 W
WA television advertisement is a span of television programming produced and paid for by an organization. It conveys a message promoting, and aiming to market, a product or service. Advertisers and marketers may refer to television commercials as TVCs.
 W
WAdvertising is a marketing communication that employs an openly sponsored, non-personal message to promote or sell a product, service or idea. Sponsors of advertising are typically businesses wishing to promote their products or services. Advertising is differentiated from public relations in that an advertiser pays for and has control over the message. It differs from personal selling in that the message is non-personal, i.e., not directed to a particular individual. Advertising is communicated through various mass media, including traditional media such as newspapers, magazines, television, radio, outdoor advertising or direct mail; and new media such as search results, blogs, social media, websites or text messages. The actual presentation of the message in a medium is referred to as an advertisement, or "ad" or advert for short.
 W
WAn advertising campaign is a series of advertisement messages that share a single idea and theme which make up an integrated marketing communication (IMC). An IMC is a platform in which a group of people can group their ideas, beliefs, and concepts into one large media base. Advertising campaigns utilize diverse media channels over a particular time frame and target identified audiences.
 W
WAdvertising media selection is the process of choosing the most efficient media for an advertising campaign. To evaluate media efficiency, planners consider a range of factors including: the required coverage and number of exposures in a target audience; the relative cost of the media advertising and the media environment. Media planning may also involve buying media space. Media planners require an intricate understanding of the strengths and weaknesses of each of the main media options. The media industry is dynamic - new advertising media options are constantly emerging. Digital and social media are changing the way that consumers use media and are also influencing how consumers acquire product information.
 W
WAn advertising postcard is a postcard used for advertising purposes. Postcards are used in advertising as an alternative to or to complement other print advertising such as catalogs, letters, and flyers. Advertising postcards may be mailed or distributed in other ways.
 W
WAerial advertising is a form of advertising that incorporates the use of flogos, manned aircraft, or drones to create, transport, or display, advertising media. The media can be static, such as a banner, logo, lighted sign or sponsorship branding. It can also be dynamic, such as animated lighted signage, skywriting, or audio.
 W
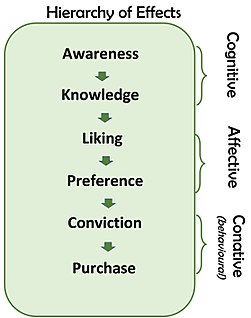
WThe AIDA model is just one of a class of models known as hierarchy of effects models or hierarchical models, all of which imply that consumers move through a series of steps or stages when they make purchase decisions. These models are linear, sequential models built on an assumption that consumers move through a series of cognitive (thinking) and affective (feeling) stages culminating in a behavioural stage.
 W
Waisle411 Inc. is a St. Louis based company that has developed a consumer service called aisle411, which allows customers to use their phones to find products in stores. Founded in 2008 by Nathan Pettyjohn (Founder) and Matthew Kulig (Co-Founder), aisle411 entered the market in August 2009 with a mobile service that allowed consumers to search retail stores for product locations inside stores using their mobile phones.
 W
WAmbush marketing or ambush advertising is a marketing strategy in which an advertiser "ambushes" an event to compete for exposure against other advertisers.
 W
WAugmented reality (AR) is an interactive experience of a real-world environment where the objects that reside in the real world are enhanced by computer-generated perceptual information, sometimes across multiple sensory modalities, including visual, auditory, haptic, somatosensory and olfactory. AR can be defined as a system that fulfills three basic features: a combination of real and virtual worlds, real-time interaction, and accurate 3D registration of virtual and real objects. The overlaid sensory information can be constructive, or destructive. This experience is seamlessly interwoven with the physical world such that it is perceived as an immersive aspect of the real environment. In this way, augmented reality alters one's ongoing perception of a real-world environment, whereas virtual reality completely replaces the user's real-world environment with a simulated one. Augmented reality is related to two largely synonymous terms: mixed reality and computer-mediated reality.
 W
WTargeted advertising is a form of advertising, including online advertising, that is directed towards an audience with certain traits, based on the product or person the advertiser is promoting. These traits can either be demographic with a focus on race, economic status, sex, age, generation, level of education, income level, and employment, or there can be a psychographic focus which is based on the consumer values, personality, attitude, opinion, lifestyle and interest. This focus can also entail behavioral variables, such as browser history, purchase history, and other recent online activities. Targeted advertising is focused on certain traits and consumers who are likely to have a strong preference. These individuals will receive messages instead of those who have no interest and whose preferences do not match a particular product's attributes. This eliminates waste.
