 W
WA riot is a form of civil disorder commonly characterized by a group lashing out in a violent public disturbance against authority, property, or people.
 W
WWomen-led uprisings are mass protests that are initiated by women as an act of resistance or rebellion in defiance of an established government. A protest is a statement or action taken part to express disapproval of or object an authority; most commonly led in order to influence public opinion or government policy. They range from village food riots against imposed taxes to protests that initiated the Russian revolution.
 W
WThe anti-NATO riot in Iceland of 30 March 1949 was prompted by the decision of the Alþingi, the Icelandic parliament, to join the newly formed NATO, thereby involving Iceland directly in the Cold War, opposing the Soviet Union and re-militarizing the country.
 W
WDuring 12–16 August 1969, there was an outbreak of political and sectarian violence in Northern Ireland, which is often seen as the beginning of the thirty-year conflict known as the Troubles. There had been sporadic violence throughout the year arising out of the civil rights campaign, which demanded an end to discrimination against Catholics and Irish nationalists. Civil rights marches had been repeatedly opposed by Ulster Protestant loyalists and also came into frequent conflict with the Royal Ulster Constabulary (RUC), the police force.
 W
W W
WA series of mass protests were held in Armenia in the wake of the Armenian presidential election of 19 February 2008. Mass protests against alleged electoral fraud were held in the capital city of Yerevan and organised by supporters of the unsuccessful presidential candidate and first President of Armenia, Levon Ter-Petrosyan.
 W
WThe 2008 Greek riots started on 6 December 2008, when Alexandros Grigoropoulos, a 15-year-old Greek student, was killed by a special officer in Exarcheia district of central Athens. The killing of the young student by police resulted in large protests and demonstrations, which escalated to widespread rioting, with numerous rioters damaging property and engaging riot police with Molotov cocktails, stones and other objects. Demonstrations and rioting soon spread to several other cities, including Thessaloniki, the country's second-largest city. Outside Greece, solidarity demonstrations, riots and, in some cases, clashes with local police also took place in more than 70 cities around the world, in Europe including Amsterdam, Barcelona, Berlin, Bordeaux, Brussels, Cologne, Copenhagen, Dublin, Frankfurt, the Hague, London, Madrid, Nicosia, Paphos, Paris, Rome and Seville and globally from São Paulo, San Francisco and Wellington to Buenos Aires and Siberia. Newspaper Kathimerini called the rioting "the worst Greece has seen since the restoration of democracy in 1974".
 W
WWidespread protests and riots in Serbia and North Kosovo followed the proclamation of independence by the Republic of Kosovo on February 17, 2008. Protests were also held by Serbs in Bosnia and Herzegovina and Montenegro.
 W
WWidespread protests and riots in Serbia and North Kosovo followed the proclamation of independence by the Republic of Kosovo on February 17, 2008. Protests were also held by Serbs in Bosnia and Herzegovina and Montenegro.
 W
W2009 Riga riot was a civil unrest in Riga, Latvia on January 13, 2009.
 W
WOn 10 April and 13–19 May 2010, the Thai military cracked down on the United Front for Democracy Against Dictatorship (UDD) protests in central Bangkok, the capital of Thailand. The crackdown was the culmination of months of protests that called for the Democrat Party-led government of Abhisit Vejjajiva to dissolve parliament and hold elections. The crackdowns occurred in the vicinity of protest sites near Phan Fa Lilat Bridge and Ratchaprasong intersection. More than 85 were killed, including more than 80 civilians according to the Erawan EMS Center. Two foreigners and two paramedics were killed. More than 2,000 were injured, an undisclosed number of arrests occurred, and 51 protesters remained missing as of 8 June. The Thai media dubbed the crackdowns "Cruel April" and "Savage May". After the protest, its leaders surrendered at the conclusion of the 19 May crackdown, followed by dozens of arson attacks nationwide, including at CentralWorld.
