 W
WSugar was first produced from sugarcane plants in Northern India sometime after the first century AD. The derivation of the word “sugar” is thought to be from Sanskrit शर्करा (śarkarā), meaning "ground or candied sugar," originally "grit, gravel". Sanskrit literature from ancient India, written between 1500 - 500 BC provides the first documentation of the cultivation of sugar cane and of the manufacture of sugar in the Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent. The Sanskrit name for a crudely made sugar substance was guda, meaning “to make into a ball or to conglomerate."
 W
WFranz Karl Achard was a German (Prussian) chemist, geoscientist, physicist, and biologist. His principal discovery was the production of sugar from sugar beets.
 W
WThe terms acid egg and montejus are sometimes used interchangeably to refer to a device with no moving parts formerly used instead of a pump in order to transfer difficult liquids. The principle is that a strong vessel containing the liquid is pressurized with gas or steam, forcing the liquid into a pipe thereby causing flow. When the liquid has been transferred, the pressure is released and more liquid is put in via gravity. It is thus cyclic in operation. The same principle has been used to lift water and called an air displacement pump or intermittent gas-lift pump, and has been applied to pumping oil up from the formation. Its use has largely been superseded by modern pumps, but it is still used sometimes for special tasks.
 W
WThe Amelioration Act 1798 was a statute passed by the Leeward Islands to improve the conditions of slaves in the British Caribbean colonies.
 W
WAnnaberg Historic District is a historic section of Saint John, United States Virgin Islands where the Annaberg sugar plantation ruins are located. The district is located on the north shore of the island west of Mary's Point in the Maho Bay quarter.
 W
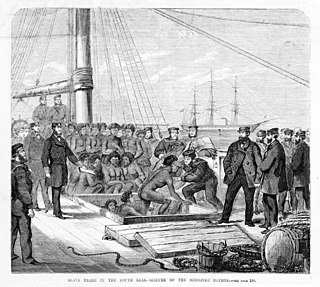
WThe Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of various enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Passage, and existed from the 16th to the 19th centuries. The vast majority of those who were enslaved and transported in the transatlantic slave trade were people from Central and West Africa, who had been sold by other West Africans, or by half-European "merchant princes" to Western European slave traders, who brought them to the Americas. Except for the Portuguese, European slave traders generally did not participate in the raids because life expectancy for Europeans in sub-Saharan Africa was less than one year during the period of the slave trade. The South Atlantic and Caribbean economies were particularly dependent on labour for the production of sugarcane and other commodities. This was viewed as crucial by those Western European states that, in the late 17th and 18th centuries, were vying with each other to create overseas empires.
 W
WBlackbirding involves the coercion of people through deception or kidnapping to work as slaves or poorly paid labourers in countries distant to their native land. The term has been most commonly applied to the large-scale taking of people indigenous to the numerous islands in the Pacific Ocean during the 19th and 20th centuries. These blackbirded people were called Kanakas or South Sea Islanders. They were taken from places such as the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Niue, Easter Island, Gilbert Islands, Tuvalu and the islands of the Bismarck Archipelago amongst others.
 W
WCasa Rosita Serrallés is a historic building in the city of Ponce, Puerto Rico, located between the former Escuela Libre de Música Juan Morel Campos and the Museo de la Historia de Ponce, and immediately behind Teatro La Perla, on Calle Salud street. It was built for one of the heirs of Juan Eugenio Serrallés Perez, son of businessman Juan Serrallés Colón, founder of Destilería Serrallés, and himself the CEO of the company that founded Ron Don Q. The building was purchased by the government of the Autonomous Municipality of Ponce in 2008 for its architectural, historic, and cultural value. As of February 2012, the building was being restored to convert it into an annex of the Museo de la Historia de Ponce to depict the 1985 Mameyes tragedy of barrio Portugues Urbano in Ponce. In 2014 it opened as "Museo de la Recordacion Barrio Mameyes" under Ponce mayor María Meléndez at Calle Salud 67. It is also known as "Sala Memorial del Barrio Mameyes" as it operates as a part of the Museo de la Historia de Ponce.
 W
WThe colonial molasses trade occurred throughout the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries in the British colonies of the Americas. Molasses was a major trading product.
 W
WConfections of the English Renaissance span a wide range of products. All were heavily based on sugar, which was a relatively new development. Many were considered to have medicinal properties – a belief that was influenced by the Arabic use of sugar as a medicine and that carried over from medieval sugar usage. In the mid-sixteenth century, sugar became cheaper and more widely available to the general populace due to European colonization of the New World. It began to be used more as a flavouring, preservative, and sweetener, as it is today, rather than as medicine.