 W
WA billboard is a large outdoor advertising structure, typically found in high-traffic areas such as alongside busy roads. Billboards present large advertisements to passing pedestrians and drivers. Typically showing witty slogans and distinctive visuals, billboards are highly visible in the top designated market areas.
 W
WA blurb is a short promotional piece accompanying a piece of creative work. It may be written by the author or publisher or quote praise from others. Blurbs were originally printed on the back or rear dust jacket of a book, and are now found on web portals and news websites. A blurb may introduce a newspaper or a book.
 W
WBoosterism is the act of promoting ("boosting") a town, city, or organization, with the goal of improving public perception of it. Boosting can be as simple as talking up the entity at a party or as elaborate as establishing a visitors' bureau. It has been somewhat associated with American small towns. Boosting is also done in political settings, especially in regard to disputed policies or controversial events, or saying upbeat things and spending public money in the hope that reality can be wished away. The UK prime minister Boris Johnson is strongly associated with such behaviour.
 W
WA broadside is a large sheet of paper printed on one side only. Historically, broadsides were used as posters, announcing events or proclamations, commentary in the form of ballads, or simply advertisements.
 W
WA cigar band is a loop made of paper or foil fitted around the body of a cigar to denote its brand or variety. Although origins of the device are the subject of several legends, modern historians credit a European immigrant to Cuba named Gustave Bock with invention of the cigar band in the 1830s. Within two decades, banding of cigars exported from Havana became almost universal.
 W
WCity marketing is the promotion of a city, or a district within it, with the aim of encouraging certain activities to take place there. It is used to alter the external perceptions of a city in order to encourage tourism, attract inward migration of residents, or enable business relocation. A significant feature of city marketing is the development of new landmark, or 'flagship', buildings and structures. The development of cities as a marketable product has led to competition between them for inward investment and government funding. It is often manifested in the attempts by cities to attract international sporting events, such as the Olympic Games. Competition between cities exists at the regional, national and international level; and is an effect of globalisation.Some places are associated with certain brands and build on each other, but sometimes the commercial brand is so powerful that eclipses the place brand. An example of this is Maranello, Italy, which uses the Ferrari headquarters as a primary attraction for tourists.
 W
WContent marketing is a form of marketing focused on creating, publishing, and distributing content for a targeted audience online. It is often used by businesses in order to achieve the following goals: attract attention and generate lead, expand their customer base, generate or increase online sales, increase brand awareness or credibility, and engage an online community of users. Content marketing attracts new customers by creating and sharing valuable free content. It helps companies create sustainable brand loyalty, provides valuable information to consumers, and creates a willingness to purchase products from the company in the future.
 W
WA corporate identity or corporate image is the manner in which a corporation, firm or business enterprise presents itself to the public. The corporate identity is typically visualized by branding and with the use of trademarks,but it can also include things like product design, advertising, public relations etc. Corporate identity is a primary goal of the corporate communications, in order to maintain and build the identity to accord with and facilitate the corporate business objectives.
 W
WCorporate social media is the use of social media websites and social media marketing techniques by and within corporations, ranging from small businesses and tiny entrepreneurial startups to mid-size businesses to huge multinational firms. Within the definition of social media there are varies types of them. Although there is no systematic way in which social media applications can be categorized. In the 2010s, an increasing number of corporations, across most industries, have adopted the use of social media either within in the workplace, for employees, as part of an Intranet or using the publicly available Internet. As a result, corporate use of social networking and micro blogging sites such as Facebook, Twitter, Pinterest, and LinkedIn, has substantially increased. According to an article by the Harvard Business Review, "Fifty-eight percent of companies are currently engaged in social networks like Facebook, micro blogs like Twitter, and sharing multimedia on platforms such as YouTube." The Harvard Business Review cites an additional 21% of companies as being in the process of implementing a formal social media initiative. The 2014 HBR report indicates 79% of companies have or will have social media initiatives in place. This percentage is an increase over a similar 2010 report that indicated that two-thirds of companies had or would have social media initiatives in place. Social media currently can be crucial to the success of growing numbers in a companies value chain activities. For marketers, Social media is a mandatory element within the promotional mix. Marketers also need to understand that marketing on social media can come with difficulties and challenges, and face both reputation and economic risks. This big push to move to Social Media to is thought to create a better experience with the consumers, as corporations are able to target specific content to their target audience. Another benefit for corporations through usage of media is that this will attract more people, and in return also create a more well known brand.
