 W
W2052 – A Global Forecast for the Next Forty Years is a 2012 book describing trends in global development. It is written by Jørgen Randers and is a follow-up to The Limits to Growth, which in 1972 was the first worldwide report by the Club of Rome.
 W
WThe added worker effect refers to an increase in the labor supply of married women when their husbands become unemployed. Underlying the theory is the assumption that married women are secondary workers with a less permanent attachment to the labor market than their partners. As statistics show, married women do not always behave as secondary workers; therefore, the effect is not a universal phenomenon.
 W
WThe crude birth rate in a period is the total number of live births per 1,000 population divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registration system for births; population counts from a census, and estimation through specialized demographic techniques. The birth rate is used to calculate population growth. The estimated average population may be taken as the mid-year population.
 W
WBlack billionaires are individuals of African ancestry with a net worth of at least US$1 billion. According to the 2019 Forbes 2019 ranking of the world's billionaires, Nigerian business magnate Aliko Dangote had a net worth of $10.9 billion and was the world's richest black person. Other black billionaires on the 2019 Forbes list included Nigerian businessman Mike Adenuga with $9.1 billion, American investor Robert Smith with $5 billion, American businessman David Steward with $3 billion, American media mogul Oprah Winfrey with $2.5 billion, Zimbabwean businessman Strive Masiyiwa with $2.4 billion, Angolan businesswoman Isabel dos Santos with $2.3 billion, South African gold magnate Patrice Motsepe with $2.3 billion, American sports executive Michael Jordan with $2.1 billion, Jamaican-Canadian businessman Michael Lee-Chin with $1.9 billion, Nigerian businessman Abdul Samad Rabiu with $1.6 billion, American rapper Kanye West with $1.3 billion, Nigerian businesswoman Folorunsho Alakija with $1.1 billion, Mo Ibrahim of the United Kingdom with $1.1 billion, American rapper Jay-Z with $1 billion, and American media mogul Tyler Perry with $1 billion.
 W
WThe Coal Question; An Inquiry Concerning the Progress of the Nation, and the Probable Exhaustion of Our Coal Mines is a book that economist William Stanley Jevons wrote in 1865 to explore the implications of Britain's reliance on coal. Given that coal was a finite, non-renewable energy resource, Jevons raised the question of sustainability. "Are we wise," he asked rhetorically, "in allowing the commerce of this country to rise beyond the point at which we can long maintain it?" His central thesis was that the supremacy of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland over global affairs was transitory, given the finite nature of its primary energy resource. In propounding this thesis, Jevons covered a range of issues central to sustainability, including limits to growth, overpopulation, overshoot, energy return on energy input (EROEI), taxation of energy resources, renewable energy alternatives, and resource peaking—a subject widely discussed today under the rubric of peak oil.
 W
WCrisis in the Population Question was a 1934 book by Alva and Gunnar Myrdal, who discussed the declining birthrate in Sweden and proposed possible solutions. The book was influential in the debate that created the Swedish welfare model.
 W
WDemographic window is defined to be that period of time in a nation's demographic evolution when the proportion of population of working age group is particularly prominent. This occurs when the demographic architecture of a population becomes younger and the percentage of people able to work reaches its height. Typically, the demographic window of opportunity lasts for 30–40 years depending upon the country. Because of the mechanical link between fertility levels and age structures, the timing and duration of this period is closely associated to those of fertility decline: when birth rates fall, the age pyramid first shrinks with gradually lower proportions of young population and the dependency ratio decreases as is happening in various parts of East Asia over several decades. After a few decades, low fertility however causes the population to get older and the growing proportion of elderly people inflates again the dependency ratio as is observed in present-day Europe.
 W
WThe demographic features of the population of Japan include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects regarding the population.
 W
WThe book An Essay on the Principle of Population was first published anonymously in 1798, but the author was soon identified as Thomas Robert Malthus. The book warned of future difficulties, on an interpretation of the population increasing in geometric progression while food production increased in an arithmetic progression, which would leave a difference resulting in the want of food and famine, unless birth rates decreased.
 W
WFemale participation and advancement in majority Muslim countries, or nations in which more than 50% of the population identifies as an adherent of the Islamic faith, have traditionally been areas of controversy. Several Western nations, such as the United States and Western Europe, have criticised majority Muslim nations for the lack of involvement and opportunity for women in the private sector.
 W
WIn economics, the Gini coefficient, sometimes called the Gini index or Gini ratio, is a measure of statistical dispersion intended to represent the income inequality or wealth inequality within a nation or any other group of people. It was developed by the Italian statistician and sociologist Corrado Gini and published in his 1912 paper Variability and Mutability.
 W
WHuman migration involves the movement of people from one place to another with intentions of settling, permanently or temporarily, at a new location. The movement often occurs over long distances and from one country to another, but internal migration is also possible; indeed, this is the dominant form of human migration globally. Migration is often associated with better human capital at both individual and household level, and with better access to migration networks. Age is very also important for both work and non-work migration. People may migrate as individuals, in family units or in large groups. There are four major forms of migration: invasion, conquest, colonization and emigration/immigration.
 W
WStep migration is a migration pattern conceptualized in 1885 by Ernst Georg Ravenstein who observed migration as occurring stage by stage as rural inhabitants move closer to urban areas of growth. It is a migration pattern regarded by some scholars to be a widely popular form of international migration in the twenty-first century globalized world. There is a large breadth of study proving the existence of step migration in many international migration patterns, although there is lack of consensus over its exact specification and measurement. Step migration scholars deem it to be an important international trend that has the power to aid in the design of policy development efforts in both rural and urban areas worldwide.
