 W
WAssistive technology (AT) is a term for assistive, adaptive, and rehabilitative devices for people with disabilities or the elderly population. People with disabilities often have difficulty performing activities of daily living (ADLs) independently, or even with assistance. ADLs are self-care activities that include toileting, mobility (ambulation), eating, bathing, dressing, grooming, and personal device care. Assistive technology can ameliorate the effects of disabilities that limit the ability to perform ADLs. Assistive technology promotes greater independence by enabling people to perform tasks they were formerly unable to accomplish, or had great difficulty accomplishing, by providing enhancements to, or changing methods of interacting with, the technology needed to accomplish such tasks. For example, wheelchairs provide independent mobility for those who cannot walk, while assistive eating devices can enable people who cannot feed themselves to do so. Due to assistive technology, people with disability have an opportunity of a more positive and easygoing lifestyle, with an increase in "social participation," "security and control," and a greater chance to "reduce institutional costs without significantly increasing household expenses."
 W
WAn assistive cane is a walking stick used as a crutch or mobility aid. A cane can help redistribute weight from a lower leg that is weak or painful, improve stability by increasing the base of support, and provide tactile information about the ground to improve balance. In the US, ten percent of adults older than 65 years use a cane, and 4.6 percent use walkers.
 W
WAssistive eating devices include devices ranging from low-tech utensils to high-tech powered robotic eating equipment. Low tech eating devices include utensils, plates and bowls with lips that make scooping food easier. Cups and mugs, and even a standard disposable straw can be considered assistive drinking devices. They are used by people when they have difficulty eating or drinking independently. These devices are typically used for people with disabilities, but can also be used for children or people that have poor dexterity. They can promote independence during meal times, but in many cases also can reduce the caregiver workload during meals. "Assistive eating devices can increase self-care, increase self-esteem associated with increased independence, increase safety during meals, and make meal-time better for caregiver staff…".
 W
WAn assistive listening device (ALD) is part of a system used to improve hearing ability for people in a variety of situations where they are unable to distinguish speech in noisy environments. Often, in a noisy or crowded room it is almost impossible for an individual who is hard of hearing to distinguish one voice among many. This is often exacerbated by the effect of room acoustics on the quality of perceived speech. Hearing aids are able to amplify and process these sounds, and improve the speech to noise ratio. However, if the sound is too distorted by the time it reaches the listener, even the best hearing aids will struggle to unscramble the signal. Assistive listening devices offer a more adaptive alternative to hearing aids, but can be more complex and cumbersome.
 W
WAssistive technology in sport is an area of technology design that is growing. Assistive technology is the array of new devices created to enable sports enthusiasts who have disabilities to play. Assistive technology may be used in disabled sports, where an existing sport is modified to enable players with a disability to participate; or, assistive technology may be used to invent completely new sports with athletes with disabilities exclusively in mind.
 W
WATutor is an Open Source Web-based Learning Content Management System (LCMS).
 W
WAudio induction loop systems, also called audio-frequency induction loops (AFILs) or hearing loops, are an assistive listening technology for individuals with reduced ranges of hearing.
 W
WBone conduction is the conduction of sound to the inner ear primarily through the bones of the skull, allowing the hearer to perceive audio content without blocking the ear canal. Bone conduction transmission occurs constantly as sound waves vibrate bone, specifically the bones in the skull, although it is hard for the average individual to distinguish sound being conveyed through the bone as opposed to the sound being conveyed through the air via the ear canal. Intentional transmission of sound through bone can be used with individuals with normal hearing — as with bone-conduction headphones — or as a treatment option for certain types of hearing impairment. Bone generally conveys lower-frequency sounds better than higher frequency sounds.
 W
WBraille is a tactile writing system used by people who are visually impaired. It is traditionally written with embossed paper. Braille users can read computer screens and other electronic supports using refreshable braille displays. They can write braille with the original slate and stylus or type it on a braille writer, such as a portable braille notetaker or computer that prints with a braille embosser.
 W
WThe Canadian currency tactile feature is a feature on the Canadian Journey and Frontier series of Canadian banknotes to aid people who are visually impaired to identify the notes. The feature indicates the banknote denomination in the upper left corner of the face side of the bill using a series of raised dots. It was suggested by Bruno Thériault, an administrator for the Canadian National Institute for the Blind, and designed by Susan Lederman, a professor of psychology at Queen's University.
