 W
WThe Alice is a very small "sugarcube" mobile robot (2x2x2cm) developed at the Autonomous Systems Lab (ASL) at the EPFL in Lausanne, Switzerland between 1998 and 2004. It has been part of the Institute of Robotics and Intelligent Systems (IRIS) at ETH Zurich since 2006.
 W
WIn computer science and operations research, the ant colony optimization algorithm (ACO) is a probabilistic technique for solving computational problems which can be reduced to finding good paths through graphs. Artificial ants stand for multi-agent methods inspired by the behavior of real ants. The pheromone-based communication of biological ants is often the predominant paradigm used. Combinations of artificial ants and local search algorithms have become a method of choice for numerous optimization tasks involving some sort of graph, e.g., vehicle routing and internet routing.
 W
WCentibots were robots created around 2003 and designed to coordinate in large numbers in order to achieve a single goal, an early example of swarm robotics. The $2.2 million project was sponsored by DARPA and had principal investigator SRI International along with other investigators University of Washington's Robotics and State Estimation Lab, Stanford University and ActivMedia Robotics. SRI's Artificial Intelligence Center was known for previous work in robotics, in particular Shakey the robot and related research.
 W
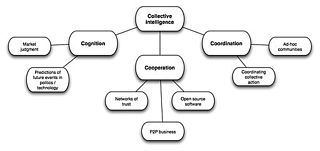
WCollective intelligence (CI) is shared or group intelligence that emerges from the collaboration, collective efforts, and competition of many individuals and appears in consensus decision making. The term appears in sociobiology, political science and in context of mass peer review and crowdsourcing applications. It may involve consensus, social capital and formalisms such as voting systems, social media and other means of quantifying mass activity. Collective IQ is a measure of collective intelligence, although it is often used interchangeably with the term collective intelligence. Collective intelligence has also been attributed to bacteria and animals.
 W
WA drone display is the use of multiple unmanned aerial vehicles (drones), often quadcopters, flying in a coordinated fashion for public display. They are usually equipped with LEDs, and the display held at night. The first drone display was presented in 2012 in Linz/Austria, where the Ars Electronica Futurelab introduced SPAXELS for the first time. The displays may be for entertainment, where the drones may use flocking or swarming behaviour. The drones may also be coordinated to produce images. Using this emerging technology, displays have been employed for advertising purposes as well.
 W
WThe e-puck is a small (7 cm) differential wheeled mobile robot. It was originally designed for micro-engineering education by Michael Bonani and Francesco Mondada at the ASL laboratory of Prof. Roland Siegwart at EPFL. The e-puck is open hardware and its onboard software is open-source, and is built and sold by several companies.
 W
WA multi-agent system is a computerized system composed of multiple interacting intelligent agents. Multi-agent systems can solve problems that are difficult or impossible for an individual agent or a monolithic system to solve. Intelligence may include methodic, functional, procedural approaches, algorithmic search or reinforcement learning.
 W
WThe s-bot is a small (15 cm) differential wheeled mobile robot developed at the LIS at the EPFL in Lausanne, Switzerland between 2001 and 2004. Targeted to swarm robotics, a field of artificial intelligence, it was developed within the Swarm-bots project, a Future and Emerging Technologies project coordinated by Prof. Marco Dorigo. Built by a small team of engineers of the group of Prof. Dario Floreano and with the help of student projects, it is considered at the time of completion as one of the most complex and featured robots ever for its size. The s-bot was ranked on position 39 in the list of “The 50 Best Robots Ever” by the Wired magazine in 2006.
 W
WSwarm robotics is an approach to the coordination of multiple robots as a system which consist of large numbers of mostly simple physical robots. It is supposed that a desired collective behavior emerges from the interactions between the robots and interactions of robots with the environment. This approach emerged on the field of artificial swarm intelligence, as well as the biological studies of insects, ants and other fields in nature, where swarm behaviour occurs.
 W
WSymbrion is a project funded by the European Commission between 2008 and 2013 to develop a framework in which a homogeneous swarm of miniature interdependent robots can co-assemble into a larger robotic organism to gain problem-solving momentum.
 W
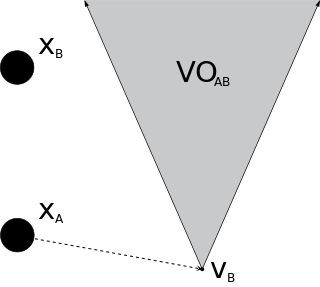
WIn robotics and motion planning, a velocity obstacle, commonly abbreviated VO, is the set of all velocities of a robot that will result in a collision with another robot at some moment in time, assuming that the other robot maintains its current velocity. If the robot chooses a velocity inside the velocity obstacle then the two robots will eventually collide, if it chooses a velocity outside the velocity obstacle, such a collision is guaranteed not to occur.