 W
WCorona Borealis is a small constellation in the Northern Celestial Hemisphere. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Its brightest stars form a semicircular arc. Its Latin name, inspired by its shape, means "northern crown". In classical mythology Corona Borealis generally represented the crown given by the god Dionysus to the Cretan princess Ariadne and set by him in the heavens. Other cultures likened the pattern to a circle of elders, an eagle's nest, a bear's den, or even a smokehole. Ptolemy also listed a southern counterpart, Corona Australis, with a similar pattern.
 W
WAbell 2065 is a highly concentrated galaxy cluster in the constellation of Corona Borealis containing over 400 member galaxies, the brightest of which are 16th magnitude. The cluster is more than one billion light-years from Earth. On a larger scale still, Abell 2065, along with Abell 2061, Abell 2067, Abell 2079, Abell 2089, and Abell 2092, make up the Corona Borealis Supercluster.
 W
WAbell 2142, or A2142, is a huge, X-ray luminous galaxy cluster in the constellation Corona Borealis. It is the result of a still ongoing merger between two galaxy clusters. The combined cluster is six million light years across, contains hundreds of galaxies and enough gas to make a thousand more. It is "one of the most massive objects in the universe."
 W
WAlpha Coronae Borealis, officially named Alphecca, is an eclipsing binary star in the constellation of Corona Borealis. It is located about 75 light years from the Sun and contains two main sequence stars, one class A and one class G.
 W
WBeta Coronae Borealis is a binary star in the constellation of Corona Borealis. It appears to the naked eye to be a single star and is the second-brightest star in its constellation with an apparent visual magnitude varying between 3.65 and 3.72. Based on parallax measurements taken during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 112 light-years from the Sun.
 W
WThe Corona Borealis Supercluster is a supercluster located in the constellation Corona Borealis and the most prominent example of its kind in the Northern Celestial Hemisphere. Dense and compact compared with other superclusters, its mass has been calculated to lie somewhere between 0.6 and 12 × 1016 solar masses (M⊙). It contains the galaxy clusters Abell 2056, Abell 2061, Abell 2065 (the most massive galaxy cluster within the supercluster), Abell 2067, Abell 2079, Abell 2089, and Abell 2092. Of these, Abell 2056, 2061, 2065, 2067 and A2089 are gravitationally bound and in the process of collapsing to form a massive cluster. This entity has an estimated mass of around 1 × 1016 M⊙. If there is inter-cluster mass present, then Abell 2092 may also be involved. It has been estimated to be 100 megaparsecs (330 million light-years) wide and 40 megaparsecs (130 million light years) deep. It has a redshift of 0.07, which is equivalent to a distance of around 265.5 megaparsecs (964 million light-years).
 W
WEpsilon Coronae Borealis, Latinized from ε Coronae Borealis, is a multiple star system in the constellation Corona Borealis located around 230 light-years from the Solar System. It shines with a combined apparent magnitude of 4.13, meaning it is visible to the unaided eye in all night skies except those brightly lit in inner city locations. It is an orange giant around 1.7 times as massive as the Sun of spectral type K2III, which has exhausted its core fuel supply of hydrogen and swollen to 21 times the Sun's diameter and 151 times its luminosity. That is, Epsilon Coronae Borealis's diameter is about one-quarter of Mercury's orbit. Its surface temperature has been calculated to be 4365 ± 9 K, or 4406 ± 15 K. It is thought to be around 1.74 billion years old.
 W
WEta Coronae Borealis is a stellar system that lies approximately 58 light-years away. The primary component is a mid-wide binary, while a brown dwarf component is located at a wide separation.
 W
WFSC15307+3253 is an ultraluminous infrared galaxy (ULIRG), with a luminosity between 8 and 1000 µm of approximately 2×1013 L⊙, possibly the highest currently known. The "FSC" refers to Faint Source Catalogue, one of the source catalogs produced by the IRAS infrared survey mission. The emission is believed due to some combination of starburst activity and accretion onto a super-massive black hole, producing primary radiation at shorter wavelengths which is mostly blocked by obscuring dust, which is in turn heated and re-radiates in the infrared. The redshift of the source is z = 0.93, indicating a distance of the order of 7 billion light years.
 W
WHercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall or the Great Wall is the largest known structure in the observable universe, measuring approximately 10 billion light years in length. This massive superstructure is a region of the sky seen in the data set mapping of gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) that has been found to have an unusually higher concentration of similarly distanced GRBs than the expected average distribution. It was discovered in early November 2013 by a team of American and Hungarian astronomers led by István Horváth, Jon Hakkila and Zsolt Bagoly while analyzing data from the Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission, together with other data from ground-based telescopes. It is the largest known formation in the universe, exceeding the size of the prior Huge-LQG by about two times.