 W
WClosed captioning (CC) and subtitling are both processes of displaying text on a television, video screen, or other visual display to provide additional or interpretive information. Both are typically used as a transcription of the audio portion of a program as it occurs, sometimes including descriptions of non-speech elements. Other uses have included providing a textual alternative language translation of a presentation's primary audio language that is usually burned-in to the video and unselectable.
 W
WClosed-circuit television (CCTV), also known as video surveillance, is the use of video cameras to transmit a signal to a specific place, on a limited set of monitors. It differs from broadcast television in that the signal is not openly transmitted, though it may employ point-to-point (P2P), point-to-multipoint (P2MP), or mesh wired or wireless links. Even though almost all video cameras fit this definition, the term is most often applied to those used for surveillance in areas that require additional security or ongoing monitoring.
 W
WA crutch is a mobility aid that transfers weight from the legs to the upper body. It is often used by people who cannot use their legs to support their weight, for reasons ranging from short-term injuries to lifelong disabilities.
 W
WDragon NaturallySpeaking is a speech recognition software package developed by Dragon Systems of Newton, Massachusetts, which was acquired first by Lernout & Hauspie Speech Products and later by Nuance Communications. It runs on Windows personal computers. Version 15, which supports 32-bit and 64-bit editions of Windows 7, 8 and 10, was released in August 2016. The macOS version is called Dragon Professional Individual for Mac, version 6 or Dragon for Mac.
 W
WEnglish Braille, also known as Grade 2 Braille, is the braille alphabet used for English. It consists of around 250 letters (phonograms), numerals, punctuation, formatting marks, contractions, and abbreviations (logograms). Some English Braille letters, such as ⠡ ⟨ch⟩, correspond to more than one letter in print.
 W
WFaceTime is a proprietary videotelephony product developed by Apple Inc. FaceTime is available on supported iOS mobile devices running iOS 4 and later and Mac computers that run Mac OS X 10.6.6 and later. FaceTime supports any iOS device with a forward-facing camera and any Mac computer equipped with a FaceTime Camera. FaceTime Audio, an audio-only version, is available on any iOS device that supports iOS 7 or newer, and any Mac with a forward-facing camera running Mac OS X 10.9.2 and later. FaceTime is included for free in iOS and in macOS from Mac OS X Lion (10.7) onwards.
 W
WFS Me is a typeface/font that has been described as the first to have been designed in consultation with a group of people with learning disabilities and designed for use by this population. It was developed by Jason Smith in response to a commission from the charity Mencap in 2008. It was the only font featured in the D&AD Annual 2009 covering advertising and design work.
 W
WThe Hybrid Assistive Limb is a powered exoskeleton suit developed by Japan's Tsukuba University and the robotics company Cyberdyne. It is designed to support and expand the physical capabilities of its users, particularly people with physical disabilities. There are two primary versions of the system: HAL 3, which only provides leg function, and HAL 5, which is a full-body exoskeleton for the arms, legs, and torso.
 W
WHebrew Braille is the braille alphabet for Hebrew. The International Hebrew Braille Code is widely used. It was devised in the 1930s and completed in 1944. It is based on international norms, with additional letters devised to accommodate differences between English Braille and the Hebrew alphabet. Unlike Hebrew, but in keeping with other braille alphabets, Hebrew Braille is read from left to right instead of right to left., and unlike English Braille, it is an Abjad, all consonants.
 W
WThe iBOT is a powered wheelchair developed by Dean Kamen in a partnership between DEKA and Johnson and Johnson's Independence Technology division.
 W
WKey finders, also known as keyfinders, key locators, or electronic finders, are small electronic devices used to locate misplaced or stolen objects, such as keys, luggage, pets, or tools, and to transmit alerts, e.g., that one's restaurant table is ready or a nurse is needed. Some key finders beep or flash lights on demand.
 W
WLightwriters are a type of speech-generating device. The person who cannot speak types a message on the keyboard, and this message is displayed on two displays, one facing the user and a second outfacing display facing the communication partner or partners. A speech synthesiser is also used to provide speech output, and some models offer the facility to connect to a printer to provide printed output.
