 W
WA unit of time or midst unit is any particular time interval, used as a standard way of measuring or expressing duration. The base unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) and by extension most of the Western world, is the second, defined as about 9 billion oscillations of the caesium atom. The exact modern definition, from the National Institute of Standards and Technology is: "The duration of 9192631770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the caesium-133 atom."
 W
WA year is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked.
 W
WA year is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked.
 W
WA calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A date is the designation of a single, specific day within such a system. A calendar is also a physical record of such a system. A calendar can also mean a list of planned events, such as a court calendar or a partly or fully chronological list of documents, such as a calendar of wills.
 W
WChronology is the science of arranging events in their order of occurrence in time. Consider, for example, the use of a timeline or sequence of events. It is also "the determination of the actual temporal sequence of past events".
 W
WThe Cosmic Calendar is a method to visualize the chronology of the universe, scaling its current age of 13.8 billion years to a single year in order to help intuit it for pedagogical purposes in science education or popular science.
 W
WA day is approximately the period of time during which the Earth completes one rotation around its axis. A solar day is the length of time which elapses between the Sun reaching its highest point in the sky two consecutive times. Days on other planets are defined similarly and vary in length due to differing rotation periods, that of Mars being slightly longer and sometimes called a sol.
 W
WDecimal time is the representation of the time of day using units which are decimally related. This term is often used specifically to refer to the time system used in France for a few years beginning in 1792 during the French Revolution, which divided the day into 10 decimal hours, each decimal hour into 100 decimal minutes and each decimal minute into 100 decimal seconds, as opposed to the more familiar UTC time standard, which divides the day into 24 hours, each hour into 60 minutes and each minute into 60 seconds.
 W
WSome historical calendars had "weeks" consisting of eight days.
 W
WA Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) is an internationally agreed upon reference point on a stratigraphic section which defines the lower boundary of a stage on the geologic time scale. The effort to define GSSPs is conducted by the International Commission on Stratigraphy, a part of the International Union of Geological Sciences. Most, but not all, GSSPs are based on paleontological changes. Hence GSSPs are usually described in terms of transitions between different faunal stages, though far more faunal stages have been described than GSSPs. The GSSP definition effort commenced in 1977. As of 2020, 74 of the 104 stages that need a GSSP have a ratified GSSP.
 W
WAn hour is a unit of time conventionally reckoned as 1⁄24 of a day and scientifically reckoned as 3,599–3,601 seconds, depending on conditions. There are 60 minutes in an hour, and 24 hours in a day.
 W
WIn lunar calendars, a lunar month is the time between two successive syzygies. The precise definition varies, especially for the beginning of the month.
 W
WA moment (momentum) was a medieval unit of time. The movement of a shadow on a sundial covered 40 moments in a solar hour, a twelfth of the period between sunrise and sunset. The length of a solar hour depended on the length of the day, which, in turn, varied with the season. Although the length of a moment in modern seconds was therefore not fixed, on average, a moment corresponded to 90 seconds. A solar day can be divided into 24 hours of either equal or unequal lengths, the former being called natural or equinoctial, and the latter artificial. The hour was divided into four puncta (quarter-hours), ten minuta, or 40 momenta.
 W
WNychthemeron, occasionally nycthemeron or nuchthemeron, is a period of 24 consecutive hours. It is sometimes used, especially in technical literature, to avoid the ambiguity inherent in the term day.
 W
WAn Olympiad is a period of four years associated with the Olympic Games of the Ancient Greeks. Although the Ancient Olympic Games were established during Archaic Greece, it was not until the Hellenistic period, beginning with Ephorus, that the Olympiad was used as a calendar epoch. Converting to the modern BC/AD dating system, the first Olympiad began in the summer of 776 BC and lasted until the summer of 772 BC, when the second Olympiad would begin with the commencement of the next games. Thus, Olympiad N for N less than 195 started in the year BC and ended four years later. For N greater than 194, Olympiad N started in AD and ended four years later.
 W
WIn Sanskrit, Samay (समय) is the, "appointed or proper time, [the] right moment for doing anything." On a general parlance, samay is a unit of time. The samay chakra is the great chariot wheel of time which turns relentlessly forward.
 W
WA season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. In popular culture, seasons are often divided by calendar date irrespective of weather and other deciding factors. On Earth, seasons are the result of Earth's orbit around the Sun and Earth's axial tilt relative to the ecliptic plane. In temperate and polar regions, the seasons are marked by changes in the intensity of sunlight that reaches the Earth's surface, variations of which may cause animals to undergo hibernation or to migrate, and plants to be dormant. Various cultures define the number and nature of seasons based on regional variations, and as such there are a number of both modern and historical cultures whose number of seasons vary.
