 W
WThe Hindenburg Line was a German defensive position built during the winter of 1916–1917 on the Western Front during the First World War. The line ran from Arras to Laffaux, near Soissons on the Aisne. In 1916, the Battle of Verdun and the Battle of the Somme left the German western armies exhausted and on the Eastern Front, the Brusilov Offensive had inflicted huge losses on the Austro-Hungarian armies and forced the Germans to take over more of the front. The declaration of war by Romania had placed additional strain on the German army and war economy.
 W
WThe Bar Lev Line was a chain of fortifications built by Israel along the eastern bank of the Suez Canal after it occupied the Sinai Peninsula from Egypt during the 1967 Six-Day War. It was considered impregnable and was a symbol of Israeli military perfection. It was overrun in 1973 by the Egyptian military during Operation Badr.
 W
WThe Commission for Organizing the Fortified Regions, is a French military organization created on 30 September 1927 by the Minister of War Paul Painlevé to study and carry out border fortification. Its creation was not a spontaneous decision but the result of a long and deep reflection on how best to defend the borders of France.
 W
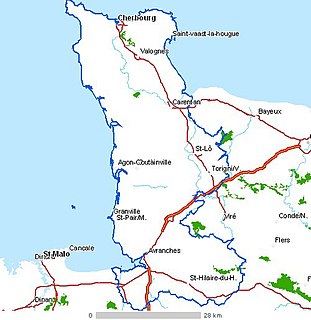
WThe Danevirke or Danework is a system of Danish fortifications in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. This historically important linear defensive earthwork across the neck of the Cimbrian peninsula was initiated by the Danes in the Nordic Iron Age about AD 650. It was later expanded multiple times during Denmark's Viking Age and High Middle Ages. The Danevirke was last used for military purposes in 1864 during the Second War of Schleswig.
 W
WFortress Europe was a military propaganda term used by both sides of the Second World War which referred to the areas of Continental Europe occupied by Nazi Germany, as opposed to the United Kingdom across the Channel.
 W
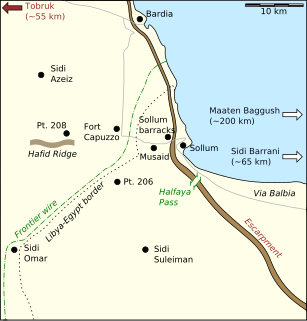
WThe Frontier Wire was a 271 km (168 mi) obstacle in Italian Libya, along the length of the border of British-held Egypt, running from El Ramleh, in the Gulf of Sollum south to Jaghbub parallel to the 25th meridian east, the Libya–Egypt and Libya–Sudan borders. The frontier wire and line of covering forts, were built by the Italians during the Second Italo-Senussi War (1923–1931), as a defensive system to contain the Senussi population, who crossed from Egypt during their resistance against the Italian colonisers. From the Italian declaration of war on 10 June 1940 to late 1942, it was the scene of military engagements between Italian, British and German forces as the fighting ebbed and flowed across the frontier.
 W
WThe Línea P, officially the Pyrenees Defense Organisation, was a fortified line of defense built in the Pyrenees between 1944 and 1948 to prevent an invasion of the Spanish territory.
 W
WThe Maginot Line, named after the French Minister of War André Maginot, is a line of concrete fortifications, obstacles, and weapon installations built by France in the 1930s to deter invasion by Germany and force them to move around the fortifications.
 W
WThe so-called Molotov Line was a system of border fortified regions built by the Soviet Union in the years 1940–1941 along its new western borders. These borders were the result of the Occupation of the Baltic States, Eastern Poland and Bessarabia in 1940.
 W
WThe Siegfried Line, known in German as the Westwall, was a German defensive line built during the 1930s opposite the French Maginot Line. It stretched more than 630 km (390 mi); from Kleve on the border with the Netherlands, along the western border of the old German Empire, to the town of Weil am Rhein on the border to Switzerland – and featured more than 18,000 bunkers, tunnels and tank traps.
 W
WThe Taunton Stop Line was a World War II defensive line in southwest England. It was designed "to stop an enemy's advance from the west and in particular a rapid advance supported by armoured fighting vehicles which may have broken through the forward defences."