 W
WKappa Coronae Borealis, Latinized from κ Coronae Borealis, is a star approximately 98 light years away in the constellation of Corona Borealis. The apparent magnitude is +4.82 and the absolute magnitude is +2.35. It is an orange K-type subgiant star of spectral type K1IV, meaning it has nearly completely exhausted its hydrogen supply in its core. It is 1.32 times as massive as the Sun yet has brightened to 11.6 times its luminosity. Around 2.5 billion years old, it was formerly an A-type main sequence star.
 W
WLambda Coronae Borealis, Latinised from λ Coronae Borealis, is a star located in the constellation Corona Borealis, at a distance of 41.6 parsecs (136 ly). It is also known as HR 5936, and HD 142908.
 W
WNGC 6085 is a spiral galaxy in the constellation of Corona Borealis. It is classified as a LINER galaxy and is a member of Abell 2162.
 W
WNGC 6086 is an elliptical galaxy in the constellation of Corona Borealis. It has an apparent magnitude of 12.7. A Type-cD galaxy, it is the brightest cluster galaxy in the cluster Abell 2162. In 2010, a supermassive black hole was discovered in NGC 6086.
 W
WNGC 6104 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Corona Borealis. It is designated as S(R)Pec in the galaxy morphological classification scheme, though it is clearly a barred spiral, and was discovered by William Herschel on 16 May 1787. The galaxy is approximately 388 million light-years away.
 W
WNGC 6120 is a spiral galaxy located probably 135 million light years away from Earth. It is visible at coordinates of right ascension 16h 19m 48.1s and the declination of +37° 46′ 28″, in the constellation Corona Borealis.
 W
WNu1 Coronae Borealis is a solitary, red-hued star located in the northern constellation of Corona Borealis. It is faintly visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 5.20. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 5.0 mas, it is located roughly 650 light years from the Sun. At that distance, the visual magnitude is diminished by an extinction of 0.1 due to interstellar dust. This object is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −13 km/s.
 W
WNu2 Coronae Borealis is a solitary, orange-hued star located in the northern constellation of Corona Borealis. It is faintly visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of +5.4. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 5.49 mas, it is located roughly 590 light years from the Sun. At that distance, the visual magnitude is diminished by an extinction of 0.1 due to interstellar dust.
 W
WOmicron Coronae Borealis, Latinized from o Coronae Borealis, is a star in the northern constellation of Corona Borealis. It is a faint star but visible to the naked eye on a dark night with an apparent visual magnitude of +5.53. The annual parallax shift of the star as seen from Earth is 12.08 mas, which provides a distance estimate of around 270 light years. It is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −54 km/s.
 W
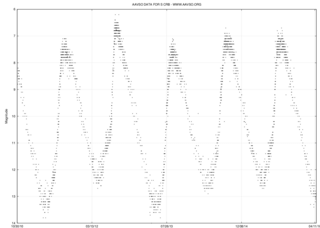
WR Coronae Borealis is a low-mass yellow supergiant star in the constellation of Corona Borealis. It is the prototype of the R Cor Bor class of variable stars, which fade by several magnitudes at irregular intervals. R Coronae Borealis itself normally shines at approximately magnitude 6, just about visible to the naked eye, but at intervals of several months to many years fades to as faint as 15th magnitude. Over successive months it then gradually returns to its normal brightness, giving it the nickname "reverse nova", after the more common type of star which rapidly increases in brightness before fading.
 W
WRho Coronae Borealis is a yellow dwarf star approximately 57 light-years away in the constellation of Corona Borealis. The star is thought to be similar to the Sun with nearly the same mass, radius, and luminosity. It is orbited by two known exoplanets.
 W
WS Coronae Borealis is a Mira variable star in the constellation Corona Borealis. Its apparent magnitude varies between 5.8 and 14.1, with a period of 360 days—just under a year. Within the constellation, it lies to the west of Theta Coronae Borealis, and around 1 degree southeast of the eclipsing binary star U Coronae Borealis.
 W
WV Coronae Borealis is a Mira-type long period variable star and carbon star in the constellation Corona Borealis. Its apparent magnitude varies between 6.9 and 12.6 over a period of 357 days
 W
WXO-1 is a magnitude 11 G-type main-sequence star located approximately 536 light-years away in the constellation Corona Borealis. XO-1 has a mass and radius similar to the Sun. In 2006 the extrasolar planet XO-1b was discovered orbiting XO-1 by the transit method using the XO Telescope.
 W
WXO-1b is an extrasolar planet approximately 536 light-years away.
 W
Wζ Coronae Borealis, Latinised as Zeta Coronae Borealis, is the Bayer designation of a double star in the constellation Corona Borealis. The two components are separated by six arc-seconds and share the same Hipparcos catalogue number and Flamsteed designation. Each of the two is also a spectroscopic multiple system, with a total of five stars in the group.