 W
WThe 2045 Initiative is a nonprofit organization that develops a network and community of researchers in the field of life extension, focusing on combining brain emulation and robotics to create forms of cyborgs. It was founded by Russian entrepreneur Dmitry Itskov in February 2011 with the participation of Russian specialists in the field of neural interfaces, robotics, artificial organs and systems. Philippe van Nedervelde serves as the Director of International Development
 W
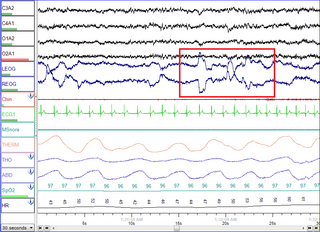
WAmplitude integrated electroencephalography (aEEG) or cerebral function monitoring (CFM) is a technique for monitoring brain function in intensive care settings over longer periods of time than the traditional electroencephalogram (EEG), typically hours to days. By placing electrodes on the scalp of the patient, a trace of electrical activity is produced which is then displayed on a semilogarithmic graph of peak-to-peak amplitude over time; amplitude is logarithmic and time is linear. In this way, trends in electrical activity in the cerebral cortex can be interpreted to inform on events such as seizures or suppressed brain activity. aEEG is useful especially in neonatology where it can be used to aid in diagnosis of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), and to monitor and diagnose seizure activity.
 W
WBrainsWay is an Israeli company with international operations that is engaged in the development of a medical device that uses H-coil for deep transcranial magnetic stimulation as a noninvasive treatment for depression. The company was founded in 2003 and has offices in the US and Jerusalem, Israel.
 W
WA cyborg, a portmanteau of "cybernetic organism", is a being with both organic and biomechatronic body parts. The term was coined in 1960 by Manfred Clynes and Nathan S. Kline.
 W
WRyan C.N. D'Arcy is a Canadian neuroscientist, researcher, innovator and entrepreneur. D'Arcy co-founded HealthTech Connex Inc. and serves as President and Chief Scientific Officer. HealthTech Connex translates neuroscience advances into health technology breakthroughs. D'Arcy is most known for coining the term "brain vital signs" and for leading the research and development of the brain vital signs framework.
 W
WDeep brain stimulation (DBS) is a neurosurgical procedure involving the placement of a medical device called a neurostimulator, which sends electrical impulses, through implanted electrodes, to specific targets in the brain for the treatment of movement disorders, including Parkinson's disease, essential tremor, and dystonia. While its underlying principles and mechanisms are not fully understood, DBS directly changes brain activity in a controlled manner.
 W
WEar-EEG is a method for measuring dynamics of brain activity through the minute voltage changes observable on the skin, typically by placing electrodes on the scalp. In ear-EEG, the electrodes are exclusively placed in or around the outer ear, resulting in both a much greater invisibility and wearer mobility compared to full scalp electroencephalography (EEG), but also significantly reduced signal amplitude, as well as reduction in the number of brain regions in which activity can be measured. It may broadly be partitioned into two groups: those using electrode positions exclusively within the concha and ear canal, and those also placing electrodes close to the ear, usually hidden behind the ear lobe. Generally speaking, the first type will be the most invisible, but also offer the most challenging (noisy) signal. Ear-EEG is a good candidate for inclusion in a hearable device, however, due to the high complexity of ear-EEG sensors, this has not yet been done.
 W
WElectroconvulsive therapy (ECT), formerly known as electroshock therapy, is a psychiatric treatment in which seizures in the brain are electrically induced in patients to provide relief from mental disorders. Typically, 70 to 120 volts are applied externally to the patient's head resulting in approximately 800 milliamperes of direct current passed through the brain, for 100 milliseconds to 6 seconds duration, either from temple to temple or from front to back of one side of the head.
 W
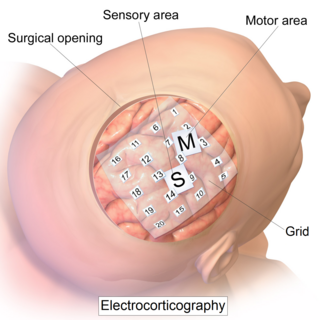
WElectrocorticography (ECoG), or intracranial electroencephalography (iEEG), is a type of electrophysiological monitoring that uses electrodes placed directly on the exposed surface of the brain to record electrical activity from the cerebral cortex. In contrast, conventional electroencephalography (EEG) electrodes monitor this activity from outside the skull. ECoG may be performed either in the operating room during surgery or outside of surgery. Because a craniotomy is required to implant the electrode grid, ECoG is an invasive procedure.
 W
WElectroencephalography (EEG) is an electrophysiological monitoring method to record electrical activity of the brain. It is typically noninvasive, with the electrodes placed along the scalp, although invasive electrodes are sometimes used, as in electrocorticography, sometimes called intracranial EEG.
 W
WElectromyography (EMG) is an electrodiagnostic medicine technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyograph detects the electric potential generated by muscle cells when these cells are electrically or neurologically activated. The signals can be analyzed to detect medical abnormalities, activation level, or recruitment order, or to analyze the biomechanics of human or animal movement. In Computer Science, EMG is also used as middleware in gesture recognition towards allowing the input of physical action to a computer as a form of human-computer interaction.
