 W
WA business model describes the rationale of how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value, in economic, social, cultural or other contexts. The process of business model construction and modification is also called business model innovation and forms a part of business strategy.
 W
WAdvertising is a marketing communication that employs an openly sponsored, non-personal message to promote or sell a product, service or idea. Sponsors of advertising are typically businesses wishing to promote their products or services. Advertising is differentiated from public relations in that an advertiser pays for and has control over the message. It differs from personal selling in that the message is non-personal, i.e., not directed to a particular individual. Advertising is communicated through various mass media, including traditional media such as newspapers, magazines, television, radio, outdoor advertising or direct mail; and new media such as search results, blogs, social media, websites or text messages. The actual presentation of the message in a medium is referred to as an advertisement, or "ad" or advert for short.
 W
WAirDine was a supper club mobile app based on the sharing economy principles where individuals stand as both supplier and customer, similar to Airbnb in the short time rental market.
 W
WAn auction is usually a process of buying and selling goods or services by offering them up for bid, taking bids, and then selling the item to the highest bidder or buying the item from the lowest bidder. Some exceptions to this definition exist and are described in the section about different types. The branch of economic theory dealing with auction types and participants' behavior in auctions is called auction theory.
 W
WIn the video game industry, a battle pass is a type of monetization approach that provides additional content for a game usually through a tiered system, rewarding the player with in-game items for playing the game and completing specific challenges. Inspired by the season pass ticketing system and originating with Dota 2 in 2013, the battle pass model gained more use as an alternative to subscription fees and loot boxes beginning in the late 2010s. Battle Passes tend to offer free passes, which are available to all users, and a premium pass that require annual or seasonal charges in exchange for enhanced items and cosmetics.
 W
WBlended Value refers to an emerging conceptual framework in which non-profit organizations, businesses, and investments are evaluated based on their ability to generate a blend of financial, social, and environmental value. The term is usually attributed to Jed Emerson, and sometimes used interchangeably with triple bottom line. Blended value propositions are founded on the notion that value cannot be bifurcated, and is inherently made up of more than one measurement of performance. For example, under a blended value proposition, a for-profit business would consider their social and environmental impact on society alongside their financial performance measurement. Within the same context, non-profits would consider their financial efficiency and sustainability in tandem with their social and environmental performance. Blended value suggests the true measure of any organization is in its ability to holistically perform in all 3 areas.
 W
WBricks and clicks, or omnichannel retail strategy, is a jargon term for a business model by which a company integrates both offline (bricks) and online (clicks) presences, sometimes with the third extra flips. Many retailers also offer telephone ordering and mobile phone apps, with most providing telephone sales support. The wide uptake of smartphones made the model even more popular, as customers could browse and order from their smartphone whenever they had spare time. The model has historically also been known by such terms as clicks and bricks, click and mortar, bricks, clicks and flips, and WAMBAM, i.e. "web application meets bricks and mortar".)
 W
WBusiness Model Canvas is a strategic management and lean startup template for developing new or documenting existing business models. It is a visual chart with elements describing a firm's or product's value proposition, infrastructure, customers, and finances. It assists firms in aligning their activities by illustrating potential trade-offs.
 W
WCo-operative economics is a field of economics that incorporates co-operative studies and political economy toward the study and management of co-operatives.
 W
WA co-operative wholesale society, or CWS, is a form of co-operative federation, in this case, the members are usually consumer cooperatives. According to co-operative economist Charles Gide, the aim of a co-operative wholesale society is to arrange “bulk purchases, and, if possible, organise production.” In other words, a co-operative wholesale society is a form of federal co-operative through which consumers co-operatives can collectively purchase goods at wholesale prices, and in some cases collectively own factories or farms.
 W
WA concession or concession agreement is a grant of rights, land or property by a government, local authority, corporation, individual or other legal entity.
 W
WA consumers' co-operative is an enterprise owned by consumers and managed democratically which aims at fulfilling the needs and aspirations of their members. They operate within the market system, independently of the state, as a form of mutual aid, oriented toward service rather than pecuniary profit. Consumers' cooperatives often take the form of retail outlets owned and operated by their consumers, such as food co-ops. However, there are many types of consumers' cooperatives, operating in areas such as health care, insurance, housing, utilities and personal finance.
