collection of measurements or other kinds of data (monitoring), usually of natural resources and biodiversity, undertaken by local residents of the monitored area, who rely on local natural resources and thus have more local knowledge of those resources. Those involved usually live in communities with considerable social cohesion, where they regularly cooperate on shared projects.
 W
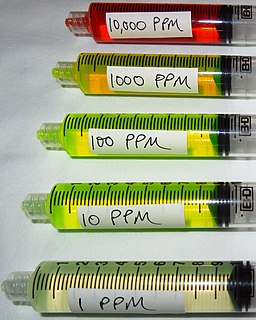
WIn science and engineering, the parts-per notation is a set of pseudo-units to describe small values of miscellaneous dimensionless quantities, e.g. mole fraction or mass fraction. Since these fractions are quantity-per-quantity measures, they are pure numbers with no associated units of measurement. Commonly used are parts-per-million, parts-per-billion, parts-per-trillion and parts-per-quadrillion. This notation is not part of the International System of Units (SI) system and its meaning is ambiguous.
 W
WIn geology, a piercing point is defined as a feature that is cut by a fault, then moved apart. Reconfiguring the piercing point back in its original position is the primary way geologists can find out the minimum slip, or displacement, along a fault. This can be done on a large scale, a small scale or even a single hand sample/rock.
 W
WPlanar laser-induced fluorescence (PLIF) is an optical diagnostic technique widely used for flow visualization and quantitative measurements. PLIF has been shown to be used for velocity, concentration, temperature and pressure measurements.
 W
WThe scale of a map is the ratio of a distance on the map to the corresponding distance on the ground. This simple concept is complicated by the curvature of the Earth's surface, which forces scale to vary across a map. Because of this variation, the concept of scale becomes meaningful in two distinct ways.
 W
WA sewing gauge is a ruler, typically 6 inches long, used for measuring short spaces. It is typically a metal scale, marked in both inches and centimeters with a sliding pointer, similar in use to a caliper. It is used to mark hems for alterations as well as intervals between pleats and buttonholes and buttonhole lengths. It can be also used as a compass to draw arcs and circles by anchoring the slider with a pin and placing the tip of a marking pencil in the hole located at the end of the scale. Some models also incorporate a button shank and a blunt point for turning corners right side out.
 W
WA shot glass is a glass originally designed to hold or measure spirits or liquor, which is either imbibed straight from the glass or poured into a cocktail. An alcoholic beverage served in a shot glass and typically consumed quickly, in one gulp, may also be known as a "shooter".
 W
WA synthetic instrument is a term in metrology. A Synthetic Instrument is software that runs on a Synthetic Measurement System to perform a specific synthesis, analysis, or measurement function. A Synthetic Measurement System (SMS) is a common, general purpose, physical hardware platform that is intended to perform many kinds of synthesis, analysis, or measurement functions using Synthetic Instruments.
 W
WTelemetry is the in situ collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek roots tele, "remote", and metron, "measure". Systems that need external instructions and data to operate require the counterpart of telemetry, telecommand.
 W
WThin filament pyrometry (TFP) is an optical method used to measure temperatures. It involves the placement of a thin filament in a hot gas stream. Radiative emissions from the filament can be correlated with filament temperature. Filaments are typically silicon carbide (SiC) fibers with a diameter of 15 micrometres. Temperatures of about 800–2500 K can be measured.
 W
WUncertainty refers to epistemic situations involving imperfect or unknown information. It applies to predictions of future events, to physical measurements that are already made, or to the unknown. Uncertainty arises in partially observable or stochastic environments, as well as due to ignorance, indolence, or both. It arises in any number of fields, including insurance, philosophy, physics, statistics, economics, finance, psychology, sociology, engineering, metrology, meteorology, ecology and information science.
 W
WThe uncertainty parameter U is a parameter introduced by the Minor Planet Center (MPC) to quantify concisely the uncertainty of a perturbed orbital solution for a minor planet. The parameter is a logarithmic scale from 0 to 9 that measures the anticipated longitudinal uncertainty in the minor planet's mean anomaly after 10 years. The larger the number, the larger the uncertainty. The uncertainty parameter is also known as condition code in JPL's Small-Body Database Browser. The U value should not be used as a predictor for the uncertainty in the future motion of near-Earth objects.
 W
WA unit of measurement is a definite magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other quantity of that kind can be expressed as a multiple of the unit of measurement. For example, a length is a physical quantity. The metre is a unit of length that represents a definite predetermined length. When we say 10 metres, we actually mean 10 times the definite predetermined length called "metre". Measurement is a process of determining how large or small a physical quantity is as compared to a basic reference quantity of the same kind.
 W
WVelocimetry is the measurement of the velocity of fluids. This is a task often taken for granted, and involves far more complex processes than one might expect. It is often used to solve fluid dynamics problems, study fluid networks, in industrial and process control applications, as well as in the creation of new kinds of fluid flow sensors. Methods of velocimetry include particle image velocimetry and particle tracking velocimetry, Molecular tagging velocimetry, laser-based interferometry, ultrasonic Doppler methods, Doppler sensors, and new signal processing methodologies.
 W
WVelocity interferometer system for any reflector (VISAR) is a time-resolved velocity measurement system that uses laser interferometry to measure the surface velocity of solids moving at high speeds. For solids experiencing high velocity impact or explosive conditions, VISAR plots the free-surface velocity against time to show the shock wave profile of a material. VISAR is a useful tool in determining the pressure-density relationship of a material known as the Rankine-Hugoniot conditions or simply the "Hugoniot".
 W
WA vernier scale, named after Pierre Vernier, is a visual aid to take an accurate measurement reading between two graduation markings on a linear scale by using mechanical interpolation; thereby increasing resolution and reducing measurement uncertainty by using vernier acuity to reduce human estimation error.
 W
WVibration calibrators , sometimes also called reference shakers, are electromechanical instruments which enable calibration of vibration sensors and measuring instruments to traceable standards. They produce sinusoidal mechanical vibration signals with known amplitudes and frequencies. The vibrating part of the instrument is usually a cylindrical steel stud with an internal thread for attachment of the test object. An electrodynamic or piezoelectric actuator system is used to produce the vibrations. With older instruments it was necessary to adjust the vibration amplitude according to the weight of the test object. However, modern instruments contain a built-in reference accelerometer and closed-loop control, with which the amplitude is kept constant up to a maximum specified weight of test object. Older models can be used to calibrate objects weighing up to a maximum of approximately 100 g, whereas the latest instruments can work stably with test objects weighing over 500 g.