 W
WThe 2010 Thai political protests were a series of political protests that were organised by the United Front for Democracy Against Dictatorship (UDD) in Bangkok, Thailand from 12 March–19 May 2010 against the Democrat Party-led government. The UDD called for Prime Minister Abhisit Vejjajiva to dissolve parliament and hold elections earlier than the end of term elections scheduled in 2012. The UDD demanded that the government stand down, but negotiations to set an election date failed. The protests escalated into prolonged violent confrontations between the protesters and the military, and attempts to negotiate a ceasefire failed. More than 80 civilians and six soldiers were killed, and more than 2,100 injured by the time the military violently put down the protest on 19 May.
 W
WThe 2010–11 Ivorian crisis was a political crisis in Ivory Coast which began after Laurent Gbagbo, the President of Ivory Coast since 2000, was proclaimed the winner of the Ivorian election of 2010, the first election in the country in 10 years. The opposition candidate, Alassane Ouattara, and a number of countries, organisations and leaders worldwide claimed Ouattara had won the election. After months of attempted negotiation and sporadic violence, the crisis entered a decisive stage as Ouattara's forces began a military offensive in which they quickly gained control of most of the country and besieged key targets in Abidjan, the country's largest city. At the time, international organizations reported numerous human rights violations, and the UN undertook its own military action with the stated objective to protect itself and civilians.
 W
WA wave of demonstrations and civil unrest in Turkey began on 28 May 2013, initially to contest the urban development plan for Istanbul's Taksim Gezi Park. The protests were sparked by outrage at the violent eviction of a sit-in at the park protesting the plan. Subsequently, supporting protests and strikes took place across Turkey, protesting against a wide range of concerns at the core of which were issues of freedom of the press, of expression and of assembly, as well as the alleged political Islamist government's erosion of Turkey's secularism. With no centralised leadership beyond the small assembly that organised the original environmental protest, the protests have been compared to the Occupy movement and the May 1968 events. Social media played a key part in the protests, not least because much of the Turkish media downplayed the protests, particularly in the early stages. Three and a half million people are estimated to have taken an active part in almost 5,000 demonstrations across Turkey connected with the original Gezi Park protest. Twenty-two people were killed and more than 8,000 were injured, many critically.
 W
WFrom the end of February 2014, demonstrations by pro-Russian and anti-government groups took place in major cities across the eastern and southern regions of Ukraine, in the aftermath of the Euromaidan movement and the 2014 Ukrainian revolution. During the first stage of the unrest, known as the "Russian Spring", the Ukrainian territory of Crimea was annexed by the Russian Federation after a Russian military intervention, and an internationally criticized Crimean referendum. Protests in Donetsk and Luhansk regions (oblasts) escalated into an armed pro-Russian separatist insurgency. From late 2014, cities outside of the Donbas combat zone, such as Kharkiv, Odessa, Kyiv and Mariupol, were struck by bombings that targeted pro-Ukrainian unity organizations. To maintain control over southern and eastern Ukraine, the government launched an "Anti-Terrorist Operation" (ATO), sending in the armed forces to quell the unrest.
 W
WA political crisis in Montenegro was initiated by the opposition parties which staged protests requesting fair elections and transitional government. Opposition coalition Democratic Front organised continuous protests in October 2015 which culminated in a large riot in Podgorica on 24 October. A split in the ruling coalition followed in January 2016, leaving the government functioning as a de facto minority government.
 W
WThe 2021 Farmers' Republic Day protest was a protest on 26 January 2021 in Delhi, India. Part of the 2020–2021 Indian farmers' protest, it turned violent when a group of protestors deviated from the parade to storm the Red Fort. The protest took place on the 72nd Republic Day against the decision by Narendra Modi-led National Democratic Alliance (NDA) to implement three farm acts.
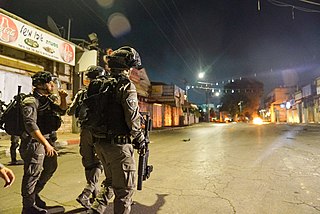 W
WAn outbreak of violence in the ongoing Israeli–Palestinian conflict commenced on 10 May 2021, though disturbances took place earlier, and continued until a ceasefire came into effect on 21 May. It was marked by protests and police riot control, rocket attacks on Israel by Hamas and Palestinian Islamic Jihad, and Israeli airstrikes targeting the Gaza Strip. The crisis was triggered on 6 May, when Palestinians began protests in East Jerusalem over an anticipated decision of the Supreme Court of Israel on the eviction of six Palestinian families in Sheikh Jarrah. Under international law, the area, effectively annexed by Israel, is a part of the occupied Palestinian territories. Israel applies its laws there. On 7 May, according to Israel's Channel 12, Palestinians threw stones at Israeli police forces, who then stormed the compound of the al-Aqsa Mosque using tear gas, rubber bullets and stun grenades. The crisis prompted protests around the world and reactions from world leaders.