 W
WA cooperative is "an autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social, and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly-owned enterprise". Cooperatives are democratically owned by their members, with each member having one vote in electing the board of directors. Cooperatives may include:businesses owned and managed by the people who use their services organizations managed by the people who work there multi-stakeholder or hybrid cooperatives that share ownership between different stakeholder groups. For example, care cooperatives where ownership is shared between both care-givers and receivers. Stakeholders might also include non-profits or investors. second- and third-tier cooperatives whose members are other cooperatives platform cooperatives that use a cooperatively owned and governed website, mobile app or a protocol to facilitate the sale of goods and services.
 W
WDisintermediation is the removal of intermediaries in economics from a supply chain, or "cutting out the middlemen" in connection with a transaction or a series of transactions. Instead of going through traditional distribution channels, which had some type of intermediary, companies may now deal with customers directly, for example via the Internet.
 W
WThe razor and blades business model is a business model in which one item is sold at a low price in order to increase sales of a complementary good, such as consumable supplies. For example, inkjet printers require ink cartridges, and game consoles require accessories and software. It is different from loss leader marketing and free sample marketing, which do not depend on complementary products or services.
 W
WFreemium, a portmanteau of the words "free" and "premium", is a pricing strategy by which a basic product or service is provided free of charge, but money is charged for additional features, services, or virtual (online) or physical (offline) goods that expand the functionality of the free version of the software. This business model has been used in the software industry since the 1980s. A subset of this model used by the video game industry is called free-to-play.
 W
WThe India Way: How India’s Top Business Leaders Are Revolutionizing Management is published by the Harvard Business Press. It's a non-fictional book written by Peter Cappelli, Harbir Singh, Jitendra Singh and Michael Useem of the Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania. The book was released in the United States on March 23, 2010, and was released in India in May 2010. The India Way primarily focuses on the contrast in business management styles between the U.S. and India. Topics discussed in the book include topics such as leadership skills, company governance, human resources management and innovation. The authors’ conclusions are based on an analysis of nearly 130 interviews conducted with Indian CEOs and executives.
 W
WA lemonade stand is a business that is commonly owned and operated by a child or children, to sell lemonade. The concept has become iconic of youthful summertime Americana to the degree that parodies and variations on the concept exist across media. The term may also be used to refer to stands that sell similar beverages like iced tea. In the United States, unlicensed lemonade stands have gotten in trouble with rules about permits.
 W
WA low-cost carrier or low-cost airline is an airline that is operated with an especially high emphasis on minimizing operating costs and without some of the traditional services and amenities provided in the fare, resulting in lower fares and fewer comforts. To make up for revenue lost in decreased ticket prices, the airline may charge extra fees – such as for carry-on baggage. As of April 2020, the world's largest low-cost carrier is Southwest Airlines, which operates primarily in the United States, as well as in some surrounding areas.
 W
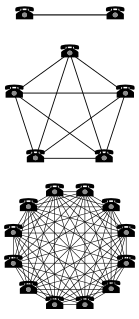
WIn economics, a network effect is the phenomenon by which the value or utility a user derives from a good or service depends on the number of users of compatible products. Network effects are typically positive, resulting in a given user deriving more value from a product as other users join the same network. The adoption of a product by an additional user can be broken into two effects: an increase in the value to all other users and also the enhancement of other non-users motivation for using the product.
 W
WIn R&D management and systems development, open coopetition or open-coopetition is a neologism to describe cooperation among competitors in the open-source arena. The term was first coined by the scholars Jose Teixeira and Tingting Lin to describe how rival firms that, while competing with similar products in the same markets, collaborate which each other in the development of open-source projects.
 W
WOrganizational architecture has two very different meanings. In one sense it literally refers to the organization's built environment and in another sense it refers to architecture metaphorically, as a structure which fleshes out the organizations. The various features of a business's organizational architecture has to be internally consistent in strategy, architecture and competitive environment.Organizational architecture or organizational space: the influence of the spatial environment on humans in and around organizations. Organizational architecture or organization design: the creation of roles, processes, and formal reporting relationships in an organization.
 W
WA philanthropreneur is an entrepreneurial philanthropist. The term is claimed to be coined by Internet entrepreneur Mark Desvaux in 2004; however, The Wall Street Journal used the term in a 1999 article, and a publication entitled The Philanthropreneur Newsletter existed as far back as 1997. Philanthropreneurship is often considered the start of a new era in philanthropy, characterized by the development of the philanthropist’s role and the integration of business practices.