 W
WCross-promotion is a form of marketing promotion where customers of one product or service are targeted with promotion of a related product. A typical example is cross-media marketing of a brand; for example, Oprah Winfrey's promotion on her television show of her books, magazines and website. Cross-promotion may involve two or more companies working together in promoting a service or product, in a way that benefits both. For example, a mobile phone network may work together with a popular music artist and package some of their songs as exclusive ringtones; promoting these ringtones can benefit both the network and the artist. Some major corporations—Burger King, for example—have a long history of cross-promotion with a range of partners. The Disney Channel has also made extensive use of cross-promotion. Movie tie-ins are good examples of cross-promotion. On occasion, badly planned cross-promotions can backfire spectacularly such as 1992 Hoover free flights promotion fiasco.
 W
WDirect marketing is a form of communicating an offer, where organizations communicate directly to a pre-selected customer and supply a method for a direct response. Among practitioners, it is also known as direct response marketing. By contrast, advertising is of a mass-message nature.
 W
WA display stand is an advertising and merchandising tool that has a direct impact on product sales.
 W
WEmail spam, also referred to as junk email, is unsolicited messages sent in bulk by email (spamming).
 W
WThe elaboration likelihood model (ELM) of persuasion is a dual process theory describing the change of attitudes. The ELM was developed by Richard E. Petty and John Cacioppo in 1980. The model aims to explain different ways of processing stimuli, why they are used, and their outcomes on attitude change. The ELM proposes two major routes to persuasion: the central route and the peripheral route.Under the central route, persuasion will likely result from a person's careful and thoughtful consideration of the true merits of the information presented in support of an advocacy. The central route involves a high level of message elaboration in which a great amount of cognition about the arguments are generated by the individual receiving the message. The results of attitude change will be relatively enduring, resistant, and predictive of behavior. On the other hand, under the peripheral route, persuasion results from a person's association with positive or negative cues in the stimulus or making a simple inference about the merits of the advocated position. The cues received by the individual under the peripheral route are generally unrelated to the logical quality of the stimulus. These cues will involve factors such as the credibility or attractiveness of the sources of the message, or the production quality of the message. The likelihood of elaboration will be determined by an individual's motivation and ability to evaluate the argument being presented.Examples: Routes of ELM
 W
WAn exhibition, in the most general sense, is an organized presentation and display of a selection of items. In practice, exhibitions usually occur within a cultural or educational setting such as a museum, art gallery, park, library, exhibition hall, or World's fairs. Exhibitions can include many things such as art in both major museums and smaller galleries, interpretive exhibitions, natural history museums and history museums, and also varieties such as more commercially focused exhibitions and trade fairs.
 W
WEye tracking is the process of measuring either the point of gaze or the motion of an eye relative to the head. An eye tracker is a device for measuring eye positions and eye movement. Eye trackers are used in research on the visual system, in psychology, in psycholinguistics, marketing, as an input device for human-computer interaction, and in product design. Eye trackers are also being increasingly used for rehabilitative and assistive applications . There are a number of methods for measuring eye movement. The most popular variant uses video images from which the eye position is extracted. Other methods use search coils or are based on the electrooculogram.
 W
WThe term immersion marketing or immersive marketing includes traditional advertising, public relations, word-of-mouth advertising, digital marketing, samples, coupons, retail partnerships and other ways of surrounding the consumer with a consistent message about a brand. In essence, immersion marketing envelopes a brand or product or company issue so that the marketing, advertising, and public relations departments or representatives work holistically towards delivering the same brand message across multiple distribution channels. Unlike "Shotgun marketing"(communicate the message to anyone who listens), immersive marketing is cheaper and more effective, focusing directly on the customer's needs.
 W
WThe Instagram egg is a photo of an egg posted by the account @world_record_egg on the social media platform Instagram, notable for becoming a global phenomenon and an internet meme within days of its creation. It has 54.8 million likes, making it both the most-liked Instagram post and most liked online post on any website in history. The owner of the account was revealed to be Chris Godfrey, an advertising creative, who later worked with his two friends Alissa Khan-Whelan and CJ Brown on a Hulu commercial featuring the egg, intended to raise awareness of mental health.
 W
WAn interactive kiosk is a computer terminal featuring specialized hardware and software that provides access to information and applications for communication, commerce, entertainment, or education.
 W
WInteractive media normally refers to products and services on digital computer-based systems which respond to the user's actions by presenting content such as text, moving image, animation, video, audio, and video games.
 W
WInternal communications (IC) is the function responsible for effective communications among participants within an organization. The scope of the function varies by organization and practitioner, from producing and delivering messages and campaigns on behalf of management, to facilitating two-way dialogue and developing the communication skills of the organization's participants.