 W
WLogitech Harmony is a line of remote controls and home automation products produced by Logitech. The line includes universal remote products designed for controlling the components of home theater systems and other devices that can be controlled via infrared, as well as newer "Hub" products that can be used to additionally control supported Internet of things (IoT) and Smart home products, and allow the use of mobile apps to control devices. On April 10, 2021, Logitech announced that they would discontinue Harmony Remote manufacturing.
 W
WA monocular is a modified refracting telescope used to magnify the images of distant objects by passing light through a series of lenses and usually also prisms. Most modern monoculars use prisms instead of relay lenses to ensure an erect image, resulting in a lightweight, compact telescope. The typical volume and weight of a monocular are less than half of a pair of binoculars having similar optical properties, making a monocular easier to carry and also proportionally less expensive. This is due to the fact that binoculars are essentially two sets of monoculars packed together — one for each eye. Monoculars only produce one 2-dimensional image, while binoculars produce two parallaxed images to allow stereopsis and depth perception.
 W
WThe Mountbatten Brailler is an electronic machine used to type braille on braille paper. It uses the traditional "braille typewriter keyboard" of the Perkins Brailler with modern technology, giving it a number of additional features such as word processing, audio feedback and embossing. The machine was pioneered and developed at the United Kingdom's Royal National College for the Blind in Hereford by Ernest Bate.
 W
WParatransit is the term used in North America, also known by other names such as community transport (UK) for transportation services that supplement fixed-route mass transit by providing individualized rides without fixed routes or timetables. Paratransit services may vary considerably on the degree of flexibility they provide their customers. At their simplest they may consist of a taxi or small bus that will run along a more or less defined route and then stop to pick up or discharge passengers on request. At the other end of the spectrum—fully demand responsive transport—the most flexible paratransit systems offer on-demand call-up door-to-door service from any origin to any destination in a service area. In addition to public transit agencies, paratransit services may be operated by community groups or not-for-profit organizations, and for-profit private companies or operators.
 W
WThe Perkins Brailler is a "braille typewriter" with a key corresponding to each of the six dots of the braille code, a space key, a backspace key, and a line space key. Like a manual typewriter, it has two side knobs to advance paper through the machine and a carriage return lever above the keys. The rollers that hold and advance the paper have grooves designed to avoid crushing the raised dots the brailler creates.
 W
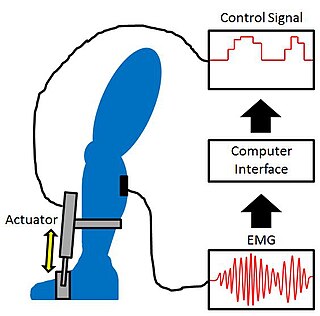
WProportional myoelectric control can be used to activate robotic lower limb exoskeletons. A proportional myoelectric control system utilizes a microcontroller or computer that inputs electromyography (EMG) signals from sensors on the leg muscle(s) and then activates the corresponding joint actuator(s) proportionally to the EMG signal.
 W
WThe Rear Window captioning system (RWC) is a method for presenting, through captions, a transcript of the audio portion of a film in theatres for deaf and hard-of-hearing people. The system was co-developed by WGBH and Rufus Butler Seder.
 W
WIn electronics, a remote control or clicker is an electronic device used to operate another device from a distance, usually wirelessly. In consumer electronics, a remote control can be used to operate devices such as a television set, DVD player or other home appliance. A remote control can allow operation of devices that are out of convenient reach for direct operation of controls. They function best when used from a short distance. This is primarily a convenience feature for the user. In some cases, remote controls allow a person to operate a device that they otherwise would not be able to reach, as when a garage door opener is triggered from outside.
 W
WThe Royal National College for the Blind (RNC) is a co-educational specialist residential college of further education based in the English city of Hereford. Students who attend the college are aged over 16 and blind or partially sighted. They can study a wide range of qualifications at RNC, from academic subjects such as English and mathematics to more vocational topics such as performing arts. Alongside regular further education subjects and vocational training, the College offers training in mobility, independent living and personal development.
