 W
WAstrophysical X-ray sources are astronomical objects with physical properties which result in the emission of X-rays.
 W
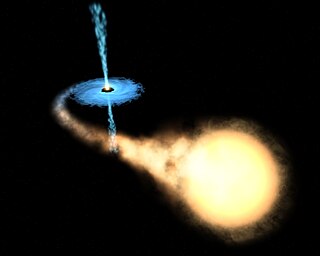
WAn ultraluminous X-ray source (ULX) is an astronomical source of X-rays that is less luminous than an active galactic nucleus but is more consistently luminous than any known stellar process (over 1039 erg/s, or 1032 watts), assuming that it radiates isotropically (the same in all directions). Typically there is about one ULX per galaxy in galaxies which host them, but some galaxies contain many. The Milky Way has not been shown to contain a ULX. The main interest in ULXs stems from their luminosity exceeding the Eddington luminosity of neutron stars and even stellar black holes. It is not known what powers ULXs; models include beamed emission of stellar mass objects, accreting intermediate-mass black holes, and super-Eddington emission.
 W
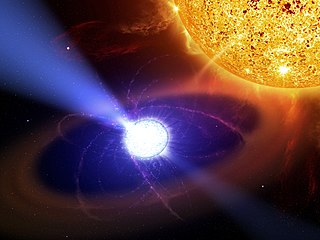
WX-ray binaries are a class of binary stars that are luminous in X-rays. The X-rays are produced by matter falling from one component, called the donor, to the other component, called the accretor, which is very compact: a neutron star or black hole. The infalling matter releases gravitational potential energy, up to several tenths of its rest mass, as X-rays. The lifetime and the mass-transfer rate in an X-ray binary depends on the evolutionary status of the donor star, the mass ratio between the stellar components, and their orbital separation.
 W
W12 Camelopardalis is a binary star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Camelopardalis, located 700 light years away from the Sun as determined from parallax measurements. It forms a double star with 11 Camelopardalis, which is only 3 arcminutes away. The system has the variable star designation BM Camelopardalis; 12 Camelopardalis is the Flamsteed designation. It is just visible to the naked eye, appearing as a dim, orange-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 6.08. The system is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −2 km/s.
 W
W36 Persei is a solitary, variable star located 121 light years away from the Sun in the northern constellation of Perseus. It is visible to the naked eye as a dim, yellow-white hued point of light with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 5.32. The star is drifting closer to the Sun with a heliocentric radial velocity of −47.5 km/s, and may come as close as 36.6 light-years in 661,000 years.
 W
WAE Aquarii is a cataclysmic variable binary star of the DQ Herculis type. Based upon parallax measurements, the system is located at a distance of about 280 light-years from the Earth. Because of its unique properties, this system has been subject to a number of scientific studies.
 W
WArp 147 is an interacting pair of ring galaxies. It lies 430 million to 440 million light years away in the constellation Cetus and does not appear to be part of any significant galaxy group. The system was originally discovered in 1893 by Stephane Javelle and is listed in the Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies.
 W
WAZ Cancri (AZ Cnc) is a M-type flare star in the constellation Cancer. It has an apparent visual magnitude of approximately 17.59.
 W
WThe Cygnus Loop is a large supernova remnant (SNR) in the constellation Cygnus, an emission nebula measuring nearly 3° across. Some arcs of the loop, known collectively as the Veil Nebula or Cirrus Nebula, emit in the visible electromagnetic range. Radio, infrared, and X-ray images reveal the complete loop.
 W
WGamma Apodis (γ Aps, γ Apodis) is the Bayer designation for a star in the southern circumpolar constellation of Apus. From parallax measurements, the distance to this star can be estimated as 150 ± 4 light-years (46.0 ± 1.2 pc). It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.86. A stellar classification of G9 III identifies it as a giant star in the later stages of its evolution. It is an active X-ray source with a luminosity of 1.607 × 1030 erg s−1, making it one of the 100 strongest stellar X-ray sources within 50 parsecs of the Sun.
 W
WIGR J17091-3624 is a stellar mass black hole 28,000 light-years away. It lies in the constellation Scorpius in the Milky Way galaxy.
 W
WMessier 15 or M15 is a globular cluster in the constellation Pegasus. It was discovered by Jean-Dominique Maraldi in 1746 and included in Charles Messier's catalogue of comet-like objects in 1764. At an estimated 12.0 billion years old, it is one of the oldest known globular clusters.
 W
WMS 0735.6+7421 is a galaxy cluster located in the constellation Camelopardalis, approximately 2.6 billion light-years away. It is notable as the location of one of the largest central galactic black holes in the known universe, which has also apparently produced the most powerful active galactic nucleus eruption discovered until 2020 when evidence for the Ophiuchus Supercluster explosion of about five times the energy of the MS 0735.6+7421 eruption was published.
 W
WNGC 4151 is an intermediate spiral Seyfert galaxy with weak inner ring structure located 15.8 megaparsecs from Earth in the constellation Canes Venatici. The galaxy was first mentioned by William Herschel on March 17, 1787; it was one of the two Seyfert galaxies described in the paper which defined the term. It is one of the nearest galaxies to Earth to contain an actively growing supermassive black hole; it was speculated that the nucleus may host a binary black hole, with about 40 million and about 10 million solar masses respectively, orbiting with a 15.8-year period. This is, however, still a matter of active debate.
 W
WRX J1131-1231 is a distant, supermassive-black-hole-containing quasar located about 6 billion light years from Earth in the constellation Crater.
 W
WSGR 1900+14 is a soft gamma repeater (SGR), located in the constellation of Aquila about 20,000 light-years away. It is assumed to be an example of an intensely magnetic star, known as a magnetar. It is thought to have formed after a fairly recent supernova explosion.
 W
WTau Scorpii, formally known as Paikauhale, is a star in the southern zodiac constellation of Scorpius. The apparent visual magnitude of Tau Scorpii is +2.8, while parallax measurements yield a distance estimate of roughly 470 light-years (150 parsecs) from Earth.
 W
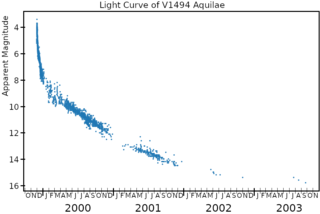
WV1494 Aquilae or Nova Aquilae 1999 b was a nova which occurred during 1999 in the constellation Aquila and reached a brightness of magnitude 3.9 on 2 December 1999. making it easily visible to the naked eye. The nova was discovered with 14×100 binoculars by Alfredo Pereira of Cabo da Roca, Portugal at 18:50 UT on 1 December 1999, when it had a visual magnitude of 6.0.
 W
WX-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to high altitude by balloons, sounding rockets, and satellites. X-ray astronomy is the space science related to a type of space telescope that can see farther than standard light-absorption telescopes, such as the Mauna Kea Observatories, via x-ray radiation.