 W
WThe Internet is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a network of networks that consists of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the inter-linked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), electronic mail, telephony, and file sharing.
 W
WHistorically, a kiosk was a small garden pavilion open on some or all sides common in Persia, the Indian subcontinent, and in the Ottoman Empire from the 13th century onward. Today, several examples of this type of kiosk still exist in and around the Topkapı Palace in Istanbul, and they can be seen in Balkan countries.
 W
WA magazine is a periodical publication which is printed in gloss-coated and matte paper. Magazines are generally published on a regular schedule and contain a variety of content. They are generally financed by advertising, by a purchase price, by prepaid subscriptions, or a combination of the three.
 W
WMilk Queen is the title awarded to the winner of regularly-organized competitions by Dairy Associations in many countries.
 W
WA promotional model is a model hired to drive consumer demand for a product, service, brand, or concept by directly interacting with potential customers. Most promotional models are conventionally attractive in physical appearance. They serve to make a product or service more appealing and can provide information to journalists and consumers at trade show and convention events. Promotional models are used in motorsports, other sports or at trade shows, or they can act as "spokesmodels" to promote a specific brand or product in advertisements.
 W
WA movie theater, cinema, or cinema hall, also known as a picture house, the pictures, picture theatre, or the movies, is a building that contains auditoria for viewing films for entertainment. Most, but not all, theaters are commercial operations catering to the general public, who attend by purchasing a ticket. Some movie theaters, however, are operated by non-profit organizations or societies that charge members a membership fee to view films.
 W
WA newspaper is a periodical publication containing written information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background.
 W
WA panel discussion, or simply a panel, involves a group of people gathered to discuss a topic in front of an audience, typically at scientific, business, or academic conferences, fan conventions, and on television shows. Panels usually include a moderator who guides the discussion and sometimes elicits audience questions, with the goal of being informative and entertaining. Film panels at fan conventions have been credited with boosting box office returns by generating advance buzz.
 W
WProduct placement, also known as embedded marketing, is a marketing technique where references to specific brands or products are incorporated into another work, such as a film or television program, with specific promotional intent.
 W
WA promotional recording, or promo, or plug copy, is an audio or video recording distributed free, usually in order to promote a recording that is or soon will be commercially available. Promos are normally sent directly to broadcasters, such as music radio and television stations, and to tastemakers, such as DJs and music journalists, in advance of the release of commercial editions, in the hope that airplay, reviews, and other forms of exposure will result and stimulate the public's interest in the commercial release.
 W
WA number of propaganda techniques based on social psychological research are used to generate propaganda. Many of these same techniques can be classified as logical fallacies, since propagandists use arguments that, while sometimes convincing, are not necessarily valid.
 W
WRadio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates the waves, and received by a radio receiver connected to another antenna. Radio is very widely used in modern technology, in radio communication, radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing and other applications.
 W
WA sailing card is a printed advertisement with information on a ship and its sailing dates, especially clipper ships. Mystic Seaport in Mystic Connecticut has a collection of sailing cards. They were used from the mid-1850s in the U.S. to promote sailings and sometimes included engraved pictures and several colors and were displayed in the windows of port area businesses. Many were printed during the California Gold Rush era to attract voyagers and cargo in New York City and Boston. They were widely used until the 1880s and are now considered collectable.
 W
WThe She Spot: Why Women are the Market for Changing the World – And How to Reach Them is a 2008 non-fiction book by Lisa Witter and Lisa Chen.
 W
WSocial media and television broadcasting have a number of connections and interrelationships. In the 2010s, social media technologies and websites allow for television shows to be accessed online on a range of desktop and mobile computer devices, smartphones and smart TVs. As well, online users can use social media websites to share digital video clips or excerpts from TV shows with fellow fans or even share an entire show online. Many social media websites enable users to post online comments on the programs—both negative and positive—in a variety of ways. Viewers can actively participate while watching a TV program by posting comments online, and have their interactions viewed and responded to in real time by other viewers. Technologies such as smartphones, tablets, and laptop computers allow viewers to watch downloaded digital files of TV shows or "stream" digital files of TV shows on a range of devices, both in the home and while on the go. In the 2010s, some television producers and broadcasters are encouraging active social media participation by viewers by posting "hashtags" on the TV screen during shows; these hashtags enable viewers to post online comments about the show, which may either be read by other social media users, or even, in some cases, displayed on the screen.
 W
WA step and repeat banner is a publicity backdrop used primarily for event photography, printed with a repeating pattern such that brand logos or emblems are visible in photographs of the individuals standing in front of it. Step and repeat banners are common fixtures of red carpet or fashion events, or custom-printed for weddings or galas in order to give a more "celebrity-like" feel to attendees' photos.
