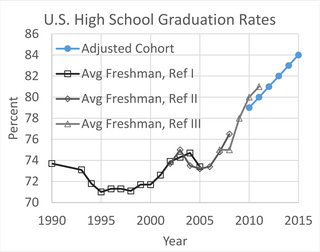
 W
WThe graduation completion rate is the measure reflecting the number of students who complete their graduation and receive a degree from an educational institution. The drop-out rate is the measure reflecting the number of students who disengage with the educational institutions they are enrolled in. Those measures are calculated by the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), the primary federal U.S. entity for collecting and analyzing data related to education.
 W
WThe Higher Education Statistics Agency (HESA) is the official agency for the collection, analysis and dissemination of quantitative information about higher education in the United Kingdom.
 W
WHomeschooling is legal in many countries. Countries with the most prevalent homeschooling movements include Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and the United States. Some countries have highly regulated homeschooling programs as an extension of the compulsory school system; few others, such as Germany, have outlawed it entirely. In some other countries, while not restricted by law, homeschooling is not socially acceptable, or considered undesirable and is virtually non-existent.
 W
WThe University of York is a collegiate research university, located in the city of York, England. Established in 1963, the university has expanded to more than thirty departments and centres, covering a wide range of subjects.
 W
WThis list of largest United States public university campuses by enrollment includes only individual four-year campuses, not four-year universities. Universities can have multiple campuses with a single administration.
 W
WThis list of largest United States universities by undergraduate enrollment includes only individual four-year campuses, not four-year universities. Universities can have multiple campuses with a single administration.
 W
WA standardized test is a test that is administered and scored in a consistent, or "standard", manner. Standardized tests are designed in such a way that the questions, conditions for administering, scoring procedures, and interpretations are consistent and are administered and scored in a predetermined, standard manner.
 W
WEducation in France is organized in a highly centralized manner, with many subdivisions. It is divided into the three stages of primary education, secondary education, and higher education. The main age that a child starts school in France is age 3. Three year olds do not start primary school, they start preschool. Then, by the age of six, a child in France starts primary school and soon moves onto higher and higher grade levels until they graduate.
 W
WMany scholars and policymakers have noted that the fields of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) have remained predominantly male with historically low participation among women since the origins of these fields in the 18th century during the Age of Enlightenment.