 W
WAn integer is colloquially defined as a number that can be written without a fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, 5+1/2, and √2 are not.
 W
W59 (fifty-nine) is the natural number following 58 and preceding 60.
 W
W120, read as one hundred [and] twenty, is the natural number following 119 and preceding 121.
 W
W146 is the natural number following 145 and preceding 147.
 W
W216 is the natural number following 215 and preceding 217.
 W
W1024 is the natural number following 1023 and preceding 1025.
 W
W65537 is the integer after 65536 and before 65538.
 W
WIn mathematics, monstrous moonshine, or moonshine theory, is the unexpected connection between the monster group M and modular functions, in particular, the j function. The term was coined by John Conway and Simon P. Norton in 1979.
 W
WOne million (1,000,000), or one thousand thousand, is the natural number following 999,999 and preceding 1,000,001. The word is derived from the early Italian millione, from mille, "thousand", plus the augmentative suffix -one. It is commonly abbreviated as m or M and MM, mm, or mn in financial contexts.
 W
W1,000,000,000 is the natural number following 999,999,999 and preceding 1,000,000,001. One billion can also be written as b or bn.
 W
WThe number 2,147,483,647 is the eighth Mersenne prime, equal to 231 − 1. It is one of only four known double Mersenne primes.
 W
WIn recreational mathematics, an almost integer is any number that is not an integer but is very close to one. Almost integers are considered interesting when they arise in some context in which they are unexpected.
 W
WIn arithmetic and algebra, the cube of a number n is its third power, that is, the result of multiplying three instances of n together. The cube of a number or any other mathematical expression is denoted by a superscript 3, for example 23 = 8 or (x + 1)3.
 W
WLegendre's constant is a mathematical constant occurring in a formula conjectured by Adrien-Marie Legendre to capture the asymptotic behavior of the prime-counting function . Its value is now known to be exactly 1.
 W
WIn mathematics, the natural numbers are those used for counting and ordering. In common mathematical terminology, words colloquially used for counting are "cardinal numbers", and words used for ordering are "ordinal numbers". The natural numbers can, at times, appear as a convenient set of codes ; that is, as what linguists call nominal numbers, forgoing many or all of the properties of being a number in a mathematical sense. The set of natural numbers is often denoted by the symbol .
 W
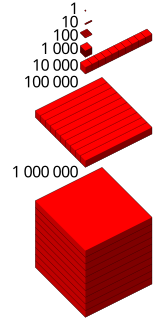
WA power of 10 is any of the integer powers of the number ten; in other words, ten multiplied by itself a certain number of times. By definition, the number one is a power of ten. The first few non-negative powers of ten are:1, 10, 100, 1,000, 10,000, 100,000, 1,000,000, 10,000,000. ...
 W
WA power of two is a number of the form 2n where n is an integer, that is, the result of exponentiation with number two as the base and integer n as the exponent.