 W
WAuthentication is the act of proving an assertion, such as the identity of a computer system user. In contrast with identification, the act of indicating a person or thing's identity, authentication is the process of verifying that identity. It might involve validating personal identity documents, verifying the authenticity of a website with a digital certificate, determining the age of an artifact by carbon dating, or ensuring that a product or document is not counterfeit.
 W
WBitium was a developer of the cloud service Bitium, which provided single sign-on and identity management for software as a service (SaaS) cloud-based applications before its merger into Google Cloud. Bitium allows end users to access all of their cloud software accounts using a single set of login credentials. The product can integrate with cloud apps using SAML for enhanced security.
 W
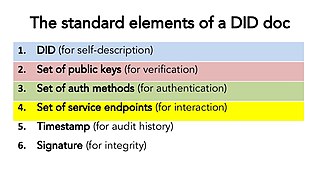
WDecentralized identifiers (DIDs) are a type of identifier that enables a verifiable, decentralized digital identity. They are based on the Self-sovereign identity paradigm. A DID identifies any subject that the controller of the DID decides that it identifies. These identifiers are designed to enable the controller of a DID to prove control over it and to be implemented independently of any centralized registry, identity provider, or certificate authority. DIDs are URLs that associate a DID subject with a DID document allowing trustable interactions associated with that subject. Each DID document can express cryptographic material, verification methods, or service endpoints, which provide a set of mechanisms enabling a DID controller to prove control of the DID. Service endpoints enable trusted interactions associated with the DID subject. A DID document might contain semantics about the subject that it identifies. A DID document might contain the DID subject itself.
 W
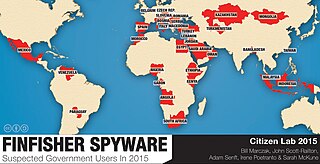
WFinFisher, also known as FinSpy, is surveillance software marketed by Lench IT Solutions plc, which markets the spyware through law enforcement channels.
 W
WFreeOTP is a free and open-source software token that can be used for two-factor authentication. It provides implementations of HOTP and TOTP. Tokens can be added by scanning a QR code or by manually entering in the token configuration. It is maintained by Red Hat under the Apache 2.0 license, and supports Android and iOS.
 W
WGigya, Inc. is a technology company founded in Tel Aviv, Israel and headquartered in Mountain View, California with additional offices in New York, Tel Aviv, London, Paris, Hamburg, and Sydney.
 W
W W
WHTTP+HTML form-based authentication, typically presently colloquially referred to as simply form-based authentication, is a technique whereby a website uses a web form to collect, and subsequently authenticate, credential information from a user agent, typically a web browser.
 W
WIn computer security, logging in is the process by which an individual gains access to a computer system by identifying and authenticating themselves. The user credentials are typically some form of "username" and a matching "password", and these credentials themselves are sometimes referred to as a login. In practice, modern secure systems often require a second factor such as email or SMS confirmation for extra security.
 W
WMicrosoft Fingerprint Reader was a device sold by Microsoft, primarily for homes and small businesses. The underlying software providing the biometrics was developed by Digital Persona.
 W
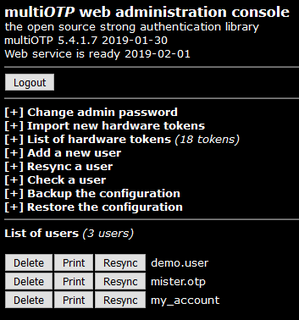
WmultiOTP is an open source PHP class, a command line tool and a web interface that can be used to provide an operating system independent strong authentication system. multiOTP is OATH certified since version 4.1.0 and is developed under the LGPL license. Starting with version 4.3.2.5, multiOTP open source is also available as a virtual appliance - as a standard OVA file, a customized OVA file with open-vm-tools, and also as an Hyper-V downloadable file.
 W
WNemID is a common log-in solution for Danish Internet banks, government websites and some other private companies. NemID is managed by the Nets DanID A/S company and came into use on July 1, 2010. Everyone in Denmark who is over 15 years old and has a CPR-Number is eligible for a NemID that can be used with their bank as well as public institutions. Anyone over 13 years old may use a NemID for internet banking.
