 W
WInterpersonal communication is an exchange of information between two or more people. It is also an area of research that seeks to understand how humans use verbal and nonverbal cues to accomplish a number of personal and relational goals.
 W
WNorman Kent Denzin is an American professor of sociology. He is an emeritus professor in the Department of Sociology at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, where he was research professor of communications, College of Communications scholar, professor of sociology, professor of cinema studies, professor in the Unit for Criticism and Interpretive Theory. Denzin's academic interests include interpretive theory, performance studies, qualitative research methodology, and the study of media, culture and society.
 W
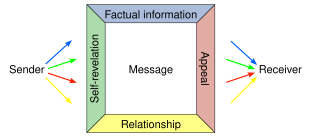
WThe four-sides model is a communication model by Friedemann Schulz von Thun. According to this model every message has four facets though not the same emphasis might be put on each. The four sides of the message are fact, self-revealing, relationship, and appeal.
 W
WThe Jewish-Palestinian Living Room Dialogue Group is a non-violent conflict resolution group established in 1992 in San Mateo, California. Its first meeting was held in a local neighborhood residence. As of September 2019, the group remained active and continued to meet monthly in members' homes. The one-to-one, face-to-face method of conflict resolution, modeled by this dialogue group, was increasingly looked to globally by educators, researchers, journalists, activists, trainers, and strategists including the U.S. Department of State, which distributes the dialogue group's instructive films in Africa.
 W
WIn sociology, popularity is how much a person, idea, place, item or other concept is either liked or accorded status by other people. Liking can be due to reciprocal liking, interpersonal attraction, and similar factors. Social status can be due to dominance, superiority, and similar factors. For example, a kind person may be considered likable and therefore more popular than another person, and a wealthy person may be considered superior and therefore more popular than another person.
 W
WSocial exchange theory is a sociological and psychological theory that studies the social behavior in the interaction of two parties that implement a cost-benefit analysis to determine risks and benefits. The theory also involves economic relationships—the cost-benefit analysis occurs when each party has goods that the other parties value. Social exchange theory suggests that these calculations occur in romantic relationships, friendships, professional relationships, and ephemeral relationships as simple as exchanging words with a customer at the cash register. Social exchange theory says that if the costs of the relationship are higher than the rewards, such as if a lot of effort or money were put into a relationship and not reciprocated, then the relationship may be terminated or abandoned.
 W
WSymbolic interactionism is a sociological theory that develops from practical considerations and alludes to people's particular utilization of dialect to make images and normal implications, for deduction and correspondence with others. In other words, it is a frame of reference to better understand how individuals interact with one another to create symbolic worlds, and in return, how these worlds shape individual behaviors. It is a framework that helps understand how society is preserved and created through repeated interactions between individuals. The interpretation process that occurs between interactions helps create and recreate meaning. It is the shared understanding and interpretations of meaning that affect the interaction between individuals. Individuals act on the premise of a shared understanding of meaning within their social context. Thus, interaction and behavior is framed through the shared meaning that objects and concepts have attached to them. From this view, people live in both natural and symbolic environments.
 W
WTie signs are signs, signals, and symbols, that are revealed through people's actions as well as objects such as engagement rings, wedding bands, and photographs of a personal nature that suggest a relationship exists between two people. For romantic couples, public displays of affection (PDA) including things like holding hands, an arm around a partner's shoulders or waist, extended periods of physical contact, greater-than-normal levels of physical proximity, grooming one's partner, and “sweet talk” are all examples of common tie signs. Tie signs inform the participants, as well as outsiders, about the nature of a relationship, its condition, and even what stage a relationship is in.