 W
WThe 1982–83 South Pacific cyclone season was one of the most active and longest South Pacific tropical cyclone seasons on record, with 16 tropical cyclones occurring within the South Pacific basin between 160°E and 120°W. During the season tropical cyclones were monitored by the meteorological services of Australia, Fiji, French Polynesia and New Zealand. The United States Armed Forces through the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) and Naval Pacific Meteorology and Oceanography Center (NPMOC), also monitored the basin and issued unofficial warnings for American interests. The first tropical cyclone of the season developed a day before the season officially began on October 30, while the last tropical cyclone of the season dissipated on May 16. Most of the activity during the season occurred within the central and eastern parts of the basin with French Polynesia affected by several systems.
 W
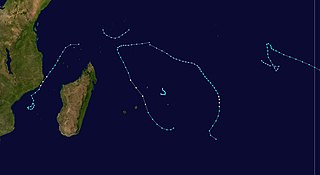
WThe 1982–83 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season was least active cyclone season in the basin since 1961–1962. There were six systems that were named, although three of them – Arilisy, Clera, and Fely – failed to intensify beyond tropical depression status. No storms reached tropical cyclone status, according to the official warning agency for the basin, Météo-France, although the two strongest storms – Bemany and Elinah – peaked just below that intensity. The first named storm, Arilisy, formed on October 27, and dissipated without having affected land. However, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC), which is an unofficial warning center for the basin, briefly tracked a tropical depression in July. The next storm was Bemany, which passed east of Mauritius near peak intensity in early December. Tropical Depression Clera existed briefly in the middle of September, and Tropical Storm Dadafy moved across the eastern portion of the basin in late December.
 W
WThe 1983 Atlantic hurricane season holds a record for the lowest number of confirmed storms in the modern satellite era that began in 1967, with only 4 named storms forming. The season was also the least active season since 1930. The season officially began on June 1, 1983, and lasted until November 30, 1983. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most storms form in the Atlantic basin. The season had very little activity, with only seven tropical depressions, four of which reached tropical storm strength or higher. This led to the lowest Accumulated Cyclone Energy count since 1950, but not since 1900.
 W
WThe 1983 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual tropical cyclone season in the north Atlantic Ocean. It was the least active Atlantic hurricane season in 53 years, during which four storms formed. The season officially began on June 1, 1983 and ended November 30, 1983. These dates, adopted by convention, historically describe the period in each year when most systems form. The first named storm, Hurricane Alicia, formed on August 15. The last storm of the season, Tropical Storm Dean, dissipated on September 30.
 W
WThe 1982–83 Australian region cyclone season was the third-latest starting Australian season on record, only behind 1987 and 2020. Was a below average tropical cyclone season. It officially started on 1 November 1982, and officially ended on 30 April 1983.
 W
WThe 1983 Pacific hurricane season was the longest season ever recorded at that time, which was later surpassed by the 2015 and 2016 seasons. It was a very active Pacific hurricane season. The season started on May 15, 1983 in the eastern Pacific, and on June 1, 1983 in the central Pacific, and lasted until November 30, 1983. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean. During the 1983 season, there were 21 named storms, which was slightly less than the previous season. Furthermore, twelve of those storms became hurricanes. And eight of the storms reached major hurricane status, or Category 3 or higher on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS). The decaying 1982–83 El Niño event likely contributed to this level of activity. That same El Niño influenced a very quiet Atlantic hurricane season.
 W
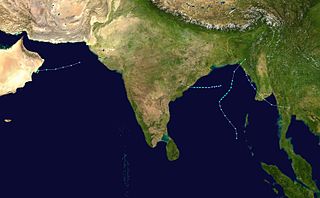
WThe 1983 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was part of the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. The season has no official bounds but cyclones tend to form between April and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) releases unofficial advisories. An average of five tropical cyclones form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November. Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD.
 W
WThe 1983 Pacific typhoon season was the latest start for a Pacific typhoon season on record. It has no official bounds, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. Tropical storms formed in the entire west Pacific basin were assigned a name by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Tropical depressions that enter or form in the Philippine area of responsibility are assigned a name by the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration or PAGASA. This can often result in the same storm having two names.
 W
WThe 1983–84 Australian region cyclone season was the most active season on record. It officially started on 1 November 1983, and officially ended on 30 April 1984.
 W
WThe 1983–84 South Pacific tropical cyclone season was a slightly below-average season.
