 W
WConversica is a US-based cloud software technology company. Conversica offers a suite of Intelligent Virtual Assistants for business, with a focus on Customer Experience business functions. Powered by Artificial Intelligence, the Intelligent Virtual Assistants (IVA) interact with leads and customers in a human-like way, like an entry level employee. The IVA software interacts over multiple channels, including email and SMS text messages, and in multiple languages. Conversica is a pioneer in providing AI-driven lead engagement software for marketing and sales organizations. Conversica is headquartered in Silicon Valley,.
 W
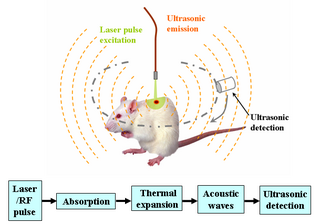
WDeep learning in photoacoustic imaging combines the hybrid imaging modality of photoacoustic imaging (PA) with the rapidly evolving field of deep learning. Photoacoustic imaging is based on the photoacoustic effect, in which optical absorption causes a rise in temperature, which causes a subsequent rise in pressure via thermo-elastic expansion. This pressure rise propagates through the tissue and is sensed via ultrasonic transducers. Due to the proportionality between the optical absorption, the rise in temperature, and the rise in pressure, the ultrasound pressure wave signal can be used to quantify the original optical energy deposition within the tissue.
 W
WDeepfakes are synthetic media in which a person in an existing image or video is replaced with someone else's likeness. While the act of faking content is not new, deepfakes leverage powerful techniques from machine learning and artificial intelligence to manipulate or generate visual and audio content with a high potential to deceive. The main machine learning methods used to create deepfakes are based on deep learning and involve training generative neural network architectures, such as autoencoders or generative adversarial networks (GANs).
 W
WFaceApp is a photo and video editing application for iOS and Android developed by Wireless Lab, a company based in Russia. The app generates highly realistic transformations of human faces in photographs by using neural networks based on artificial intelligence. The app can transform a face to make it smile, look younger, look older, or change gender.
 W
WHorovod is a free and open-source software framework for distributed deep learning training using TensorFlow, Keras, PyTorch, and Apache MXNet. Horovod is hosted under the Linux Foundation AI. Horovod has the goal of improving the speed, scale, and resource allocation when training a machine learning model
 W
WKeras is an open-source software library that provides a Python interface for artificial neural networks. Keras acts as an interface for the TensorFlow library.
 W
WArtificial neural networks are a class of models used in machine learning, and inspired by biological neural networks. They are the core component of modern deep learning algorithms. Computation in artificial neural networks is usually organized into sequential layers of artificial neurons. The number of neurons in a layer is called the layer width. Theoretical analysis of artificial neural networks sometimes considers the limiting case that layer width becomes large or infinite. This limit enables simple analytic statements to be made about neural network predictions, training dynamics, generalization, and loss surfaces. This wide layer limit is also of practical interest, since finite width neural networks often perform strictly better as layer width is increased.
 W
WMicrosoft Cognitive Toolkit, previously known as CNTK and sometimes styled as The Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit, is a deprecated deep learning framework developed by Microsoft Research. Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit describes neural networks as a series of computational steps via a directed graph.
 W
WML.NET is a free software machine learning library for the C# and F# programming languages. It also supports Python models when used together with NimbusML. The preview release of ML.NET included transforms for feature engineering like n-gram creation, and learners to handle binary classification, multi-class classification, and regression tasks. Additional ML tasks like anomaly detection and recommendation systems have since been added, and other approaches like deep learning will be included in future versions.
 W
WBayesian networks are a modeling tool for assigning probabilities to events, and thereby characterizing the uncertainty in a model's predictions. Deep learning and artificial neural networks are approaches used in machine learning to build computational models which learn from training examples. Bayesian neural networks merge these fields. They are a type of artificial neural network whose parameters and predictions are both probabilistic. While standard artificial neural networks often assign high confidence even to incorrect predictions, Bayesian neural networks can more accurately evaluate how likely their predictions are to be correct.
 W
Wrnn is an open-source machine learning framework that implements recurrent neural network architectures, such as LSTM and GRU, natively in the R programming language, that has been downloaded over 100,000 times.
 W
WApache SINGA is an Apache top-level project for developing an open source machine learning library. It provides a flexible architecture for scalable distributed training, is extensible to run over a wide range of hardware, and has a focus on health-care applications.
 W
WStyleGAN is a novel generative adversarial network (GAN) introduced by Nvidia researchers in December 2018, and made source available in February 2019.
 W
WTensorFlow is a free and open-source software library for machine learning. It can be used across a range of tasks but has a particular focus on training and inference of deep neural networks.
 W
WTorch is an open-source machine learning library, a scientific computing framework, and a script language based on the Lua programming language. It provides a wide range of algorithms for deep learning, and uses the scripting language LuaJIT, and an underlying C implementation. As of 2018, Torch is no longer in active development. However PyTorch, which is based on the Torch library, is actively developed as of December 2020.