 W
WThomas Daniel was a slave owner and sugar merchant in Bristol who was known as the 'King of Bristol' because of his omnipotence in corporate affairs for over 50 years.
 W
WSugar production in the United States Virgin Islands was an important part of the Economy of the United States Virgin Islands for over two hundred years. Long before the islands became part of the United States in 1917, the islands, particular the island of Saint Croix, was exploited by the Danish from the early 18th century and by 1800 over 30,000 acres were under cultivation, earning Saint Croix a reputation as "The Garden of the West Indies". Since the closing of the last sugar factory on Saint Croix in 1966, the industry has become only a memory.
 W
WPhilip DeLaMare was a convert to Mormonism who was a key figure in the attempts to introduce the sugar beet industry to Utah in the late-19th century. The modern neighborhood Sugar House, Salt Lake City is named for that trial sugar factory.
 W
WThe Demerara rebellion of 1823 was an uprising involving more than 10,000 enslaved people that took place in the colony of Demerara-Essequibo (Guyana). The rebellion, which began on August 18, 1823, and lasted for two days, was led by slaves with the highest status. In part they were reacting to poor treatment and a desire for freedom; in addition, there was a widespread, mistaken belief that Parliament had passed a law for emancipation, but it was being withheld by the colonial rulers. Instigated chiefly by Jack Gladstone, a slave at "Success" plantation, the rebellion also involved his father, Quamina, and other senior members of their church group. Its English pastor, John Smith, was implicated.
 W
WThe history of draining and development of the Everglades dates back to the 19th century. A national push for expansion and progress toward the latter part of the 19th century stimulated interest in draining the Everglades for agricultural use. According to historians, "From the middle of the nineteenth century to the middle of the twentieth century, the United States went through a period in which wetland removal was not questioned. Indeed, it was considered the proper thing to do."
 W
WThe Dutch East India Company, officially the United East India Company, was a megacorporation founded by a government-directed consolidation of several rival Dutch trading companies (voorcompagnieën) in the early 17th century. It was established on 20 March 1602, as a chartered company to trade with Mughal India in the early modern period, from which 50% of textiles and 80% of silks were imported, chiefly from its most developed region known as Bengal Subah. In addition, the company traded with Indianised Southeast Asian countries when the Dutch government granted it a 21-year monopoly on the Dutch spice trade.
 W
WEbenezer Herrick Dyer was an American businessman who established the first successful commercial beet sugar mill in the U.S., and as such was called the "father of the American beet sugar industry".
 W
WThe Everglades Agricultural Area Environmental Protection District, better known as simply the Everglades Agricultural Area (EAA), is an area extending south from Lake Okeechobee to the northern levee of Water Conservation Area 3A, from its eastern boundary at the L-8 canal to the western boundary along the L-1, L-2, and L-3 levees. The EAA incorporates almost 3,000 square kilometers of highly productive agricultural land. The EAA was established by the State Legislature as a special district representing landowners within the EAA Basin for the purposes of ensuring environmental protection. Means include conducting scientific research on environmental matters related to air and water and land management practices and implementing the financing, construction, and operation of works and facilities designed to prevent, control, abate or correct environmental problems and improve the environmental quality of air and water resources.
 W
WThomas Henry Fitzgerald was a pioneer in sugar cane farming in the early days of the colony of Queensland, Australia. He was a politician, first in New Zealand, then in Queensland. His descendants went on to become notable names in Queensland politics, business and law. He will be best remembered for founding the town of Innisfail.
 W
WThe 2008 Georgia sugar refinery explosion was an industrial disaster that occurred on February 7, 2008, in Port Wentworth, Georgia, United States. Fourteen people were killed and forty injured when a dust explosion occurred at a sugar refinery owned by Imperial Sugar. Dust explosions had been an issue of concern among United States authorities since three fatal accidents in 2003, with efforts made to improve safety and reduce the risk of recurrence.
 W
WThe Haʻikū Sugar Mill was a processing factory for sugarcane from 1861 to 1879 on the island of Maui in Hawaii.
 W
WThe Haitian Revolution was a successful insurrection by self-liberated slaves against French colonial rule in Saint-Domingue, now the sovereign state of Haiti. The revolt began on 22 August 1791, and ended in 1804 with the former colony's independence. It involved blacks, mulattoes, French, Spanish, and British participants—with the ex-slave Toussaint Louverture emerging as Haiti's most charismatic hero. The revolution was the only slave uprising that led to the founding of a state which was both free from slavery, and ruled by non-whites and former captives. It is now widely seen as a defining moment in the history of the Atlantic World.
