 W
WAn astroid is a particular mathematical curve: a hypocycloid with four cusps. Specifically, it is the locus of a point on a circle as it rolls inside a fixed circle with four times the radius. By double generation, it is also the locus of a point on a circle as it rolls inside a fixed circle with 4/3 times the radius. It can also be defined as the envelope of a line segment of fixed length that moves while keeping an end point on each of the axes. It is therefore the envelope of the moving bar in the Trammel of Archimedes.
 W
WA cardioid is a plane curve traced by a point on the perimeter of a circle that is rolling around a fixed circle of the same radius. It can also be defined as an epicycloid having a single cusp. It is also a type of sinusoidal spiral, and an inverse curve of the parabola with the focus as the center of inversion.
 W
WIn physics and geometry, a catenary is the curve that an idealized hanging chain or cable assumes under its own weight when supported only at its ends.
 W
WIn geometry, a centered trochoid is the roulette formed by a circle rolling along another circle. That is, it is the path traced by a point attached to a circle as the circle rolls without slipping along a fixed circle. The term encompasses both epitrochoid and hypotrochoid. The center of this curve is defined to be the center of the fixed circle.
 W
WIn geometry, the cissoid of Diocles is a cubic plane curve notable for the property that it can be used to construct two mean proportionals to a given ratio. In particular, it can be used to double a cube. It can be defined as the cissoid of a circle and a line tangent to it with respect to the point on the circle opposite to the point of tangency. In fact, the curve family of cissoids is named for this example and some authors refer to it simply as the cissoid. It has a single cusp at the pole, and is symmetric about the diameter of the circle which is the line of tangency of the cusp. The line is an asymptote. It is a member of the conchoid of de Sluze family of curves and in form it resembles a tractrix.
 W
WIn geometry, a cycloid is the curve traced by a point on a circle as it rolls along a straight line without slipping. A cycloid is a specific form of trochoid and is an example of a roulette, a curve generated by a curve rolling on another curve.
 W
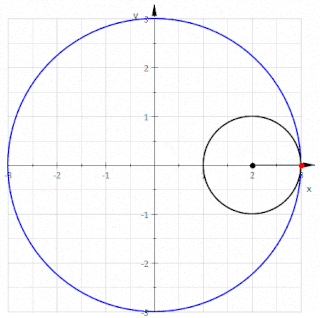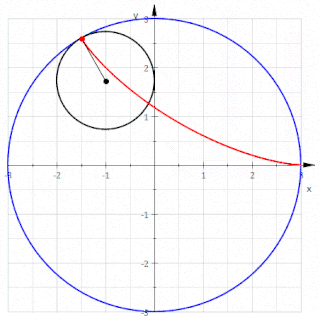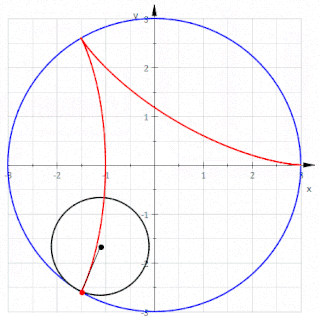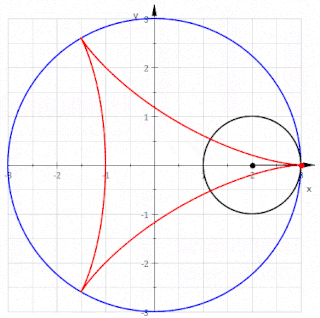
WIn geometry, a deltoid curve, also known as a tricuspoid curve or Steiner curve, is a hypocycloid of three cusps. In other words, it is the roulette created by a point on the circumference of a circle as it rolls without slipping along the inside of a circle with three or one-and-a-half times its radius. It is named after the Greek letter delta which it resembles.
 W
WIn geometry, an epicycloid or hypercycloid is a plane curve produced by tracing the path of a chosen point on the circumference of a circle—called an epicycle—which rolls without slipping around a fixed circle. It is a particular kind of roulette.
 W
WAn epitrochoid is a roulette traced by a point attached to a circle of radius r rolling around the outside of a fixed circle of radius R, where the point is at a distance d from the center of the exterior circle.
 W
WIn geometry, a hypocycloid is a special plane curve generated by the trace of a fixed point on a small circle that rolls within a larger circle. As the radius of the larger circle is increased, the hypocycloid becomes more like the cycloid created by rolling a circle on a line.
 W
WA hypotrochoid is a roulette traced by a point attached to a circle of radius r rolling around the inside of a fixed circle of radius R, where the point is a distance d from the center of the interior circle.
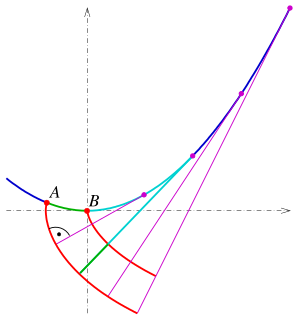 W
WIn mathematics, an involute is a particular type of curve that is dependent on another shape or curve. An involute of a curve is the locus of a point on a piece of taut string as the string is either unwrapped from or wrapped around the curve.
 W
WIn geometry, a limaçon or limacon, also known as a limaçon of Pascal, is defined as a roulette formed by the path of a point fixed to a circle when that circle rolls around the outside of a circle of equal radius. It can also be defined as the roulette formed when a circle rolls around a circle with half its radius so that the smaller circle is inside the larger circle. Thus, they belong to the family of curves called centered trochoids; more specifically, they are epitrochoids. The cardioid is the special case in which the point generating the roulette lies on the rolling circle; the resulting curve has a cusp.
 W
WIn geometry, a nephroid is a specific plane curve whose name means 'kidney-shaped'. Although the term nephroid was used to describe other curves, it was applied to the curve in this article by Proctor in 1878.
 W
WIn geometry, a trochoid is a roulette formed by a circle rolling along a line. In other words, it is the curve traced out by a point fixed to a circle as it rolls along a straight line. If the point is on the circle, the trochoid is called common ; if the point is inside the circle, the trochoid is curtate; and if the point is outside the circle, the trochoid is prolate. The word "trochoid" was coined by Gilles de Roberval.
 W
WThe Tusi couple is a mathematical device in which a small circle rotates inside a larger circle twice the diameter of the smaller circle. Rotations of the circles cause a point on the circumference of the smaller circle to oscillate back and forth in linear motion along a diameter of the larger circle. The Tusi couple is a 2-cusped hypocycloid.