 W
WStreaming media is multimedia that is constantly received by and presented to an end user while being delivered by a provider over the Internet. The verb to stream refers to the process of delivering or obtaining media in a continuous manner from a particular source. Streaming refers to the delivery method of the medium, rather than the medium itself. Distinguishing delivery method from the media distributed applies specifically to telecommunications networks, as most of the traditional media delivery systems are either inherently streaming or inherently non-streaming. There are challenges with streaming content on the Internet. For example, users whose Internet connection lacks sufficient bandwidth may experience stops, lags, or slow buffering of the content. And users lacking compatible hardware or software systems may be unable to stream certain content. With the use of buffering content just a few seconds in advance, the quality can get much better.
 W
WSubvertising is the practice of making spoofs or parodies of corporate and political advertisements. The cultural critic Mark Dery coined the term in 1991. Subvertisements are anti-ads that deflect advertising's attempts to turn the people's attention in a given direction. According to author Naomi Klein, subvertising offers a way of speaking back to advertising, ‘forcing a dialogue where before there was only a declaration.’ They may take the form of a new image or an alteration to an existing image or icon, often in a satirical manner.
 W
WA sweepstake is a type of contest where a prize or prizes may be awarded to a winner or winners. Sweepstakes began as a form of lottery that were tied to products sold. In response, the FCC and FTC refined U.S. broadcasting laws. Under these laws sweepstakes became strictly "No purchase necessary to enter or win" and "A purchase will not increase your chances of winning", especially since many sweepstakes companies skirted the law by stating only "no purchase necessary to enter", removing the consideration to stop abuse of sweepstakes. Today, sweepstakes in the USA are used as marketing promotions to reward existing consumers and to draw attention to a product. By definition, the winner is determined by luck rather than skill.
 W
WTargeted advertising is a form of advertising, including online advertising, that is directed towards an audience with certain traits, based on the product or person the advertiser is promoting. These traits can either be demographic with a focus on race, economic status, sex, age, generation, level of education, income level, and employment, or there can be a psychographic focus which is based on the consumer values, personality, attitude, opinion, lifestyle and interest. This focus can also entail behavioral variables, such as browser history, purchase history, and other recent online activities. Targeted advertising is focused on certain traits and consumers who are likely to have a strong preference. These individuals will receive messages instead of those who have no interest and whose preferences do not match a particular product's attributes. This eliminates waste.
 W
WThis Man, according to a website created in 2008 by Italian marketer Andrea Natella named Ever Dream This Man?, was a person who was claimed to have been repeatedly seen in dreams by the whole world since 2006, but was never found in real life. Natella created the site in 2008, but it was not until October 2009 that it gained attention from the press and online internet users. This Man's notoriety spawned several internet memes that spoofed flyers of the website, references in films and television shows like The X-Files, and a manga series based on the hoax by Weekly Shōnen Magazine.
 W
WThe Thomas Register of American Manufacturers, now ThomasNet, is an online platform for supplier discovery and product sourcing in the US and Canada. It was once known as the "big green books" and "Thomas Registry", and was a multi-volume directory of industrial product information covering distributors, manufacturers and service companies within thousands of industrial categories that is now published on ThomasNet.
 W
WTrade literature is a general term including advertising, customer technical communications, and catalogues.
 W
WUnboxing is the unpacking of products, especially high tech consumer products, where the process is captured on video and uploaded to the Internet. The item is then also explained in detail and also can sometimes be demonstrated as well.
 W
WValpak Direct Marketing Systems, Inc., commonly known as Valpak, is a North American direct marketing company owned by Platinum Equity. Valpak provides print, mobile and online advertising solutions and coupons. Annually, Valpak distributes some 20 billion coupons in more than 500 million envelopes and millions more through its mobile app and websites.
 W
WThe weepul is a small, spherical, fluffy toy, with large, plastic googly eyes, and no limbs. Weepuls come in various colors. Usually weepuls possess antennae and also large paper feet, with an adhesive layer on the bottom, which is protected by a layer of plastic that is peeled off before deployment.
 W
WA wordmark, word mark, or logotype is usually a distinct text-only typographic treatment of the name of a company, institution, or product name used for purposes of identification and branding. Examples can be found in the graphic identities of the Government of Canada, FedEx, Microsoft, and IBM. The organization name is incorporated as a simple graphic treatment to create a clear, visually memorable identity. The representation of the word becomes a visual symbol of the organization or product.