 W
WPaul Isenberg was a German businessman who developed the sugarcane business in the Kingdom of Hawaii.
 W
WThe Japanese Problem, also referred to as the Japanese Menace or the Japanese Conspiracy, was the name given to racial tensions in Hawaii between the European-American sugarcane plantation owners and the Japanese immigrants hired to work in the cane fields.
 W
WKing Kalākaua of the Hawaiian Kingdom made a state visit to the United States from November 28, 1874 to February 3, 1875, at the invitation of US President Ulysses S. Grant. The 91-day round-trip journey across the United States began in Honolulu on November 17, 1874 and returned to Hawaii on February 15, 1875. His arrival at San Francisco on November 28 was the beginning of a state visit, making him the first reigning monarch of any nation to set foot in the United States. Upon his arrival in Washington, DC, the United States Congress held the first joint meeting in the body's history, less formal than a joint session, to receive him. President Grant hosted him as honoree of the first state dinner at the White House.
 W
WRuth Colvin Starrett McGuire (1893–1950) was an American plant pathologist. She studied sugar cane diseases and sugarbeets.
 W
WThe Molasses Act of 1733 was an Act of the Parliament of Great Britain, which imposed a tax of six pence per gallon on imports of molasses from non-British colonies. Parliament created the act largely at the insistence of large plantation owners in the British West Indies. The Act was not passed for the purpose of raising revenue, but rather to regulate trade by making British products cheaper than those from the French West Indies. The Molasses Act greatly affected the significant colonial molasses trade.
 W
WMount Healthy windmill is a ruined windmill on the north side of Tortola in the British Virgin Islands. It was formerly used during the plantation era of the Territory to crush sugar cane. After the collapse of the sugar economy in the early nineteenth century the windmill fell into disuse and became a ruin. It crushed cane for the sugar mill and rum distillery in nearby Brewer's Bay. There are other ruins like the Boiling House, remnants of the Animal Mill Round, distillery, hospital, storage, shed, and housing. The 18th century windmill belonged to the area's wealthiest planter. Slaves harvested and processed sugar cane into sugar at this extensive sugarcane plantation.
 W
WThe Oahu sugar strike of 1920 was a multiracial strike in Hawaii of two unions, the Filipino American Filipino Labor Union and the Japanese American Federation of Japanese Labor. The labor action involved 8,300 sugar plantation field workers out on strike from January to July 1920.
 W
WThe Treaty of reciprocity between the United States of America and the Hawaiian Kingdom was a free trade agreement signed and ratified in 1875 that is generally known as the Reciprocity Treaty of 1875.
 W
WReef Bay Sugar Factory Historic District is a historic section of Saint John, United States Virgin Islands located on the south central coast adjacent to Reef Bay. The land is the site of a sugar factory. The property was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places on July 23, 1981.
 W
WThe restoration of the Everglades is an ongoing effort to remedy damage inflicted on the environment of southern Florida during the 20th century. It is the most expensive and comprehensive environmental repair attempt in history. The degradation of the Everglades became an issue in the United States in the early 1970s after a proposal to construct an airport in the Big Cypress Swamp. Studies indicated the airport would have destroyed the ecosystem in South Florida and Everglades National Park. After decades of destructive practices, both state and federal agencies are looking for ways to balance the needs of the natural environment in South Florida with urban and agricultural centers that have recently and rapidly grown in and near the Everglades.
 W
WNorbert Rillieux was an American-French inventor who was widely considered one of the earliest chemical engineers and noted for his pioneering invention of the multiple-effect evaporator. This invention was an important development in the growth of the sugar industry. Rillieux, a French-speaking Creole, was a cousin of the painter Edgar Degas.
 W
WCastillo Serrallés is a mansion located in the city of Ponce, Puerto Rico, overlooking the downtown area. It was built during the 1930s for Juan Eugenio Serrallés, son of businessman Juan Serrallés, founder of Destilería Serrallés. The structure sits on a 2.5-acre (1.0 ha) exceedingly manicured property. Nowadays, the structure functions as a museum, Museo Castillo Serrallés, with information about the sugar cane and rum industries and its impact in the economy of Puerto Rico. It is also increasingly used as a venue for social activities, including destination weddings. The property was listed in the National Register of Historic Places in 1980. In 1996, the structure was featured in the American TV series America's Castles.
 W
WThe Slave Trade Act 1807, officially An Act for the Abolition of the Slave Trade, was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom prohibiting the slave trade in the British Empire. Although it did not abolish the practice of slavery, it did encourage British action to press other nation states to abolish their own slave trades.
