 W
WAlgae fuel, algal biofuel, or algal oil is an alternative to liquid fossil fuels that uses algae as its source of energy-rich oils. Also, algae fuels are an alternative to commonly known biofuel sources, such as corn and sugarcane. When made from seaweed (macroalgae) it can be known as seaweed fuel or seaweed oil.
 W
WBiogas is the mixture of gases produced by the breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen (anaerobically), primarily consisting of methane and carbon dioxide. Biogas can be produced from raw materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste or food waste. Biogas is a renewable energy source. In India, it is also known as "Gobar Gas".
 W
WBiomass is a modern name for the ancient technology of burning plant or animal material for energy production, or in various industrial processes as raw substance for a range of products. It can be purposely grown energy crops, wood or forest residues, waste from food crops, horticulture, food processing, animal farming, or human waste from sewage plants.
 W
WThe energy tower is a device for producing electrical power. The brainchild of Dr. Phillip Carlson, expanded by Professor Dan Zaslavsky from the Technion. Energy towers spray water on hot air at the top of the tower, making the cooled air fall through the tower and drive a turbine at the tower's bottom.
 W
WForward osmosis (FO) is an osmotic process that, like reverse osmosis (RO), uses a semi-permeable membrane to effect separation of water from dissolved solutes. The driving force for this separation is an osmotic pressure gradient, such that a "draw" solution of high concentration, is used to induce a net flow of water through the membrane into the draw solution, thus effectively separating the feed water from its solutes. In contrast, the reverse osmosis process uses hydraulic pressure as the driving force for separation, which serves to counteract the osmotic pressure gradient that would otherwise favor water flux from the permeate to the feed. Hence significantly more energy is required for reverse osmosis compared to forward osmosis.
 W
WAlternative fuels, known as non-conventional and advanced fuels, are any materials or substances that can be used as fuels, other than conventional fuels like; fossil fuels, as well as nuclear materials such as uranium and thorium, as well as artificial radioisotope fuels that are made in nuclear reactors.
 W
WFusion power is a proposed form of power generation that would generate electricity by using heat from nuclear fusion reactions. In a fusion process, two lighter atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, while releasing energy. Devices designed to harness this energy are known as fusion reactors.
 W
WGeothermal power is power generated by geothermal energy. Technologies in use include dry steam power stations, flash steam power stations and binary cycle power stations. Geothermal electricity generation is currently used in 26 countries, while geothermal heating is in use in 70 countries.
 W
WGeothermal energy is the thermal energy generated and stored in the Earth. Thermal energy is the energy that determines the temperature of matter. The geothermal energy of the Earth's crust originates from the original formation of the planet and from radioactive decay of materials. The adjective geothermal originates from the Greek roots γῆ, meaning Earth, and θερμός, meaning hot.
 W
WHome Power was a bi-monthly American magazine based in Ashland, Oregon. At one time it had a circulation greater than 100,000.
 W
WISFuel Inc. is a United States company involved in research & development of synfuels. In particular, they research the use of coal and biomass to produce a fully synthetic fuel that can pass multiple fuel specifications, or “joint” fuel.
 W
WJoule Unlimited, formerly known as Joule Biotechnologies, was a producer of alternative energy technologies based in Bedford, Massachusetts. The company developed a process to generate hydrocarbon-based fuel by combining non-fresh water, nutrients, cyanobacteria, carbon dioxide, and sunlight. After ten years of operation and building a demonstration plant in New Mexico, the company shut down in August 2017. The company shut down after management was unable to raise money.
 W
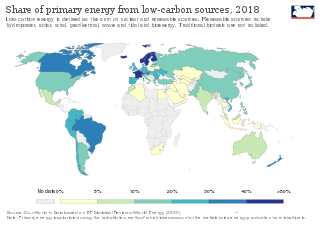
WLow-carbon power comes from processes or technologies that produce power with substantially lower amounts of carbon dioxide emissions than is emitted from conventional fossil fuel power generation. It includes low carbon power generation sources such as wind power, solar power, hydropower and nuclear power. The term largely excludes conventional fossil fuel plant sources, and is only used to describe a particular subset of operating fossil fuel power systems, specifically, those that are successfully coupled with a flue gas carbon capture and storage (CCS) system. Globally, 35% of electricity generation comes from low-carbon sources. As of 2018 the largest low-carbon energy sources globally were hydropower and nuclear power, with the latter providing over 50% of low-carbon power alone in United States and European Union.
 W
WThe State Agency on Alternative and Renewable Energy Sources, SAARES is a governmental agency under the Ministry of Industry and Energy mandated by the Cabinet of Ministers. It serves as the principal regulatory institution in the sphere of alternative and renewable energy in the Republic of Azerbaijan. The State Agency is headed by Akim Badalov.
 W
WOsmotic power, salinity gradient power or blue energy is the energy available from the difference in the salt concentration between seawater and river water. Two practical methods for this are reverse electrodialysis (RED) and pressure retarded osmosis (PRO). Both processes rely on osmosis with membranes. The key waste product is brackish water. This byproduct is the result of natural forces that are being harnessed: the flow of fresh water into seas that are made up of salt water.