 W
WOAuth is an open standard for access delegation, commonly used as a way for Internet users to grant websites or applications access to their information on other websites but without giving them the passwords. This mechanism is used by companies such as Amazon, Google, Facebook, Microsoft and Twitter to permit the users to share information about their accounts with third party applications or websites.
 W
WA one time authorization code (OTAC) is a code used to authenticate a user's identity for only one session. It is not only used in mechanisms to identify a user’s identity in daily life, but also used in the field of computer technology. For example, a desktop client for a web application might use an OTAC to securely authenticate with the web application.
 W
WIn computer security, organization-based access control (OrBAC) is an access control model first presented in 2003. The current approaches of the access control rest on the three entities to control the access the policy specifies that some subject has the permission to realize some action on some object.
 W
WPassWindow is a technique of producing one-time passwords and facilitating transaction verification that is used as an online second-factor authentication method.
 W
WEverykey designs and builds a patented universal smart key that can unlock devices and log into online accounts on those devices. The idea began as an entrepreneurship class project at Case Western Reserve University.
 W
WprivacyIDEA is a Two Factor Authentication System which is multi-tenency- and multi-instance-capable. It is opensource, written in Python and hosted at GitHub.
 W
WA registered user is a user of a website, program, or other system who has previously registered. Registered users normally provide some sort of credentials to the system in order to prove their identity: this is known as logging in. Systems intended for use by the general public often allow any user to register simply by selecting a register or sign up function and providing these credentials for the first time. Registered users may be granted privileges beyond those granted to unregistered users.
 W
WRemote Utilities is a remote desktop software that allows a user to remotely control another computer through a proprietary protocol and see the remote computer's desktop, operate its keyboard and mouse.
 W
WSelf-sovereign identity (SSI) is a concept in the digital movement that only the user should own their identity data fully without intervention from outside administration. With SSI, the individual identity holders can fully create and control their verifiable credentials, without being forced to request permission of an intermediary or centralized authority and gives control over how their personal data is shared and used. The individual has a means of generating and controlling unique identifiers as well as some facility to store identity data.
 W
WShamoon, also known as W32.DistTrack, is a modular computer virus that was discovered in 2012, targeting then-recent 32-bit NT kernel versions of Microsoft Windows. The virus was notable due to the destructive nature of the attack and the cost of recovery. Shamoon can spread from an infected machine to other computers on the network. Once a system is infected, the virus continues to compile a list of files from specific locations on the system, upload them to the attacker, and erase them. Finally the virus overwrites the master boot record of the infected computer, making it unusable.
 W
WA subscriber identity module or subscriber identification module (SIM), widely known as a SIM card, is an integrated circuit that is intended to securely store the international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) number and its related key, which are used to identify and authenticate subscribers on mobile telephony devices. It is also possible to store contact information on many SIM cards. SIM cards are always used on GSM phones; for CDMA phones, they are needed only for LTE-capable handsets. SIM cards can also be used in satellite phones, smart watches, computers, or cameras.
 W
WA subscriber identity module or subscriber identification module (SIM), widely known as a SIM card, is an integrated circuit that is intended to securely store the international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) number and its related key, which are used to identify and authenticate subscribers on mobile telephony devices. It is also possible to store contact information on many SIM cards. SIM cards are always used on GSM phones; for CDMA phones, they are needed only for LTE-capable handsets. SIM cards can also be used in satellite phones, smart watches, computers, or cameras.
 W
WThe YubiKey is a hardware authentication device manufactured by Yubico to protect access to computers, networks, and online services that supports one-time passwords, public-key cryptography, and authentication, and the Universal 2nd Factor (U2F) and FIDO2 protocols developed by the FIDO Alliance. It allows users to securely log into their accounts by emitting one-time passwords or using a FIDO-based public/private key pair generated by the device. YubiKey also allows for storing static passwords for use at sites that do not support one-time passwords. Facebook uses YubiKey for employee credentials. Google supports it for both employees and users. Some password managers support YubiKey. Yubico also manufactures the Security Key, a device similar to the YubiKey, but focused on public-key authentication.