 W
WEnterprise modelling is the abstract representation, description and definition of the structure, processes, information and resources of an identifiable business, government body, or other large organization.
 W
WThe Application Portability Profile (APP) is a 1990s framework for Open-System Environment designed by the NIST for use by the U.S. Government. It contains a selected suite of specifications that defines the interfaces, services, protocols, and data formats for a particular class or domain of applications.
 W
WArchiMate is an open and independent enterprise architecture modeling language to support the description, analysis and visualization of architecture within and across business domains in an unambiguous way.
 W
WThe ARIS concept by August-Wilhelm Scheer aims to ensure that an enterprise information system can completely meet its requirements.
 W
WBehavior trees are a formal, graphical modelling language used primarily in systems and software engineering. Behavior trees employ a well-defined notation to unambiguously represent the hundreds or even thousands of natural language requirements that are typically used to express the stakeholder needs for a large-scale software-integrated system.
 W
WBiZZdesign Enterprise Studio, formerly BiZZdesign Architect, is a visual modeling and design tool for Enterprise Architecture, that supports the application of ArchiMate and TOGAF, as well other enterprise architecture frameworks.
 W
WBusiness engineering (BE) is the development and implementation of business solutions, from business model to business processes and organizational structure to information systems and information technology (cf.).
 W
WBusiness Model Canvas is a strategic management and lean startup template for developing new or documenting existing business models. It is a visual chart with elements describing a firm's or product's value proposition, infrastructure, customers, and finances. It assists firms in aligning their activities by illustrating potential trade-offs.
 W
WThe Business Motivation Model (BMM) in enterprise architecture provides a scheme and structure for developing, communicating, and managing business plans in an organized manner. Specifically, the Business Motivation Model does all of the following:identifies factors that motivate the establishing of business plans; identifies and defines the elements of business plans; and indicates how all these factors and elements inter-relate.
 W
WA non-biological entity with a cellular organizational structure is set up in such a way that it mimics how natural systems within biology work, with individual 'cells' or 'nodes' working somewhat independently to establish goals and tasks, administer those things, and troubleshoot difficulties. These cells exist in a broader network in which they frequently communicate with each other, exchanging information, in a more or less even organizational playing field. Numerous examples have existed both in economic terms as well as for groups working towards other pursuits. This structure, as applied in areas such as business management, exists in direct contrast to traditional hierarchical leadership that is seen in institutions such as United States federal government agencies, where one type of supervisor gives specific orders to another supervisor and so on down the line.
 W
WCIMOSA, standing for "Computer Integrated Manufacturing Open System Architecture", is an enterprise modeling framework, which aims to support the enterprise integration of machines, computers and people. The framework is based on the system life cycle concept, and offers a modelling language, methodology and supporting technology to support these goals.
 W
WSparx Systems Enterprise Architect is a visual modeling and design tool based on the OMG UML. The platform supports: the design and construction of software systems; modeling business processes; and modeling industry based domains. It is used by businesses and organizations to not only model the architecture of their systems, but to process the implementation of these models across the full application development life-cycle.
 W
WEnterprise integration is a technical field of enterprise architecture, which is focused on the study of topics such as system interconnection, electronic data interchange, product data exchange and distributed computing environments.
 W
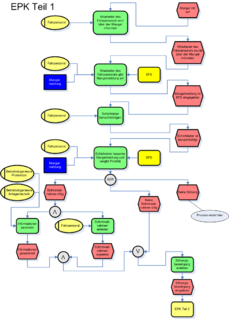
WAn event-driven process chain (EPC) is a type of flow chart for business process modeling. EPC can be used to configure enterprise resource planning execution, and for business process improvement. It can be used to control an autonomous workflow instance in work sharing.
 W
WExtended Enterprise Modeling Language (EEML) in software engineering is a modelling language used for Enterprise modelling across a number of layers.
 W
WGeneralised Enterprise Reference Architecture and Methodology (GERAM) is a generalised enterprise architecture framework for enterprise integration and business process engineering. It identifies the set of components recommended for use in enterprise engineering.
 W
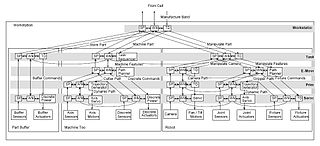
WIDEF0, a compound acronym, is a function modeling methodology for describing manufacturing functions, which offers a functional modeling language for the analysis, development, reengineering, and integration of information systems; business processes; or software engineering analysis.
 W
WIDEF3 or Integrated DEFinition for Process Description Capture Method is a business process modelling method complementary to IDEF0. The IDEF3 method is a scenario-driven process flow description capture method intended to capture the knowledge about how a particular system works.
 W
WIntegrated enterprise modeling (IEM) is an enterprise modeling method used for the admission and for the reengineering of processes both in producing enterprises and in the public area and service providers. In integrated enterprise modeling different aspects as functions and data become described in one model. Furthermore, the method supports analyses of business processes independently of the available organizational structure.
 W
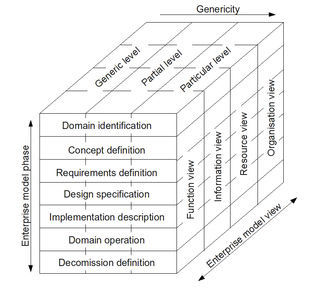
WISO 19439:2006 Enterprise integration—Framework for enterprise modelling, is an international standard for enterprise modelling and enterprise integration developed by the International Organization for Standardization, based on CIMOSA and GERAM.
 W
WNovay, formally known as the Telematica Instituut was a Dutch research institute in the field of information technology, founded in 1997, known for its development of ArchiMate. In 2009 the Telematica Instituut was reorganized and operated under the new name Novay. It filed for bankruptcy April 3, 2014, and is dissolved.
 W
WOpen-system environment (OSE) reference model (RM) or OSE reference model (OSE/RM) is a 1990 reference model for enterprise architecture. It provides a framework for describing open system concepts and defining a lexicon of terms, that can be agreed upon generally by all interested parties.
 W
WOrganizational architecture has two very different meanings. In one sense it literally refers to the organization's built environment and in another sense it refers to architecture metaphorically, as a structure which fleshes out the organizations. The various features of a business's organizational architecture has to be internally consistent in strategy, architecture and competitive environment.Organizational architecture or organizational space: the influence of the spatial environment on humans in and around organizations. Organizational architecture or organization design: the creation of roles, processes, and formal reporting relationships in an organization.
 W
WReal-time Control System (RCS) is a reference model architecture, suitable for many software-intensive, real-time computing control problem domains. It defines the types of functions needed in a real-time intelligent control system, and how these functions relate to each other.
 W
WSystems modeling or system modeling is the interdisciplinary study of the use of models to conceptualize and construct systems in business and IT development.
 W
WThe TOVE project is a project to develop an ontological framework for enterprise integration (EI) based on and suited for enterprise modeling. In the beginning of the 1990s it was initiated by Mark S. Fox and others at the University of Toronto.