 W
WAn energy-plus house produces more energy from renewable energy sources, over the course of a year, than it imports from external sources. This is achieved using a combination of microgeneration technology and low-energy building techniques, such as: passive solar building design, insulation and careful site selection and placement. A reduction of modern conveniences can also contribute to energy savings, however many energy-plus houses are almost indistinguishable from a traditional home, preferring instead to use highly energy-efficient appliances, fixtures, etc., throughout the house.
 W
WPressure retarded osmosis (PRO) is a technique to separate a solvent from a solution that is more concentrated and also pressurized. A semipermeable membrane allows the solvent to pass to the concentrated solution side by osmosis. The technique can be used to generate power from the salinity gradient energy resulting from the difference in the salt concentration between sea and river water. In PRO, the water potential between fresh water and sea water corresponds to a pressure of 26 bars. This pressure is equivalent to a column of water 270 meters high. However, the optimal working pressure is only half of this, 11 to 15 bar.
 W
WThese are modes of energy production, energy storage, or energy conservation, listed alphabetically. Note that not all sources are accepted as legitimate or have been proven to be tappable.
 W
WAlgae fuel, algal biofuel, or algal oil is an alternative to liquid fossil fuels that uses algae as its source of energy-rich oils. Also, algae fuels are an alternative to commonly known biofuel sources, such as corn and sugarcane. When made from seaweed (macroalgae) it can be known as seaweed fuel or seaweed oil.
 W
WSoil salinity is the salt content in the soil; the process of increasing the salt content is known as salinization. Salts occur naturally within soils and water. Salination can be caused by natural processes such as mineral weathering or by the gradual withdrawal of an ocean. It can also come about through artificial processes such as irrigation and road salt.
 W
WSolar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun that is harnessed using a range of ever-evolving technologies such as solar heating, photovoltaics, solar thermal energy, solar architecture, molten salt power plants and artificial photosynthesis.
 W
WSolar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV), indirectly using concentrated solar power, or a combination. Concentrated solar power systems use lenses or mirrors and solar tracking systems to focus a large area of sunlight into a small beam. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovoltaic effect.
 W
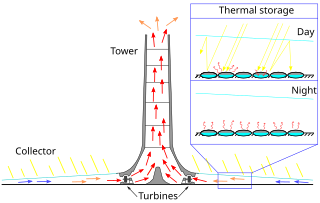
WThe solar updraft tower (SUT) is a design concept for a renewable-energy power plant for generating electricity from low temperature solar heat. Sunshine heats the air beneath a very wide greenhouse-like roofed collector structure surrounding the central base of a very tall chimney tower. The resulting convection causes a hot air updraft in the tower by the chimney effect. This airflow drives wind turbines, placed in the chimney updraft or around the chimney base, to produce electricity.
 W
WSolar water heating (SWH) is heating water by sunlight, using a solar thermal collector. A variety of configurations is available at varying cost to provide solutions in different climates and latitudes. SWHs are widely used for residential and some industrial applications.
 W
WStatkraft osmotic power prototype is the world's first osmotic power plant, based on the energy of osmosis. The power plant is run by Statkraft. The power plant is located at Tofte in Hurum, Norway, with rooms at the factory area at Södra Cell Tofte cellulose factory. The power plant uses the osmotic gradient that occurs when fresh water and salt water meet, separated by a permeable membrane. The salt water pulls fresh water through the membrane and the pressure increases on the salt water side; this pressure increase can be used to produce electrical power with the use of a normal hydroelectric turbine/generator setup.
 W
WThe Tehachapi Energy Storage Project (TSP) is a lithium-ion battery-based grid energy storage system at the Monolith Substation of Southern California Edison in Tehachapi, California. At the time of commissioning in 2014, it was the largest lithium-ion battery system operating in North America and one of the largest in the world. The TSP system can supply 32 megawatt-hours of energy, at a maximum rate of 8 megawatts. This is sufficient to power between 1,600 and 2,400 homes for four hours. TSP is considered to be a modern-day energy storage pioneer with significant accomplishments that have proven the viability of utility-scale energy storage using lithium-ion technology. While originally envisioned as a research and development project, TSP continues operation today as a distribution-level resource for Southern California Edison.
 W
WVehicle-to-grid (V2G) describes a system in which plug-in electric vehicles, such as battery electric vehicles (BEV), plug-in hybrids (PHEV) or hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEV), communicate with the power grid to sell demand response services by either returning electricity to the grid or by throttling their charging rate. V2G storage capabilities can enable EVs to store and discharge electricity generated from renewable energy sources such as solar and wind, with output that fluctuates depending on weather and time of day.
 W
WThe concept of a vortex engine or atmospheric vortex engine (AVE), independently proposed by Norman Louat and Louis M. Michaud, aims to replace large physical chimneys with a vortex of air created by a shorter, less-expensive structure. The AVE induces ground-level vorticity, resulting in a vortex similar to a naturally occurring landspout or waterspout.