 W
WBiofuel is fuel that is produced through contemporary processes from biomass, rather than by the very slow geological processes involved in the formation of fossil fuels, such as oil. Since biomass technically can be used as a fuel directly, some people use the terms biomass and biofuel interchangeably. More often than not, however, the word biomass simply denotes the biological raw material the fuel is made of, or some form of thermally/chemically altered solid end product, like torrefied pellets or briquettes.
 W
WA biorefinery is a refinery that converts biomass to energy and other beneficial byproducts. The International Energy Agency Bioenergy Task 42 defined biorefining as "the sustainable processing of biomass into a spectrum of bio-based products and bioenergy ". As refineries, biorefineries can provide multiple chemicals by fractioning an initial raw material (biomass) into multiple intermediates that can be further converted into value-added products. Each refining phase is also referred to as a "cascading phase". The use of biomass as feedstock can provide a benefit by reducing the impacts on the environment, as lower pollutants emissions and reduction in the emissions of hazard products. In addition, biorefineries are intended to achieve the following goals:Supply the current fuels and chemical building blocks Supply new building blocks for the production of novel materials with disruptive characteristics Creation of new jobs, including rural areas Valorization of waste Achieve the ultimate goal of reducing GHG emissions
 W
WCarbon capture and storage (CCS) or carbon capture and sequestration is the process of capturing carbon dioxide before it enters the atmosphere, transporting it, and storing it for centuries or millennia. Usually the CO2 is captured from large point sources, such as a chemical plant or biomass power plant, and then stored in an underground geological formation. The aim is to prevent the release of CO2 from heavy industry with the intent of mitigating the effects of climate change. Although CO2 has been injected into geological formations for several decades for various purposes, including enhanced oil recovery, the long-term storage of CO2 is a relatively new concept.
 W
WA circular economy is an economic system that tackles global challenges like climate change, biodiversity loss, waste, and pollution.
 W
WCultured meat is a meat produced by in vitro cell cultures of animal cells. It is a form of cellular agriculture.
 W
WSince about 2001 the term nuclear renaissance has been used to refer to a possible nuclear power industry revival, driven by rising fossil fuel prices and new concerns about meeting greenhouse gas emission limits.
 W
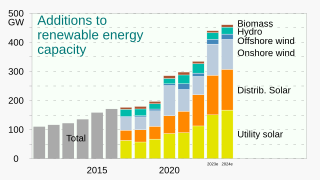
WRenewable energy is useful energy that is collected from renewable resources, which are naturally replenished on a human timescale, including carbon neutral sources like sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat. This type of energy source stands in contrast to fossil fuels, which are being used far more quickly than they are being replenished. Although most renewable energy is sustainable energy, some is not, for example some biomass is unsustainable.