 W
WA screen magnifier is software that interfaces with a computer's graphical output to present enlarged screen content. By enlarging part of a screen, people with visual impairments can better see words and images. This type of assistive technology is useful for people with some functional vision; people with visual impairments and little or no functional vision usually use a screen reader.
 W
WSip-and-puff or sip 'n' puff (SNP) is assistive technology used to send signals to a device using air pressure by "sipping" (inhaling) or "puffing" (exhaling) on a straw, tube or "wand." It is primarily used by people who do not have the use of their hands. It is commonly used to control a motorized wheelchair by quadriplegics with very high injury to their spinal cord or people with ALS.
 W
WSlideWiki is an open web-based OpenCourseWare authoring system. It supports learning content authoring and management and tools for collaboration/crowd-sourcing, translation, communication, evaluation and assessment, supporting the publication of open educational resources
 W
WA stair lift is a mechanical device for lifting people, typically those with disabilities, up and down stairs. For sufficiently wide stairs, a rail is mounted to the treads of the stairs. A chair or lifting platform is attached to the rail. A person gets onto the chair or platform and is lifted up or down the stairs by the chair which moves along the rail.
 W
WA standing frame is assistive technology that can be used by a person who relies on a wheelchair for mobility. A standing frame provides alternative positioning to sitting in a wheelchair by supporting the person in the standing position.
 W
WA standing wheelchair is assistive technology, similar to a standing frame, that allows a wheelchair user to raise the chair from a seated to a standing position. The standing wheelchair supports the person in a standing position and enables interaction with people and objects at eye level.
 W
WA stenomask is a hand-held microphone built into a padded, sound-proof enclosure that fits over the speaker's mouth or nose and mouth. Some lightweight versions may be fitted with an elastic neck strap to hold them in place while freeing the user's hands for other tasks. The purpose of a stenomask is to allow a person to speak without being heard by other people, and to keep background noise away from the microphone.
 W
WSubtitles are text derived from either a transcript or screenplay of the dialogue or commentary in films, television programs, video games, and the like, usually displayed at the bottom of the screen, but can also be at the top of the screen if there is already text at the bottom of the screen. They can either be a form of written translation of a dialogue in a foreign language, or a written rendering of the dialogue in the same language, with or without added information to help viewers who are deaf or hard-of-hearing, who cannot understand the spoken language, or who have accent recognition problems to follow the dialogue.
 W
WSurtitles, also known as supertitles, SurCaps, OpTrans, are translated or transcribed lyrics/dialogue projected above a stage or displayed on a screen, commonly used in opera, theatre or other musical performances. The word "surtitle" comes from the French language "sur", meaning "over" or "on", and the English language word "title", formed in a similar way to the related subtitle. The word Surtitle is a trademark of the Canadian Opera Company.
 W
WTactile is a real-time text-to-braille translation device currently under development at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It was conceived by a team of undergraduate students, competing as "Team 100% Enthusiasm", during a 15-hour MIT "hackathon". The device is slid over printed text and a camera captures images of the words and sends them to a microcontroller. The information moves the pins up and down, translating the text into Braille. Once on the market it is hoped to be much cheaper than existing devices.
 W
WTactile paving is a system of textured ground surface indicators found on footpaths, stairs and railway station platforms, to assist pedestrians who are vision impaired.
 W
WA telecommunications device for the deaf (TDD) is a teleprinter, an electronic device for text communication over a telephone line, that is designed for use by persons with hearing or speech difficulties. Other names for the device include teletypewriter (TTY), textphone, and minicom.
 W
WA telecommunications relay service, also known as TRS, relay service, or IP-relay, or Web-based relay service, is an operator service that allows people who are deaf, hard of hearing, deafblind, or have a speech disorder to place calls to standard telephone users via a keyboard or assistive device. Originally, relay services were designed to be connected through a TDD, teletypewriter (TTY) or other assistive telephone device. Services gradually have expanded to include almost any real-time text capable technology such as a personal computer, laptop, mobile phone, PDA, and many other devices. The first TTY was invented by deaf scientist Robert Weitbrecht in 1964. The first relay service was established in 1974 by Converse Communications of Connecticut.