 W
W2005 Ahvaz unrest or 15 April Ahvaz Protests were violent riots, initiated by Iranian Arabs in the city of Ahvaz in southwestern Iranian province of Khuzestan. The unrest erupted on 15 April 2005, and lasted for 4 days. Initially, the Iranian Interior Ministry stated that only one person had been killed, however an official at a hospital in Ahvaz said that there were between 15 and 20 mortal casualties. Government officials blamed the unrest on Britain, whose troops based just across the border in southern Iraq. Following the unrest, several bombings were carried out in Ahvaz, killing 28 people. In 2006, Iran executed five Arab separatists, convicted of carrying out the bombings in 2005.
 W
WThe anti-austerity movement in Greece involves a series of demonstrations and general strikes that took place across the country. The events, which began on 5 May 2010, were provoked by plans to cut public spending and raise taxes as austerity measures in exchange for a €110 billion bail-out, aimed at solving the Greek government-debt crisis. Three people were killed on 5 May in one of the largest demonstrations in Greece since 1973.
 W
WThe Ashura protests were a series of protests which occurred on 27 December 2009 in Iran against the outcome of the June 2009 Iranian presidential election, which demonstrators claim was rigged. The demonstrations were part of the 2009 Iranian election protests and were the largest since June. In December 2009, the protests saw an escalation in violence.
 W
WThe Baren Township conflict was a terrorist attack and armed conflict that took place between Uyghur militants and Chinese government forces in April 1990. It is unclear what happened during the armed conflict because reports of the incident vary greatly.
 W
WEl Bogotazo refers to the massive riots that followed the assassination in Bogotá, Colombia of Liberal leader and presidential candidate Jorge Eliécer Gaitán on 9 April 1948 during the government of President Mariano Ospina Pérez. The 10-hour riot left much of downtown Bogotá destroyed. The aftershock of Gaitan's murder continued extending through the countryside and escalated a period of violence which had begun eighteen years before, in 1930, and was triggered by the fall of the conservative party from government and the rise of the liberals. The 1946 presidential elections brought the downfall of the liberals allowing conservative Mariano Ospina Pérez to win the presidency. The struggle for power between both again triggered a period in the history of Colombia known as La Violencia that lasted until approximately 1958, from which the civil conflict that continues to this day grew.
 W
WThe Bronze Night, also known as the April Unrest and April Events, refers to the riots in Estonia surrounding the controversial 2007 relocation of the Bronze Soldier of Tallinn, a Soviet World War II memorial in Tallinn.
 W
WThe Battle of Cable Street was an event that took place in Cable Street and Whitechapel in the East End of London, on Sunday 4 October 1936. It was a clash between the Metropolitan Police, sent to protect a march by members of the British Union of Fascists led by Oswald Mosley, and various anti-fascist demonstrators, including local trade unionists, communists, anarchists, British Jews, Irish dockers, and socialist groups. The majority of both marchers and counter-protesters travelled into the area for this purpose.
 W
WA cacerolazo, cacerolada or casserole is a form of popular protest which consists of a group of people making noise by banging pots, pans, and other utensils in order to call for attention.
 W
WThe Cairo fire, also known as Black Saturday, was a series of riots that took place on 26 January 1952, marked by the burning and looting of some 750 buildings—retail shops, cafes, cinemas, hotels, restaurants, theatres, nightclubs, and the city's Opera House—in downtown Cairo. The direct trigger of the riots was the killing by British occupation troops of 50 Egyptian auxiliary policemen in the city of Ismaïlia in a massacre one day earlier. The spontaneous anti-British protests that followed these deaths were quickly seized upon by organized elements in the crowd, who burned and ransacked large sectors of Cairo amidst the unexplained absence of security forces. The fire is thought by some to have signalled the end of the Kingdom of Egypt. The perpetrators of the Cairo Fire remain unknown to this day, and the truth about this important event in modern Egyptian history has yet to be established.