 W
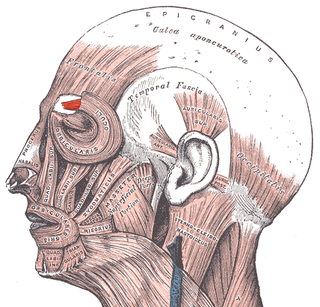
WElectrooculography (EOG) is a technique for measuring the corneo-retinal standing potential that exists between the front and the back of the human eye. The resulting signal is called the electrooculogram. Primary applications are in ophthalmological diagnosis and in recording eye movements. Unlike the electroretinogram, the EOG does not measure response to individual visual stimuli.
 W
WFacial electromyography (fEMG) refers to an electromyography (EMG) technique that measures muscle activity by detecting and amplifying the tiny electrical impulses that are generated by muscle fibers when they contract.
 W
WMagnetoencephalography (MEG) is a functional neuroimaging technique for mapping brain activity by recording magnetic fields produced by electrical currents occurring naturally in the brain, using very sensitive magnetometers. Arrays of SQUIDs are currently the most common magnetometer, while the SERF magnetometer is being investigated for future machines. Applications of MEG include basic research into perceptual and cognitive brain processes, localizing regions affected by pathology before surgical removal, determining the function of various parts of the brain, and neurofeedback. This can be applied in a clinical setting to find locations of abnormalities as well as in an experimental setting to simply measure brain activity.
 W
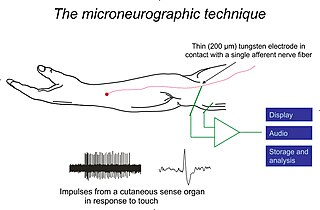
WMicroneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.
 W
WMind uploading, also known as whole brain emulation (WBE), is the hypothetical futuristic process of scanning a physical structure of the brain accurately enough to create an emulation of the mental state and copying it to a computer in a digital form. The computer would then run a simulation of the brain's information processing, such that it would respond in essentially the same way as the original brain and experience having a sentient conscious mind.
 W
WNeurofeedback (NFB), also called neurotherapy or neurobiofeedback, is a type of biofeedback that uses real-time displays of brain activity—most commonly electroencephalography (EEG)—in an attempt to teach self-regulation of brain function. Typically, sensors are placed on the scalp to measure electrical activity, with measurements displayed using video displays or sound. There is significant evidence supporting neurotherapy for generalized treatment of mental disorders and has been practiced over four decades, although never gaining prominence in the medical mainstream. NFB is relatively non-invasive and is administered as a long term treatment option, typically taking a month to complete. It is estimated over 15,000 clinicians, world-wide are using this technology.
 W
WOpenViBE is a software platform dedicated to designing, testing and using brain-computer interfaces. The package includes a Designer tool to create and run custom applications, along with several pre-configured and demo programs which are ready for use.
 W
WPsychoPy is an open source software package written in the Python programming language primarily for use in neuroscience and experimental psychology research. Developed initially as a Python library and then as an application with a graphical interface, it now also supports JavaScript outputs to run studies online and on mobile devices. Unlike most packages, it provides users with a choice of interface - they can generate experiments by writing Python scripts, use a graphical interface that will generate a script for them, or combine both methods. Its platform independence is achieved through use of the wxPython widget library for the application and OpenGL for graphics calls. It is also capable of generating and delivering auditory stimuli.
 W
WPulsed electromagnetic field therapy, also known as low field magnetic stimulation (LFMS) uses electromagnetic fields in an attempt to heal non-union fractures and depression. By 2007 the FDA had cleared several such stimulation devices.
 W
WA Spinal Cord Stimulator (SCS) or Dorsal Column Stimulator (DCS) is a type of implantable neuromodulation device that is used to send electrical signals to select areas of the spinal cord for the treatment of certain pain conditions. SCS is a consideration for people who have a pain condition that has not responded to more conservative therapy.
 W
WSyNAPSE is a DARPA program that aims to develop electronic neuromorphic machine technology, an attempt to build a new kind of cognitive computer with form, function, and architecture similar to the mammalian brain. Such artificial brains would be used in robots whose intelligence would scale with the size of the neural system in terms of total number of neurons and synapses and their connectivity.
 W
WTranscranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is a form of neuromodulation that uses constant, low direct current delivered via electrodes on the head. It was originally developed to help patients with brain injuries or psychiatric conditions like major depressive disorder. It can be contrasted with cranial electrotherapy stimulation, which generally uses alternating current the same way.
 W
WTranscranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive form of brain stimulation in which a changing magnetic field is used to cause electric current at a specific area of the brain through electromagnetic induction. An electric pulse generator, or stimulator, is connected to a magnetic coil, which in turn is connected to the scalp. The stimulator generates a changing electric current within the coil which induces a magnetic field; this field then causes a second inductance of inverted electric charge within the brain itself.
 W
WTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation is the use of electric current produced by a device to stimulate the nerves for therapeutic purposes. TENS, by definition, covers the complete range of transcutaneously applied currents used for nerve excitation although the term is often used with a more restrictive intent, namely to describe the kind of pulses produced by portable stimulators used to reduce pain. The unit is usually connected to the skin using two or more electrodes which are typically conductive gel pads. A typical battery-operated TENS unit is able to modulate pulse width, frequency and intensity. Generally TENS is applied at high frequency (>50 Hz) with an intensity below motor contraction or low frequency (<10 Hz) with an intensity that produces motor contraction. While the use of TENS has proved effective in clinical studies, there is controversy over which conditions the device should be used to treat.
 W
WVagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is a medical treatment that involves delivering electrical impulses to the vagus nerve. It is used as an add-on treatment for certain types of intractable epilepsy and treatment-resistant depression. Frequent side effects include coughing and shortness of breath. Serious side effects may include trouble talking and cardiac arrest.