 W
WIn physics, potential energy is the energy held by an object because of its position relative to other objects, stresses within itself, its electric charge, or other factors.
 W
WThe demagnetizing field, also called the stray field, is the magnetic field (H-field) generated by the magnetization in a magnet. The total magnetic field in a region containing magnets is the sum of the demagnetizing fields of the magnets and the magnetic field due to any free currents or displacement currents. The term demagnetizing field reflects its tendency to act on the magnetization so as to reduce the total magnetic moment. It gives rise to shape anisotropy in ferromagnets with a single magnetic domain and to magnetic domains in larger ferromagnets.
 W
WThe electric potential is the amount of work energy needed to move a unit of electric charge from a reference point to the specific point in an electric field with negligible acceleration of the test charge to avoid producing kinetic energy or radiation by test charge. Typically, the reference point is the Earth or a point at infinity, although any point can be used. More precisely it is the energy per unit charge for a small test charge that does not disturb significantly the field and the charge distribution producing the field under consideration.
 W
WEquipotential or isopotential in mathematics and physics refers to a region in space where every point in it is at the same potential. This usually refers to a scalar potential, although it can also be applied to vector potentials. An equipotential of a scalar potential function in n-dimensional space is typically an (n−1)dimensional space. The del operator illustrates the relationship between a vector field and its associated scalar potential field. An equipotential region might be referred as being 'of equipotential' or simply be called 'an equipotential'.
 W
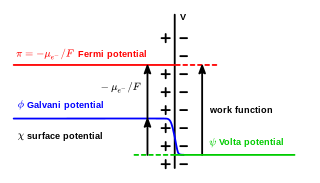
WIn electrochemistry, the Galvani potential is the electric potential difference between two points in the bulk of two phases. These phases can be two different solids, or a solid and a liquid.
 W
WIn classical mechanics, the gravitational potential at a location is equal to the work per unit mass that would be needed to move an object to that location from a fixed reference location. It is analogous to the electric potential with mass playing the role of charge. The reference location, where the potential is zero, is by convention infinitely far away from any mass, resulting in a negative potential at any finite distance.
 W
WA homoeoid is a shell bounded by two concentric, similar ellipses or ellipsoids . When the thickness of the shell becomes negligible, it is called a thin homoeoid. The name homoeoid was coined by Lord Kelvin and Peter Tait.
 W
WThe Lennard-Jones potential is an intermolecular pair potential. Among the intermolecular potentials, the Lennard-Jones potential has a central role as water among real fluids: It is the potential that has been studied most extensively and most thoroughly. It is considered as archetype model for simple yet realistic intermolecular interactions.
 W
WMagnetic scalar potential, ψ, is a quantity in classical electromagnetism analogous to electric potential. It is used to specify the magnetic H-field in cases when there are no free currents, in a manner analogous to using the electric potential to determine the electric field in electrostatics. One important use of ψ is to determine the magnetic field due to permanent magnets when their magnetization is known. The potential is valid in any region with zero current density, thus if currents are confined to wires or surfaces, piecemeal solutions can be stitched together to provide a description of the magnetic field at all points in space.
 W
WMagnetic vector potential, A, is the vector quantity in classical electromagnetism defined so that its curl is equal to the magnetic field: . Together with the electric potential φ, the magnetic vector potential can be used to specify the electric field E as well. Therefore, many equations of electromagnetism can be written either in terms of the fields E and B, or equivalently in terms of the potentials φ and A. In more advanced theories such as quantum mechanics, most equations use potentials rather than fields.
 W
WMagnetostatics is the study of magnetic fields in systems where the currents are steady. It is the magnetic analogue of electrostatics, where the charges are stationary. The magnetization need not be static; the equations of magnetostatics can be used to predict fast magnetic switching events that occur on time scales of nanoseconds or less. Magnetostatics is even a good approximation when the currents are not static — as long as the currents do not alternate rapidly. Magnetostatics is widely used in applications of micromagnetics such as models of magnetic storage devices as in computer memory. Magnetostatic focussing can be achieved either by a permanent magnet or by passing current through a coil of wire whose axis coincides with the beam axis.
 W
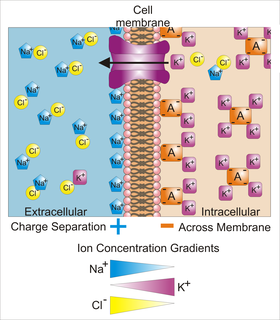
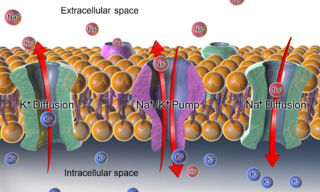
WMembrane potential is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell. For the exterior of the cell, typical values of membrane potential, normally given in units of millivolts and denoted as mV, range from –40 mV to –80 mV.
 W
WThe Morse potential, named after physicist Philip M. Morse, is a convenient interatomic interaction model for the potential energy of a diatomic molecule. It is a better approximation for the vibrational structure of the molecule than the quantum harmonic oscillator because it explicitly includes the effects of bond breaking, such as the existence of unbound states. It also accounts for the anharmonicity of real bonds and the non-zero transition probability for overtone and combination bands. The Morse potential can also be used to model other interactions such as the interaction between an atom and a surface. Due to its simplicity, it is not used in modern spectroscopy. However, its mathematical form inspired the MLR (Morse/Long-range) potential, which is the most popular potential energy function used for fitting spectroscopic data.
 W
WThe relatively static membrane potential of quiescent cells is called the resting membrane potential, as opposed to the specific dynamic electrochemical phenomena called action potential and graded membrane potential.
 W
WIn electrodynamics, the retarded potentials are the electromagnetic potentials for the electromagnetic field generated by time-varying electric current or charge distributions in the past. The fields propagate at the speed of light c, so the delay of the fields connecting cause and effect at earlier and later times is an important factor: the signal takes a finite time to propagate from a point in the charge or current distribution to another point in space, see figure below.
 W
WScalar potential, simply stated, describes the situation where the difference in the potential energies of an object in two different positions depends only on the positions, not upon the path taken by the object in traveling from one position to the other. It is a scalar field in three-space: a directionless value (scalar) that depends only on its location. A familiar example is potential energy due to gravity.
 W
WIn protein structure prediction, a statistical potential or knowledge-based potential is a scoring function derived from an analysis of known protein structures in the Protein Data Bank (PDB).
 W
WA thermodynamic potential is a scalar quantity used to represent the thermodynamic state of a system. The concept of thermodynamic potentials was introduced by Pierre Duhem in 1886. Josiah Willard Gibbs in his papers used the term fundamental functions. One main thermodynamic potential that has a physical interpretation is the internal energy U. It is the energy of configuration of a given system of conservative forces and only has meaning with respect to a defined set of references. Expressions for all other thermodynamic energy potentials are derivable via Legendre transforms from an expression for U. In thermodynamics, external forces, such as gravity, are typically disregarded when formulating expressions for potentials. For example, while all the working fluid in a steam engine may have higher energy due to gravity while sitting on top of Mount Everest than it would at the bottom of the Mariana Trench, the gravitational potential energy term in the formula for the internal energy would usually be ignored because changes in gravitational potential within the engine during operation would be negligible. In a large system under even homogeneous external force, like the earth atmosphere under gravity, the intensive parameters should be studied locally having even in equilibrium different values in different places far from each other (see thermodynamic models of troposphere].