 W
WThe 2008 Cameroon protests were a series of violent demonstrations in Cameroon's biggest cities that took place from 25 to 29 February 2008. The protests followed on the heels of a strike by transport workers, who were opposing high fuel prices and poor working conditions. Further political turmoil had been caused by President Paul Biya's announcement that he wanted the constitution to be amended to remove term limits; without such an amendment, he would have to leave office at the end of his term in 2011. Large groups of youths, whom the opposition Social Democratic Front (SDF) political party and the government blame one another for organising, took to the streets of Douala, Yaoundé, Bamenda, and other major cities, looting and vandalising property. The government sent in troops to crack down on the unrest, and protesters and troops alike were killed. The official government tally is that 40 people were killed, but human rights groups claim that the total is closer to 100. Government figures place damage to property at tens of billions of francs CFA.
 W
WThe Caracazo, or sacudón, is the name given to the wave of protests, riots and looting that started on 27 February 1989 in Guarenas, spreading to Caracas and surrounding towns. The weeklong clashes resulted in the deaths of hundreds of people, thousands by some accounts, mostly at the hands of security forces and the military. The riots and the protests began mainly in response to the government's economic reforms and the resulting increase in the price of gasoline and transportation.
 W
WThe Dharmapuri bus burning occurred on 2 February 2000 in Ilakiyampatti, on the outskirts of Dharmapuri in Tamil Nadu, India. Three students from Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore (TNAU) were burned to death in a bus by AIADMK cadres after the conviction of Jayalaitha by a special court for the Kodaikanal Pleasant Stay Hotel case.
 W
WThe Falls Curfew, also called the Battle of the Falls, was a British Army operation during 3–5 July 1970 in the Falls district of Belfast, Northern Ireland. The operation began as a search for weapons in the staunchly Irish nationalist district. As the search ended, local youths attacked the British soldiers with stones and petrol bombs and the soldiers responded with CS gas. This quickly developed into gun battles between British soldiers and the Irish Republican Army (IRA). After four hours of continuous clashes, the British commander sealed off the area, which comprised 3,000 homes, and imposed a curfew which would last for 36 hours. Thousands of British troops moved into the curfew zone and carried out house-to-house searches for weapons, while coming under intermittent attack from the IRA and rioters. The searches caused much destruction, and a large amount of CS gas was fired into the area. Many residents complained of suffering abuse at the hands of the soldiers. On 5 July, the curfew was brought to an end when thousands of women and children from Andersonstown marched into the curfew zone with food and other supplies for the locals.
 W
W#FeesMustFall was a student-led protest movement that began in mid-October 2015 in South Africa. The goals of the movement were to stop increases in student fees as well as to increase government funding of universities. The movements were started and led by the SRC leader of the University of Witwatersrand of 2015, Shaeera Kalla. On 2 October Kalla attended her last council meeting as SRC president, she is accompanied by Nompendulo as an observer heading towards being the incoming SRC President of 2016. Protests started at the University of Witwatersrand and spread to the University of Cape Town and Rhodes University before rapidly spreading to other universities across the country.
 W
WThe 27th G8 summit was held in Genoa, Italy, on 20–22 July 2001 and is remembered as the peak of the worldwide anti-globalization movement as well as for human rights crimes against demonstrators.
 W
WIn 2007, a series of anti-government protests took place across Georgia. The demonstrations peaked on 2 November 2007, when 40,000-50,000 rallied in downtown Tbilisi, the capital of Georgia. People protested against the allegedly corrupt government of president Mikheil Saakashvili. Protests triggered by detention of Georgian politician Irakli Okruashvili on charges of extortion, money laundering, and abuse of office during his tenure as defense minister of the country were organized by the National Council, an ad hoc coalition of ten opposition parties, and financed by the media tycoon Badri Patarkatsishvili. Demonstrations occurred both in September and November 2007 and were initially largely peaceful. The protests went downhill by 6 November 2007, but turned violent the next day when the police, using heavy-handed tactics, including tear gas and water cannon, unblocked Rustaveli Avenue, Tbilisi's main boulevard, dislodged the protesters from the territory adjoining to the House of Parliament, and prevented the demonstrators from resuming the protests. The government accused the Russian secret services of being involved in an attempted coup d'état and declared a nationwide state of emergency later that day which lasted until late 16 November 2007.