 W
WThe 1983–84 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season featured above normal activity and several deadly storms. There was steady storm activity from December through April due to favorable conditions, such as warm sea surface temperatures and an active monsoon. The first named storm – Andry – was tied for the strongest with Bakoly, Jaminy, and Kamisy. Cyclone Andry passed near Agaléga island within Mauritius, damaging or destroying every building there and killing one person. It later struck Madagascar, the first of three storms to strike the nation within two months, which collectively caused $25 million in damage and 42 deaths. The third of these storms, Tropical Storm Domoina, caused deadly flooding in southeastern Africa that killed 242 people and caused $199 million in damage. The storm destroyed more than 50 small dams in Madagascar and caused the worst flooding in Swaziland in 20 years. In addition three of the first storms affecting Madagascar, Cyclone Bakoly in December left $21 million in damage on Mauritius.
 W
WTyphoon Abby, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Diding, was the second typhoon to strike Japan within a span of a few days in August 1983. First noted southeast of Guam on July 31, development of this system was initially slow to occur; it was first classified on August 5, and was upgraded into a tropical storm the next day. Intensification was rapid as Abby slowly recurved northward on August 7 and 8. After reaching peak intensity with winds of 140 mph (225 km/h) early on August 9, Abby slowly weakened, though the storm briefly re-intensified on August 11. By August 14, winds had diminished to 100 mph (160 km/h). Abby finally weakened back into a tropical storm on August 17 not long after making landfall in Japan. The following day, Abby completed the transition to an extratropical cyclone after moving through central Japan. However, meteorologists continued monitoring the storm for six more days.
 W
WHurricane Alicia was a small but powerful tropical cyclone that caused significant destruction in the Greater Houston area of Southeast Texas in August 1983. Although Alicia was a relatively small hurricane, its track over the rapidly growing metropolitan area contributed to its $3 billion damage toll, making it the costliest Atlantic hurricane at the time. Alicia spawned from a disturbance that originated from the tail-end of a cold front over the northern Gulf of Mexico in mid-August 1983. The cyclone was named on August 14 when it became a tropical storm, and the combination of weak steering currents and a conducive environment allowed Alicia to quickly intensify as it drifted slowly westward. On August 17, Alicia became a hurricane and continued to strengthen, topping out as a Category 3 major hurricane as it made landfall on the southwestern end of Galveston Island, Texas. Alicia's eye passed just west of Downtown Houston as the system accelerated northwestwards across East Texas; Alicia eventually weakened into a remnant area of low pressure over Oklahoma on August 20 before they were last noted on August 21 over eastern Nebraska.
 W
WHurricane Barry was the fourth tropical depression, second hurricane and second named storm of the inactive 1983 Atlantic hurricane season. Developing out of a tropical wave on August 23, Barry quickly strengthened off the coast of Florida, reaching an initial peak intensity with winds of 60 mph (95 km/h). However, increased wind shear caused the storm to weaken to a tropical depression before making landfall near Melbourne, Florida, the next morning. Traveling almost due west, the storm regenerated and became a hurricane on August 28. The storm made landfall on the northern Mexican coastline later that day at peak intensity. Rapid weakening followed shortly after and the storm dissipated the next day. The storm had only minor effects in the United States but destroyed hundreds of homes and left over 400 homeless in northern Mexico. Despite the damage, there were no reports of fatalities or injuries.
 W
WTropical Storm Dean caused minor flooding along portions of the East Coast of the United States in September 1983. The seventh tropical cyclone and fourth named storm the 1983 Atlantic hurricane season, Dean developed from a frontal low to the northeast of the Bahamas on September 26. Initially subtropical, it gained characteristics of a tropical cyclone while tracking slowly north-northeastward. By September 27, the system was reclassified as Tropical Storm Dean. While tracking northward on September 28, Dean peaked with winds of 65 mph (100 km/h), shortly before curving west-northwestward and slowly leveling-off in intensity. Eventually, Dean made landfall in Virginia on the Delmarva Peninsula on September 29 as a weakening tropical storm. Dean rapidly weakened over land and was no longer classifiable as a tropical cyclone by early on October 1.
 W
WTyphoon Abby, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Diding, was the second typhoon to strike Japan within a span of a few days in August 1983. First noted southeast of Guam on July 31, development of this system was initially slow to occur; it was first classified on August 5, and was upgraded into a tropical storm the next day. Intensification was rapid as Abby slowly recurved northward on August 7 and 8. After reaching peak intensity with winds of 140 mph (225 km/h) early on August 9, Abby slowly weakened, though the storm briefly re-intensified on August 11. By August 14, winds had diminished to 100 mph (160 km/h). Abby finally weakened back into a tropical storm on August 17 not long after making landfall in Japan. The following day, Abby completed the transition to an extratropical cyclone after moving through central Japan. However, meteorologists continued monitoring the storm for six more days.
