 W
WArchimedes of Syracuse was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, inventor, and astronomer. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists in classical antiquity. Considered to be the greatest mathematician of ancient history, and one of the greatest of all time, Archimedes anticipated modern calculus and analysis by applying concepts of infinitesimals and the method of exhaustion to derive and rigorously prove a range of geometrical theorems, including: the area of a circle; the surface area and volume of a sphere; area of an ellipse; the area under a parabola; the volume of a segment of a paraboloid of revolution; the volume of a segment of a hyperboloid of revolution; and the area of a spiral.
 W
WArchimedes is a large lunar impact crater on the eastern edges of the Mare Imbrium. Its diameter is 81 km.
 W
WThe water screw, popularly known as the Archimedes' screw and also known as the screw pump, Archimedean screw, or Egyptian screw, is a machine used for transferring water from a low-lying body of water into irrigation ditches. Water is pumped by turning a screw-shaped surface inside a pipe. Archimedes screws are also used for materials such as powders and grains. Moreover, Archimedes screws could produce power if they are driven by flowing fluid instead of lifting fluid. Although commonly attributed to Archimedes, there is some evidence that the device had been used in Ancient Egypt long before his time.
 W
WThe Claw of Archimedes was an ancient weapon devised by Archimedes to defend the seaward portion of Syracuse's city wall against amphibious assault. Although its exact nature is unclear, the accounts of ancient historians seem to describe it as a sort of crane equipped with a grappling hook that was able to lift an attacking ship partly out of the water, then either cause the ship to capsize or suddenly drop it. It was dropped onto enemy ships, which would then swing itself and destroy the ship.
 W
WEureka is an interjection used to celebrate a discovery or invention. It is a transliteration of an exclamation attributed to Ancient Greek mathematician and inventor Archimedes.
 W
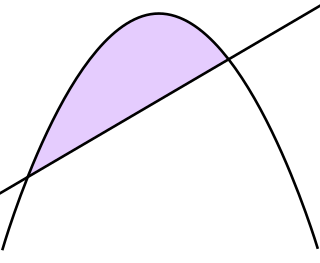
WThe Quadrature of the Parabola is a treatise on geometry, written by Archimedes in the 3rd century BC. Written as a letter to his friend Dositheus, the work presents 24 propositions regarding parabolas, culminating in a proof that the area of a parabolic segment is 4/3 that of a certain inscribed triangle.
 W
WThe salinon is a geometrical figure that consists of four semicircles. It was first introduced in the Book of Lemmas, a work attributed to Archimedes.
 W
WThe Siege of Syracuse by the Roman Republic took place in 213–212 BC, at the end of which the Hellenistic city of Syracuse, located on the east coast of Sicily, fell. The Romans stormed the city after a protracted siege giving them control of the entire island of Sicily. During the siege, the city was protected by weapons developed by Archimedes. Archimedes, the great inventor and polymath, was slain at the conclusion of the siege by a Roman soldier, in contravention of the Roman proconsul Marcellus' instructions to spare his life.
 W
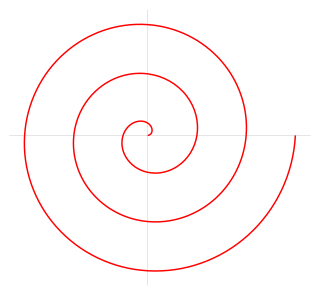
WThe Archimedean spiral is a spiral named after the 3rd-century BC Greek mathematician Archimedes. It is the locus corresponding to the locations over time of a point moving away from a fixed point with a constant speed along a line that rotates with constant angular velocity. Equivalently, in polar coordinates (r, θ) it can be described by the equation
 W
WSyracusia was an ancient Greek ship sometimes claimed to be the largest transport ship of antiquity. She was reportedly too big for any port in Sicily, and thus only sailed once from Syracuse in Sicily to Alexandria in the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt, whereupon she was given as a present to Ptolemy III Euergetes. The exact dimension of Syracusia is unknown, Michael Lahanas put it at 55 m long, 14 m wide, and 13 m high.