 W
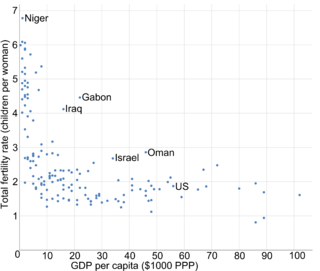
WIncome and fertility is the association between monetary gain on one hand, and the tendency to produce offspring on the other. There is generally an inverse correlation between income and the total fertility rate within and between nations. The higher the degree of education and GDP per capita of a human population, subpopulation or social stratum, the fewer children are born in any developed country. In a 1974 United Nations population conference in Bucharest, Karan Singh, a former minister of population in India, illustrated this trend by stating "Development is the best contraceptive."
 W
WInterprovincial migration in Canada is the movement by people from one Canadian province or territory to another with the intention of settling, permanently or temporarily, in the new province or territory; it is more-or-less stable over time. In fiscal year 2019–20, 374,407 Canadians migrated province, representing 0.988% of the population.
 W
WLadli Laxmi Yojana is a scheme introduced by Government of Madhya Pradesh. It was inaugurated by Chief Minister Shivraj Singh Chouhan on 2nd May 2007, which was followed by expansion to six additional states including Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Delhi, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand and Goa. It came into effect from 7th April, 2007.
 W
WLife expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, its current age, and other demographic factors including gender. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth (LEB), which can be defined in two ways. Cohort LEB is the mean length of life of an actual birth cohort and can be computed only for cohorts born many decades ago so that all their members have died. Period LEB is the mean length of life of a hypothetical cohort assumed to be exposed, from birth through death, to the mortality rates observed at a given year.
 W
WThis is a list of all sovereign states and dependencies by total fertility rate (TFR): the expected number of children born per woman in her child-bearing years.
 W
W"Lost boys" is a term used for young men who have been excommunicated or pressured to leave polygamous Mormon fundamentalist groups such as the Fundamentalist Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints (FLDS). They are alleged to be pressured to leave by adult men to reduce competition for wives within such sects, usually when they are between the ages of 13 and 21.
 W
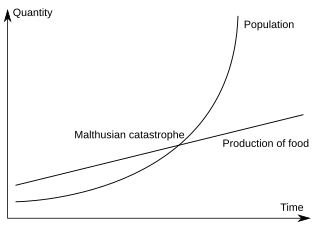
WMalthusianism is the idea that population growth is potentially exponential while the growth of the food supply or other resources is linear, which eventually reduces living standards to the point of triggering a population die off. It derives from the political and economic thought of the Reverend Thomas Robert Malthus, as laid out in his 1798 writings, An Essay on the Principle of Population. Malthus believed there were two types of ever-present "checks" that are continuously at work, limiting population growth based on food supply at any given time:preventive checks, such as moral restraints or legislative action — for example the choice by a private citizen to engage in abstinence and delay marriage until their finances become balanced, or restriction of legal marriage or parenting rights for persons deemed "deficient" or "unfit" by the government.positive checks, such as disease, starvation, and war, which lead to high rates of premature death — resulting in what is termed a Malthusian catastrophe. The adjacent diagram depicts the abstract point at which such an event would occur, in terms of existing population and food supply: when the population reaches or exceeds the capacity of the shared supply, positive checks are forced to occur, restoring balance.
 W
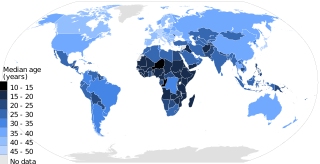
WPopulation ageing is an increasing median age in a population due to declining fertility rates and rising life expectancy. Most countries have rising life expectancy and an ageing population. This is the case for every country in the world except the 18 countries designated as "demographic outliers" by the UN. The aged population is currently at its highest level in human history. The UN predicts the rate of population ageing in the twenty-first century will exceed that of the previous century. The number of people aged 60 years and over has tripled since 1950, reaching 600 million in 2000 and surpassing 700 million in 2006. It is projected that the combined senior and geriatric population will reach 2.1 billion by 2050. Countries vary significantly in terms of the degree and pace of ageing, and the UN expects populations that began ageing later will have less time to adapt to its implications.
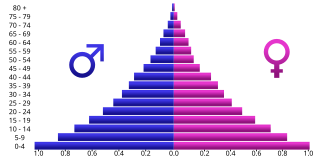 W
WA population pyramid, also called an "age-gender-pyramid", is a graphical illustration that shows the distribution of various age groups in a population, which forms the shape of a pyramid when the population is growing. Males are conventionally shown on the left and females on the right, and they may be measured by raw number or as a percentage of the total population. This tool can be used to visualize the age of a particular population. It is also used in ecology to determine the overall age distribution of a population; an indication of the reproductive capabilities and likelihood of the continuation of a species.
 W
WThe Preston curve is an empirical cross-sectional relationship between life expectancy and real per capita income. It is named after Samuel H. Preston who first described it in 1975. Preston studied the relationship for the 1900s, 1930s and the 1960s and found it held for each of the three decades. More recent work has updated this research.
 W
WThe Responsible Parenthood and Reproductive Health Act of 2012, also known as the Reproductive Health Law or RH Law, and officially designated as Republic Act No. 10354, is a law in the Philippines, which guarantees universal access to methods on contraception, fertility control, sexual education, and maternal care.
 W
WIn the economics of demography, the term spending wave refers to the economic effect of departure of children from the home. When a society experiences a high level of such family change then an economic decline follows from reduced spending overall.