 W
WThe second is the base unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), commonly understood and historically defined as 1⁄86400 of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds each. Analog clocks and watches often have sixty tick marks on their faces, representing seconds, and a "second hand" to mark the passage of time in seconds. Digital clocks and watches often have a two-digit seconds counter. The second is also part of several other units of measurement like meters per second for velocity, meters per second per second for acceleration, and cycles per second for frequency.
 W
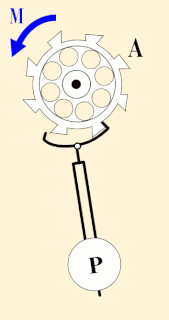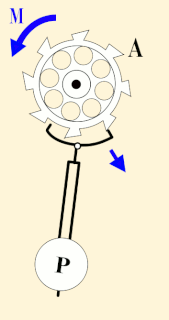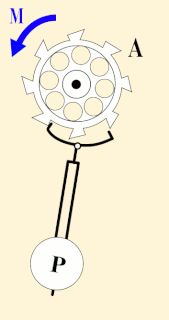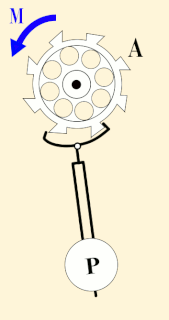
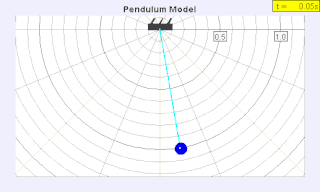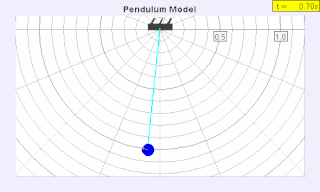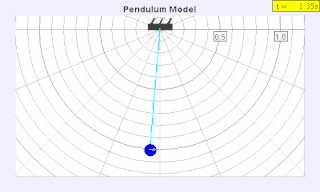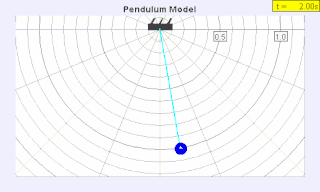
WA seconds pendulum is a pendulum whose period is precisely two seconds; one second for a swing in one direction and one second for the return swing, a frequency of 0.5 Hz.
 W
WSidereal time is a timekeeping system that astronomers use to locate celestial objects. Using sidereal time, it is possible to easily point a telescope to the proper coordinates in the night sky. Briefly, sidereal time is a "time scale that is based on Earth's rate of rotation measured relative to the fixed stars".
 W
WSol is a solar day on Mars; that is, a Mars-day. A sol is the apparent interval between two successive returns of the Sun to the same meridian as seen by an observer on Mars. It is one of several units for timekeeping on Mars.
 W
WThe Sothic cycle or Canicular period is a period of 1,461 Egyptian civil years of 365 days each or 1,460 Julian years averaging 365¼ days each. During a Sothic cycle, the 365-day year loses enough time that the start of its year once again coincides with the heliacal rising of the star Sirius on 19 July in the Julian calendar. It is an important aspect of Egyptology, particularly with regard to reconstructions of the Egyptian calendar and its history. Astronomical records of this displacement may have been responsible for the later establishment of the more accurate Julian and Alexandrian calendars.
 W
WA Svedberg unit is a non-SI metric unit for sedimentation coefficients. The Svedberg unit offers a measure of a particle's size based on its sedimentation rate under acceleration. The Svedberg is a measure of time, defined as exactly 10−13 seconds (100 fs).
 W
WSwatch Internet Time is a decimal time concept introduced in 1998 by the Swatch corporation as part of their marketing campaign for their line of "Beat" watches.
 W
WIn Vedic timekeeping, a tithi is a [duration of two faces of moon that is observed from earth], or the time it takes for the longitudinal angle between the Moon and the Sun to increase by 12°. In other words, a tithi is a time-duration between the consecutive epochs that correspond to when the longitudinal-angle between sun and moon is an integer multiple of 12°. Tithis begin at varying times of day and vary in duration from approximately 19 to approximately 26 hours. Find Out Today's Tithi.
 W
WA year is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked.
 W
WA week is a time unit equal to seven days. It is the standard time period used for cycles of rest days in most parts of the world, mostly alongside—although not strictly part of—the Gregorian calendar.