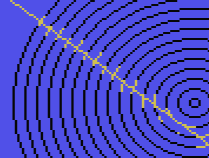
 W
WAttribute clash is a display artifact caused by limits in the graphics circuitry of some colour 8-bit home computers, most notably the Sinclair ZX Spectrum, where it meant that only two colours could be used in any 8×8 tile of pixels. The effect was also noticeable on MSX software and in some Commodore 64 titles. Workarounds to prevent this limit from becoming apparent have since been considered an element of Spectrum programmer culture.
 W
WColour banding is a problem of inaccurate colour presentation in computer graphics. In 24-bit colour modes, 8 bits per channel is usually considered sufficient to render images in Rec. 709 or sRGB. However, in some cases there is a risk of producing abrupt changes between shades of the same colour. For instance, displaying natural gradients can show minor banding.
 W
WComposite artifact colors is a designation commonly used to address several graphic modes of some 1970s and 1980s home computers. With some machines, when connected to an NTSC TV or monitor over composite video outputs, the video signal encoding allowed for extra colors to be displayed, by manipulating the pixel position on screen, not being limited by each machine's hardware color palette.
 W
WA compression artifact is a noticeable distortion of media caused by the application of lossy compression. Lossy data compression involves discarding some of the media's data so that it becomes small enough to be stored within the desired disk space or transmitted (streamed) within the available bandwidth. If the compressor cannot store enough data in the compressed version, the result is a loss of quality, or introduction of artifacts. The compression algorithm may not be intelligent enough to discriminate between distortions of little subjective importance and those objectionable to the user.
 W
WDigital artifact in information science, is any undesired or unintended alteration in data introduced in a digital process by an involved technique and/or technology.
 W
WDither is an intentionally applied form of noise used to randomize quantization error, preventing large-scale patterns such as color banding in images. Dither is routinely used in processing of both digital audio and video data, and is often one of the last stages of mastering audio to a CD.
 W
W"Jaggies" is the informal name for artifacts in raster images, most frequently from aliasing, which in turn is often caused by non-linear mixing effects producing high-frequency components, or missing or poor anti-aliasing filtering prior to sampling.
 W
WIn computer graphics, pixelation is caused by displaying a bitmap or a section of a bitmap at such a large size that individual pixels, small single-colored square display elements that comprise the bitmap, are visible. Such an image is said to be pixelated.
 W
WPosterization or posterisation of an image entails the conversion of a continuous gradation of tone to several regions of fewer tones, with abrupt changes from one tone to another. This was originally done with photographic processes to create posters. It can now be done photographically or with digital image processing and may be deliberate or an unintended artifact of color quantization.
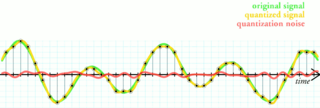 W
WQuantization, in mathematics and digital signal processing, is the process of mapping input values from a large set to output values in a (countable) smaller set, often with a finite number of elements. Rounding and truncation are typical examples of quantization processes. Quantization is involved to some degree in nearly all digital signal processing, as the process of representing a signal in digital form ordinarily involves rounding. Quantization also forms the core of essentially all lossy compression algorithms.
 W
WIn signal processing, particularly digital image processing, ringing artifacts are artifacts that appear as spurious signals near sharp transitions in a signal. Visually, they appear as bands or "ghosts" near edges; audibly, they appear as "echos" near transients, particularly sounds from percussion instruments; most noticeable are the pre-echos. The term "ringing" is because the output signal oscillates at a fading rate around a sharp transition in the input, similar to a bell after being struck. As with other artifacts, their minimization is a criterion in filter design.
 W
WVisual artifacts are anomalies apparent during visual representation as in digital graphics and other forms of imagery, especially photography and microscopy.