 W
WIn geometry, the conic constant is a quantity describing conic sections, and is represented by the letter K. The constant is given by
 W
WA degree, usually denoted by °, is a measurement of a plane angle in which one full rotation is 360 degrees.
 W
WIn mathematics, the Dottie number is a constant that is the unique real root of the equation
 W
WThe number e, also known as Euler's number, is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 2.71828, and can be characterized in many ways. It is the base of the natural logarithm. It is the limit of (1 + 1/n)n as n approaches infinity, an expression that arises in the study of compound interest. It can also be calculated as the sum of the infinite series
 W
WThe mathematical constant e can be represented in a variety of ways as a real number. Since e is an irrational number, it cannot be represented as the quotient of two integers, but it can be represented as a continued fraction. Using calculus, e may also be represented as an infinite series, infinite product, or other sort of limit of a sequence.
 W
WThe Euler–Mascheroni constant is a mathematical constant recurring in analysis and number theory, usually denoted by the lowercase Greek letter gamma.
 W
WIn mathematics, specifically bifurcation theory, the Feigenbaum constants are two mathematical constants which both express ratios in a bifurcation diagram for a non-linear map. They are named after the physicist Mitchell J. Feigenbaum.
 W
WIn mathematical analysis, the Foias constant is a real number named after Ciprian Foias.
 W
WIn mathematics, two quantities are in the golden ratio if their ratio is the same as the ratio of their sum to the larger of the two quantities. The figure on the right illustrates the geometric relationship. Expressed algebraically, for quantities a and b with a > b > 0,
 W
WThe imaginary unit or unit imaginary number is a solution to the quadratic equation x2 + 1 = 0. Although there is no real number with this property, i can be used to extend the real numbers to what are called complex numbers, using addition and multiplication. A simple example of the use of i in a complex number is 2 + 3i.
 W
WIn plane geometry, the Kepler–Bouwkamp constant is obtained as a limit of the following sequence. Take a circle of radius 1. Inscribe a regular triangle in this circle. Inscribe a circle in this triangle. Inscribe a square in it. Inscribe a circle, regular pentagon, circle, regular hexagon and so forth. The radius of the limiting circle is called the Kepler–Bouwkamp constant. It is named after Johannes Kepler and Christoffel Bouwkamp, and is the inverse of the polygon circumscribing constant.
 W
WLegendre's constant is a mathematical constant occurring in a formula conjectured by Adrien-Marie Legendre to capture the asymptotic behavior of the prime-counting function . Its value is now known to be exactly 1.
 W
WIn mathematics, the look-and-say sequence is the sequence of integers beginning as follows:1, 11, 21, 1211, 111221, 312211, 13112221, 1113213211, ....
 W
WThe Madelung constant is used in determining the electrostatic potential of a single ion in a crystal by approximating the ions by point charges. It is named after Erwin Madelung, a German physicist.
 W
WThe Meissel–Mertens constant, also referred to as Mertens constant, Kronecker's constant, Hadamard–de la Vallée-Poussin constant or the prime reciprocal constant, is a mathematical constant in number theory, defined as the limiting difference between the harmonic series summed only over the primes and the natural logarithm of the natural logarithm:
 W
WThe MRB constant, is a mathematical constant, with decimal expansion 0.187859…. The constant is named after its discoverer, Marvin Ray Burns, who published his discovery of the constant in 1999. Burns had initially called the constant "rc" for root constant but, at Simon Plouffe's suggestion, the constant was renamed the 'Marvin Ray Burns's Constant', or "MRB constant".
 W
WIn mathematics, the plastic number ρ is a mathematical constant which is the unique real solution of the cubic equation
 W
WIn mathematics, the Ramanujan–Soldner constant is a mathematical constant defined as the unique positive zero of the logarithmic integral function. It is named after Srinivasa Ramanujan and Johann Georg von Soldner.
 W
WIn mathematics, two quantities are in the silver ratio if the ratio of the smaller of those two quantities to the larger quantity is the same as the ratio of the larger quantity to the sum of the smaller quantity and twice the larger quantity. This defines the silver ratio as an irrational mathematical constant, whose value of one plus the square root of 2 is approximately 2.4142135623. Its name is an allusion to the golden ratio; analogously to the way the golden ratio is the limiting ratio of consecutive Fibonacci numbers, the silver ratio is the limiting ratio of consecutive Pell numbers. The silver ratio is denoted by δS.
 W
WThe square root of 3 is the positive real number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the number 3. It is denoted mathematically as √3. It is more precisely called the principal square root of 3, to distinguish it from the negative number with the same property. The square root of 3 is an irrational number. It is also known as Theodorus' constant, after Theodorus of Cyrene, who proved its irrationality.
 W
WThe square root of 2, or the one-half power of 2, written in mathematics as or , is the positive algebraic number that, when multiplied by itself, equals the number 2. Technically, it must be called the principal square root of 2, to distinguish it from the negative number with the same property.
 W
WIn mathematics, the Stieltjes constants are the numbers that occur in the Laurent series expansion of the Riemann zeta function:
 W
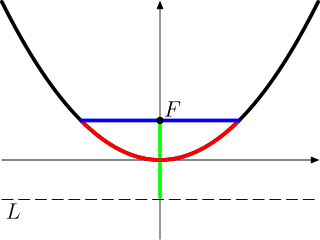
WThe universal parabolic constant is a mathematical constant.