 W
WThe platform economy is economic and social activity facilitated by platforms. Such platforms are typically online matchmakers or technology frameworks. By far the most common type are "transaction platforms", also known as "digital matchmakers". Examples of transaction platforms include Amazon, Airbnb, Uber, and Baidu. A second type is the "innovation platform", which provides a common technology framework upon which others can build, such as the many independent developers who work on Microsoft's platform.
 W
WA pyramid scheme is a business model that recruits members via a promise of payments or services for enrolling others into the scheme, rather than supplying investments or sale of products. As recruiting multiplies, recruiting becomes quickly impossible, and most members are unable to profit; as such, pyramid schemes are unsustainable and often illegal.
 W
WScentura also known as Scentura Creations is a perfume company based in the city of Chamblee, Georgia, within the Atlanta metropolitan area. It is a multilevel selling company which manufactures inexpensive imitations of designer fragrances. Independent salespeople are sent out, often in pairs, to sell perfume door-to-door, in parking lots, malls, or in other retail stores.
 W
WService economy can refer to one or both of two recent economic developments:The increased importance of the service sector in industrialized economies. The current list of Fortune 500 companies contains more service companies and fewer manufacturers than in previous decades. The relative importance of service in a product offering. The service economy in developing countries is mostly concentrated in financial services, hospitality, retail, health, human services, information technology and education. Products today have a higher service component than in previous decades. In the management literature this is referred to as the servitization of products or a product-service system. Virtually every product today has a service component to it.
 W
WSmall businesses are privately owned corporations, partnerships, or sole proprietorships that have fewer employees and/or less annual revenue than a regular-sized business or corporation. Businesses are defined as "small" in terms of being able to apply for government support and qualify for preferential tax policy varies depending on the country and industry. Small businesses range from fifteen employees under the Australian Fair Work Act 2009, fifty employees according to the definition used by the European Union, and fewer than five hundred employees to qualify for many U.S. Small Business Administration programs. While small businesses can also be classified according to other methods, such as annual revenues, shipments, sales, assets, or by annual gross or net revenue or net profits, the number of employees is one of the most widely used measures.
 W
WA social purpose corporation (SPC) is a type of for-profit entity, a corporation, in some U.S. states that enables, but does not require, considering social or environmental issues in decision making. SPCs are similar to benefit corporations and flexible purpose corporations (FPCs).
 W
WThe European Cooperative Society is, in corporate law, a European cooperative type of company, established in 2006 and related to the Societas Europaea (SE). They may be established and may operate throughout the European Economic Area. The legal form was created to remove the need for cooperatives to establish a subsidiary in each Member state of the European Union in which they operate, and to allow them to move their registered office and headquarters freely from one Member State to another, keeping their legal identity and without having to register or wind up any legal persons. No matter where they are established, SCEs are governed by a single EEA-wide set of rules and principles which are supplemented by the laws on co-operatives in each Member State, and other areas of law.
 W
WA store-within-a-store, also referred to as shop-in-shop, is an agreement in which a retailer rents a part of the retail space to be used by a different company to run another, independent shop.
 W
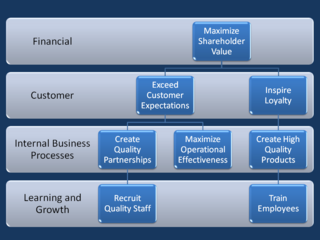
WA strategy map is a diagram that is used to document the primary strategic goals being pursued by an organization or management team. It is an element of the documentation associated with the Balanced Scorecard, and in particular is characteristic of the second generation of Balanced Scorecard designs that first appeared during the mid-1990s. The first diagrams of this type appeared in the early 1990s, and the idea of using this type of diagram to help document Balanced Scorecard was discussed in a paper by Drs. Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton in 1996.
 W
WA symbol group is a form of franchise of convenience shops, found primarily in the United Kingdom and Ireland. They do not own or operate shops, but act as suppliers to independent shops which then trade under a common banner.
 W
WA trust or corporate trust is a large grouping of business interests with significant market power, which may be embodied as a corporation or as a group of corporations that cooperate with one another in various ways. These ways can include constituting a trade association, owning stock in one another, constituting a corporate group, or combinations thereof. The term trust is often used in a historical sense to refer to monopolies or near-monopolies in the United States during the Second Industrial Revolution in the 19th century and early 20th century.