 W
WTyphoon Ellen, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Herming, was considered the worst typhoon to hit China since 1979. Typhoon Ellen was first noted as a tropical disturbance east of the International Date Line on August 26, 1983, and became a tropical storm soon after crossing the dateline on the morning of August 29. Initially, strong wind shear inhibited development over the next five days, and the cyclone began to track south of west. On September 2, conditions aloft finally improved and the cyclone strengthened into a typhoon on September 4 as it tracked west-northwest. Approaching Luzon late on September 5, Ellen intensified rapidly into a strong typhoon with winds of 200 km/h (125 mph) before interaction with Luzon began to weaken the cyclone. Its final landfall was at Portuguese Macau on the morning of September 9 as a minimal typhoon. The next day, Ellen ceased to exist.
 W
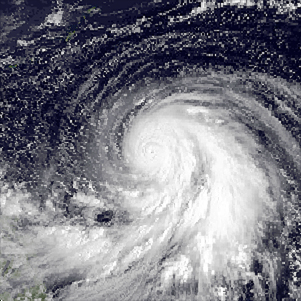
WTyphoon Forrest, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Ising, was the third-most intense typhoon on record, behind Typhoon Tip of 1979 and Typhoon June of 1975. Forrest was also the fastest-intensifying tropical cyclone on record, with its minimum barometric pressure dropping from 976 millibars to 876 millibars—a drop of 100 millibars—from September 22 to September 23, in less than a day. Forrest affected Japan in September 1983 and formed from a tropical disturbance far from land in the western Pacific Ocean. On September 20, the system was classified as a tropical storm, and thereafter began to intensify. The next day, Forrest reached typhoon status, and the intensification process accelerated. The storm prudently strengthened on September 22, and the following morning, attained peak intensity following a pressure drop of 100 mbar (3.0 inHg) in slightly less than 24 hours. Thereafter, Forrest began to weaken slowly as it moved northwest. Approaching Japan, Super Typhoon Forrest first hit Okinawa on September 27. Nearby, a tornado hit Inza Island, destroying 26 homes and injuring 26 people. Forrest then moved north, impaling the Japanese archipelago before transitioning into an extratropical cyclone on September 28, before eventually dissipating on October 4. The torrential rainfall caused by the typhoon triggered deadly landslides and flooding across Japan. In all, the typhoon killed at least 21 people, left 17 listed as missing, and injured 86. Forrest flooded 46,000 homes in muddy water, over 100 dwellings were destroyed, and 2,560 people were rendered as homeless. Seven flights were called off and 27,000 people were stranded. In addition, 67 bridges and 818 roads were damaged.
 W
WHurricane Gil was the first of several tropical cyclones to affect Hawaii during the 1983 Pacific hurricane season. Gil originated from a tropical depression that developed near Clipperton Island on July 23. Steadily intensifying, it attained tropical storm status six hours later and was upgraded to a hurricane on July 26. After attaining peak intensity on July 27, Gil encountered cooler sea surface temperatures and began to weaken. Moving west-northwest, the weakening system also accelerated and on July 31, was downgraded to a tropical depression. However, Gil began to re-intensify on August 1, becoming a tropical storm again later that day. Initially expected to veer north of Hawaii, it continued west-northwest and began to approach the Hawaiian group on August 3. While passing through the island group, Gil reached its secondary peak intensity. Subsequently, Gil began to weaken once again as it threatened the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands. After passing through the islands, Gil was downgraded to a tropical depression on August 5. Several hours later, the storm dissipated. The remnants of the storm moved into the West Pacific late on August 6 and were last noted the next morning while passing south of Midway Island.
 W
WHurricane Ismael was responsible for significant flooding throughout the Inland Empire of the United States in August 1983. The origins of Hurricane Ismael were from a northward bulge of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) in early August, which resulted in the formation of a tropical depression on August 8. Six hours later, it was upgraded into Tropical storm Ismael. Continuing to intensify, Ismael was upgraded into a hurricane late on August 10 and subsequently developed an eye. After bypassing the Revillagigedo Islands, the storm reached its peak wind speed of 100 mph (160 km/h). Late on August 11, Hurricane Ismael began to weaken as it encountered cooler waters. The following day, Ismael was downgraded into a tropical storm. On August 14, the storm was downgraded into a tropical depression approximately 250 mi (400 km) west of Point Ensenada. After turning north, Ismael dissipated later that day near Guadalupe Island.
Tropical Storm Kim, known in the Philippines as Tropical Depression Rosing, was the only storm in 1983 to move from the Western Pacific basin into the North Indian Ocean basin. Kim originated as a weak tropical disturbance that formed to the northeast of Truk during the second week of October. It drifted westward over the subsequent days, and on October 15, while located over the South China Sea, the disturbance was classified as a tropical depression. Late the following day, the system was briefly upgraded into a tropical storm, but the storm dissipated quickly after making landfall in Vietnam early on October 17. After trekking across Indochina, the remnants of Kim moved into the Andaman Sea and re-developed into a tropical cyclone on October 19. However, Kim dissipated for good the next day while located inland over Burma.