 W
WProtests against the results of the highly controversial 2009 Iranian presidential election, a disputed victory by President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad, in support of opposition candidates Mir-Hossein Mousavi and Mehdi Karroubi, occurred in major cities nationwide from 2009 into early 2010. The protests were titled the Iranian Green Movement by its proponents, reflecting Mousavi's campaign theme, and Persian Awakening, Persian Spring or Green Revolution, reflecting the "Persian identity" of Iranians and the so-called "colour revolution" theme.
 W
WThe 2001 Jos riots were riots involving Christians and Muslims in Jos, Nigeria, over the appointment of a Muslim politician, Alhaji Muktar Mohammed, as local coordinator of the federal poverty alleviation program. The clashes started on 7 September and lasted nearly two weeks, ending on 17 September. Some 1,000 people were killed during the riots.
 W
WThe 2008 Jos riots were riots involving Christians and Muslims over the result of a local election on 28 and 29 November 2008 in Jos, a city in the Middle Belt region of Nigeria. Two days of rioting left hundreds injured and at least 761 dead. The Nigerian army was deployed and by 30 November order was restored.
 W
WThe Koza riot was a violent and spontaneous protest against the US military presence in Okinawa, which occurred on the night of December 20, 1970, into the morning of the following day. Roughly 5,000 Okinawans clashed with roughly 700 American MPs in an event which has been regarded as symbolic of Okinawan anger against 25 years of US military occupation. In the riot, approximately 60 Americans and 27 Okinawans were injured, 80 cars were burned, and several buildings on Kadena Air Base were destroyed or heavily damaged.
 W
WThe 2009 Malmö Davis Cup riots were anti-Israel riots in the Swedish city of Malmö against a Davis Cup tennis match between Sweden and Israel on 7 March 2009.
 W
WThe Noemvriana of December [O.S. November] 1916, or the Greek Vespers, was a political dispute which led to an armed confrontation in Athens between the royalist government of Greece and the forces of the Allies over the issue of Greece's neutrality during World War I.
 W
WThe 2011 Northern Ireland riots were a series of riots between 20 June 2011 and 16 July 2011, starting originally in Belfast, before spreading to other parts of Northern Ireland. They were initiated by the Ulster Volunteer Force.
 W
WOn 29 December 2008, violent riots first broke out in Oslo, Norway amid protests against the Gaza War, starting outside the Israeli embassy. Riots broke out again following a protest on 4 January 2009, while the most violent and destructive riots took place on 8 and 10 January when riots spread throughout the city with widespread destruction of private and public property, clashes between rioters and police with several injuries, as well as attacks on civilians, including individuals targeted due to being thought by rioters to be Jews. Around 200 people were arrested in total, mainly Muslim youth, supported by left-wing autonomous Blitz activists.
 W
WThe Reformasi was a protest movement that began in September 1998 throughout Malaysia initiated by Anwar Ibrahim after his sacking as Deputy Prime Minister by the country's then-Prime Minister, Mahathir Mohamad in the same month. The massive movement, which occurred while the country hosted the Commonwealth Games, consisted of civil disobedience, demonstrations, sit-ins, rioting, occupations and online activism, involving thousands across Malaysia protesting against the Barisan Nasional (BN) government under the Mahathir Cabinet.
 W
WThe Reggio revolt occurred in Reggio Calabria, Italy, from July 1970 to February 1971. The cause of the protests was a government decision to make Catanzaro, not Reggio, regional capital of Calabria. The nomination of a regional capital was the result of a decentralization programme of the Italian government, under which 15 governmental regions were concretized and given their own administrative councils and a measure of local autonomy.