 W
WSlavery in the British and French Caribbean refers to slavery in the parts of the Caribbean dominated by France or the British Empire.
 W
WAdolph Claus J. Spreckels, , was a major industrialist in Hawai'i during the kingdom, republican and territorial periods of the islands' history. He also involved himself in several California enterprises, most notably the company that bears his name, Spreckels Sugar Company.
 W
WSucreries Raffineries Bulgares was a Belgian company active in Bulgaria from 1897 to 1916.
 W
WThe Sugar Act 1764, also known as the American Revenue Act 1764 or the American Duties Act, was a revenue-raising act passed by the Parliament of Great Britain on 5 April 1764. The preamble to the act stated: "it is expedient that new provisions and regulations should be established for improving the revenue of this Kingdom ... and ... it is just and necessary that a revenue should be raised ... for defraying the expenses of defending, protecting, and securing the same." The earlier Molasses Act 1733, which had imposed a tax of six pence per gallon of molasses, had never been effectively collected due to colonial evasion. By reducing the rate by half and increasing measures to enforce the tax, the British hoped that the tax would actually be collected. These incidents increased the colonists' concerns about the intent of the British Parliament and helped the growing movement that became the American Revolution.
 W
WSugar Blues is a book by William Dufty that was released in 1975 and has become a dietary classic. According to the publishers, over 1.6 million copies have been printed.
 W
WSugarcane was introduced to Hawaii by its first inhabitants in approximately 600 AD and was observed by Captain Cook upon arrival in the islands in 1778. Sugar quickly turned into a big business and generated rapid population growth in the islands with 337,000 people immigrating over the span of a century. The sugar grown and processed in Hawaii was shipped primarily to the United States and, in smaller quantities, globally. Sugarcane and pineapple plantations were the largest employers in Hawaii. Today both are gone, production having moved to other countries.
 W
WA sugar-baker was the owner of a sugar house, a factory for the refining of raw sugar from Barbados. Sugar refining would normally be combined with sugar trading, which was a lucrative business. The architectural historian Kerry Downes gives an example of one sugar baker's house in Liverpool being estimated to bring in £40,000 a year in trade from Barbados.
 W
WThe Taiwan Sugar Railways were an extensive series of 2 ft 6 in narrow gauge railways concentrated mostly in southern and central Taiwan which were originally built to haul sugarcane from the fields to the sugar mills, but also capable of providing limited passenger service. Some lines continue to operate as tourist railways.
 W
WThe Tate & Lyle Sugar Silo is a Grade II* listed building on Regent Road at Huskisson Dock in Kirkdale, north Liverpool, England.
 W
WA trapiche is a mill made of wooden rollers used to extract juice from fruit, originally olives, and since the Middle Ages, sugar cane as well. By extension the word is also sometimes applied to the location of the mill, whether the workshop or the entire plantation.
 W
WTriangular trade or triangle trade is a historical term indicating trade among three ports or regions. Triangular trade usually evolves when a region has export commodities that are not required in the region from which its major imports come. Triangular trade thus provides a method for rectifying trade imbalances between the above regions.
 W
WThomas Tryon was an English sugar merchant, author of popular self-help books, and early advocate of vegetarianism.
 W
WValle de los Ingenios, also named Valley de los Ingenios or Valley of the Sugar Mills, is a series of three interconnected valleys about 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) outside of Trinidad, Cuba. The three valleys, San Luis, Santa Rosa, and Meyer, were a centre for sugar production from the late 18th century until the late 19th century.
 W
WThe Vipeholm experiments were a series of human experiments where patients of Vipeholm Hospital for the intellectually disabled in Lund, Sweden, were fed large amounts of sweets to provoke dental caries (1945–1955). The experiments were sponsored both by the sugar industry and the dentist community, in an effort to determine whether carbohydrates affected the formation of cavities.
 W
WVoyages: The Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade Database is a database run by researchers at Emory University which aims to present all documentary material pertaining to the transatlantic slave trade. It is a sister project to African Origins.
 W
WYulee Sugar Mill Ruins Historic State Park is a Florida State Park located in Homosassa, off U.S. 19. It contains the ruins of a forced-labor farm owned by David Levy Yulee. Yulee was an enslaver and a delegate of the Florida Territorial Legislative Council. After Florida became a state, he was elected by the legislature in 1845 to the United States Senate, becoming the first American of Jewish heritage to serve there. After Florida seceded from the Union, Yulee served in the Confederate Congress. He is credited with having developed a network of railroads that tremendously boosted the state's economy.
 W
WThe zafra is the late summer or early autumn harvest; the term is common in countries with Arabic or Spanish influence.