 W
WTelehealth is the distribution of health-related services and information via electronic information and telecommunication technologies. It allows long-distance patient and clinician contact, care, advice, reminders, education, intervention, monitoring, and remote admissions. Telemedicine is sometimes used as a synonym, or is used in a more limited sense to describe remote clinical services, such as diagnosis and monitoring. When rural settings, lack of transport, a lack of mobility, decreased funding, or a lack of staff restrict access to care, telehealth may bridge the gap. as well as provider distance-learning; meetings, supervision, and presentations between practitioners; online information and health data management and healthcare system integration. Telehealth could include two clinicians discussing a case over video conference; a robotic surgery occurring through remote access; physical therapy done via digital monitoring instruments, live feed and application combinations; tests being forwarded between facilities for interpretation by a higher specialist; home monitoring through continuous sending of patient health data; client to practitioner online conference; or even videophone interpretation during a consult.
 W
WTile is an American consumer electronics company which produces tracking devices that users attach to their belongings such as keys and backpacks. A companion mobile app for Android and iOS allows users to track the devices and locate lost items through Bluetooth 4.0, or view where they were last seen. In September 2018 GoPro vet CJ Prober became CEO of Tile. In September 2015, Tile launched Generation 2 hardware that includes find-your-phone functionality and other feature upgrades, which by January 2016 sold over 4.5 million units. In August 2017, two new versions of the Tile were launched, the Tile Sport and Tile Style. As of 2019, the lineup consists of the Pro, Mate, Slim, and Sticker.
 W
WTrackR is a commercial key finder which assists in the tracking of lost belongings and devices. Trackr is produced by the company Phone Halo and was inspired by the founders' losing their keys on a beach during a surfing trip.
 W
WA transfer bench, is a bath safety mobility device which the user sits on to get into a bathtub. The user usually sits on the bench, which straddles the side of the tub, and gradually slides from the outside to the inside of the tub. Tub transfer benches are used by people who have trouble getting over the tub wall or into the shower, either because of illness or disability.
 W
WThis article is about tools for visually-impaired people. For image-processing techniques not related to the visually impaired, please create other articles such as Eulerian video magnification.
 W
WA video relay service (VRS), also sometimes known as a video interpreting service (VIS), is a video telecommunication service that allows deaf, hard-of-hearing, and speech-impaired (D-HOH-SI) individuals to communicate over video telephones and similar technologies with hearing people in real-time, via a sign language interpreter.
 W
WVideo remote interpreting (VRI) is a videotelecommunication service that uses devices such as web cameras or videophones to provide sign language or spoken language interpreting services. This is done through a remote or offsite interpreter, in order to communicate with persons with whom there is a communication barrier. It is similar to a slightly different technology called video relay service, where the parties are each located in different places. VRI is a type of telecommunications relay service (TRS) that is not regulated by the FCC.
 W
WVideotelephony, sometimes also referred to as video teleconference, comprises the technologies for the reception and transmission of audio-video signals by users in different locations, for communication between people in real time. A videophone is a telephone with a video display, capable of simultaneous video and audio for communication between people in real time. Videoconferencing implies the use of this technology for a group or organizational meeting rather than for individuals, in a videoconference. Telepresence may refer either to a high-quality videotelephony system or to meetup technology, which goes beyond video into robotics. Videoconferencing has also been called "visual collaboration" and is a type of groupware.
 W
WA virtual keyboard is a software component that allows the input of characters without the need for physical keys. The interaction with the virtual keyboard happens mostly via a touchscreen interface, but can also take place in a different form in virtual or augmented reality.
 W
WWordQ® is assistive technology software developed by Quillsoft Ltd. and Holland Bloorview Kids Rehabilitation Hospital, represented by goQSoftware and distributed in the United States by ST4Learning and in Canada by Quillsoft Ltd. WordQ's main purpose is helping individuals who struggle with writing. WordQ uses word prediction to suggest words that the user is typing into documents and emails, helping with spelling. It also uses high-quality Acapela text-to-speech voices to read back text that the user has entered, allowing for proofreading and editing. WordQ is sold alongside a companion product, SpeakQ®, which combines speech recognition with the features of WordQ to allow users to switch between speaking and typing while writing. The combined program works with Windows. WordQ also works with Mac OS X.