 W
WRussian sabotage in Ukraine is a set of actions planned, organized, and implemented by Russian special services in Ukraine with the help of local Russian agents of influence, pro-Russian separatists, trained political tourists from Russia, Russian saboteurs, and FSB officers since the end of February 2014. The aim of the Russian sabotage is to destabilize the political situation in Ukraine after the Revolution of Dignity, provoking interethnic and interregional conflicts, strengthening separatist movements in Eastern Ukraine. These subversive actions are part of the information war against Ukraine and direct military aggression — Russia's occupation of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea.
 W
WThe Saffron Revolution was a series of economic and political protests and demonstrations that took place during August, September, and October 2007 in Myanmar. The protests were triggered by the decision of the national military government to remove subsidies on the sales prices of fuel. The national government is the only supplier of fuels and the removal of the price subsidy immediately caused diesel and petrol prices to increase by 66–100% and the price of compressed natural gas for buses to increase 500% in less than a week.
 W
WThe Battle of Stockton-on-Tees, often referred to as the Battle of Stockton, took place on 10 September 1933 at Market Cross in the High Street of Stockton-on-Tees, County Durham, England. It was a clash between members of the British Union of Fascists (BUF) and anti-fascist demonstrators, including local communists and supporters of the Labour Party. The march was an early attempt by the BUF to rally support in depressed areas, but the anti-fascists protested and drove out the BUF supporters who had been shipped in from other areas.
 W
WBeginning in 2008, there was worsening conflict between the People's Alliance for Democracy (PAD) and the People's Power Party (PPP) governments of Prime Ministers Samak Sundaravej and Somchai Wongsawat. It was a continuation of the 2005–2006 political crisis, when PAD protested against the Thai Rak Thai (TRT) party government of Prime Minister Thaksin Shinawatra. PAD followers usually dressed in yellow, yellow being the royal color of King Bhumibol Adulyadej, and were called "yellow shirts". National United Front of Democracy Against Dictatorship (UDD) followers, known as supporters of the deposed prime minister Thaksin Shinawatra, dressed in red and were widely called "red shirts".
 W
WThe 2008 Tibetan unrest was a series of protests and demonstrations over the Chinese government's treatment and persecution of Tibetans. Protests in Lhasa by monks and nuns on 10 March have been viewed as the start of the demonstrations. Numerous peaceful protests and demonstrations were held to commemorate the 49th anniversary of the 1959 Tibetan Uprising Day, when the 14th Dalai Lama escaped from Tibet. The protests and demonstrations spread spontaneously to a number of monasteries and throughout the Tibetan plateau, including into counties located outside the designated Tibet Autonomous Region. The arrest of monks at Labrang Monastery increased the tension of the situation. Violence began when Chinese police and People's Liberation Army units used force on non-violent protests by monks and nuns, and spread when protesting Tibetans later clashed with security forces. Clashes also occurred between Tibetans and Chinese Han and Hui residents, resulting in Han and Hui stores and buildings being destroyed and numerous Chinese civilians being injured or killed.
 W
WThe 2017–18 Togolese protests are a significant representation of civil unrest in Togo and against the 50 year rule of the father-son combination of Gnassingbé Eyadéma and Faure Gnassingbé. The protesters demanded that the president honour the 1992 constitution, and demanding that he step down immediately. Gnassingbé offered the protesters the option of enacting the two-term limit set in the constitution effective from 2018, thus ensuring that he could stay in power until 2030. This has been rejected by the opposition. However, on 8 May 2019 the Togolese Parliament voted unanimously to accept this amendment and imposed this non-retroactive term limit on the president's office.
 W
WThe 2010 United Kingdom student protests were a series of demonstrations in November and December 2010 that took place in several areas of the country, with the focal point of protests being in central London. Largely student-led, the protests were held in opposition to planned spending cuts to further education and an increase of the cap on tuition fees by the Conservative-Liberal Democrat coalition government following their review into higher education funding in England. Student groups said that the intended cuts to education were excessive, would damage higher education, give students higher debts, and broke campaign promises made by politicians.
 W
WVenezuelan protests for and against President Hugo Chávez's proposed 2 December constitutional referendum occurred after the National Assembly approved the referendum on 2 November 2007.
 W
WWorld Youth Day 2011 was the 2011 occurrence of World Youth Day, a Catholic event held from 16–21 August 2011 in Madrid, Spain focused on youth. Media estimated the event's attendance as over a million or 1.5 million.