 W
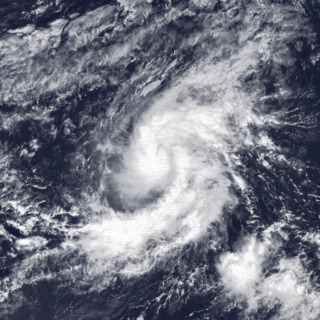
WTropical Storm Octave was considered the worst tropical cyclone in the history of Arizona. The origins of Tropical Storm Octave were from a tropical disturbance that formed south of the Gulf of Tehuantepec on September 23, 1983. Steered by a deep layer high over Mexico, the disturbance moved west for four days before becoming a tropical depression on September 27 off the southwest coast of Mexico. Over an area of warm sea surface temperatures, it was able to quickly strengthen to peak winds of 50 mph (85 km/h), through wind shear prevented much further development. By September 30, Octave was accelerating to the northeast, steadily weakening due to cooler waters. That day it weakened to tropical depression status, and on October 2, Octave dissipated.
 W
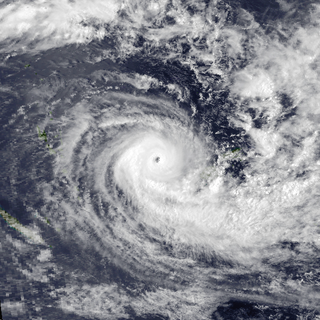
WSevere Tropical Cyclone Oscar was one of the worst tropical cyclones to affect Fiji. The system was first noted as a shallow depression on February 23, while it was located to the north of Suva, Fiji. The system subsequently developed further as it moved westwards and was named as Tropical Cyclone Oscar during the next day. Over the next few days Oscar subsequently intensified as it moved westwards and gradually developed further and equivalent to a Category 3 Severe Tropical Cyclone, on the modern day Australian tropical cyclone intensity scale during February 27. The system subsequently turned and started to move south-eastwards towards Fiji.
 W
WHurricane Tico is one of four major hurricanes to strike Mazatlan. The origins of Hurricane Tico were from a weak tropical disturbance that crossed Costa Rica into the Pacific Ocean on October 7, 1983. Over warm waters, the system was sufficiently organized to be declared Tropical Depression Twenty-One on October 11, about 575 mi (930 km) south of Acapulco. On October 12 it turned sharply northward; the depression was upgraded to Tropical Storm Tico on October 13. Tropical Storm Tico continued to intensify. Two days after becoming a tropical storm, Tico strengthened further to attain hurricane status. Early on October 19, it reached peak winds of 130 mph (215 km/h). It weakened slightly as it approached the coast, and at about 1500 UTC that day Tico made landfall near Mazatlán with winds of 125 mph (205 km/h). The remains were tracked into the Mid-Atlantic States for five more days.
 W
WTyphoon Vera, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Bebeng, brought significant flooding to the Philippines in July 1983. The monsoon trough spawned a tropical depression on July 12 east of the Philippines. Although the depression was initially slow to organize, the system headed west-northwestward, strengthening to a tropical storm the following day and a typhoon on the July 14. Vera moved onshore early the next day as a minimal typhoon in the Philippines before weakening slightly over the islands. However, Vera managed to restrengthen over the South China Sea while accelerating, later attaining winds of 85 mph (135 km/h). After crossing Hainan while still at peak intensity and moving into the northern portion of the Gulf of Tonkin, Vera gradually weakened before moving ashore in northern Vietnam on July 18. By July 19, Vera had dissipated inland.
 W
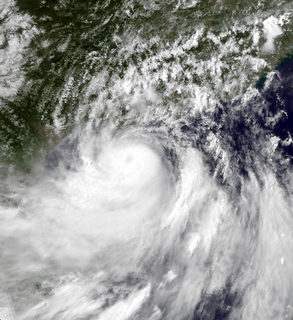
WTyphoon Wayne known in the Philippines as Typhoon Katring was an intense tropical cyclone that brought significant flooding to the Philippines in July 1983. The typhoon originated from an area of disturbed weather that formed far from land towards the end of July. Late on July 22, Wayne developed gale-force winds while moving west. The next day, it was estimated to have become a typhoon, and Wayne subsequently entered a period of rapid deepening. During the morning hours of July 24, the typhoon was estimated to have reached its peak intensity of 205 km/h (125 mph), but soon began to weaken due to interaction with land. By the time it moved ashore in southern China on July 25, Wayne had weakened considerably. After moving inland, Wayne weakened rapidly. The following day, Wayne was no longer a tropical cyclone.