 W
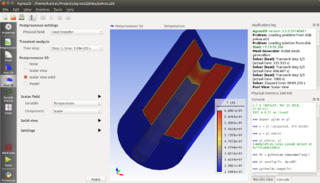
WAgros2D is an open-source code for numerical solutions of 2D coupled problems in technical disciplines. Its principal part is a user interface serving for complete preprocessing and postprocessing of the tasks. The processor is based on the library Hermes containing the most advanced numerical algorithms for monolithic and fully adaptive solution of systems of generally nonlinear and nonstationary partial differential equations (PDEs) based on hp-FEM. Both parts of the code are written in C++.
 W
WApplied Science International, LLC, aka ASI is a United States-based company headquartered in Raleigh, North Carolina, that provides advanced engineering design and analysis software and services to the DHS, United States Department of Defense, Engineering Firms, Demolition Contractors, and Universities.
 W
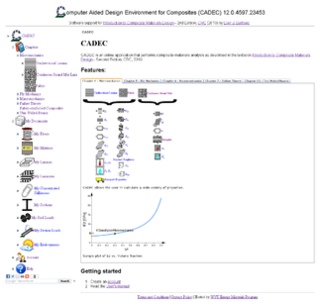
Wcadec-online.com is a multilingual web application that performs analysis of composite materials and is used primarily for teaching, especially within the disciplines of aerospace engineering, materials science, naval engineering, mechanical engineering, and civil engineering. Users navigate the application through a tree view which structures the component chapters. cadec-online is an engineering cloud application. It uses the LaTeX library to render equations and symbols, then Sprites to optimize the delivery of images to the page.
 W
WCP2K is a freely available (GPL) quantum chemistry and solid state physics program package, written in Fortran 2003, to perform atomistic simulations of solid state, liquid, molecular, periodic, material, crystal, and biological systems. It provides a general framework for different methods: density functional theory (DFT) using a mixed Gaussian and plane waves approach (GPW) via LDA, GGA, MP2, or RPA levels of theory, classical pair and many-body potentials, semi-empirical and tight-binding Hamiltonians, as well as Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics (QM/MM) hybrid schemes relying on the Gaussian Expansion of the Electrostatic Potential (GEEP). CP2K can do simulations of molecular dynamics, metadynamics, Monte Carlo, Ehrenfest dynamics, vibrational analysis, core level spectroscopy, energy minimization, and transition state optimization using NEB or dimer method.
 W
WThe Earth Simulator (ES) , developed by the Japanese government's initiative "Earth Simulator Project", was a highly parallel vector supercomputer system for running global climate models to evaluate the effects of global warming and problems in solid earth geophysics. The system was developed for Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute, and Japan Marine Science and Technology Center (JAMSTEC) in 1997. Construction started in October 1999, and the site officially opened on 11 March 2002. The project cost 60 billion yen.
 W
WEcosimPro is a simulation tool developed by Empresarios Agrupados A.I.E for modelling simple and complex physical processes that can be expressed in terms of Differential algebraic equations or Ordinary differential equations and Discrete event simulation.
 W
WFEATool Multiphysics is a physics, finite element analysis (FEA), and PDE simulation toolbox. FEATool Multiphysics features the ability to model fully coupled heat transfer, fluid dynamics, chemical engineering, structural mechanics, fluid-structure interaction (FSI), electromagnetics, as well as user-defined and custom PDE problems in 1D, 2D (axisymmetry), or 3D, all within a graphical user interface (GUI) or optionally as script files. FEATool has been employed and used in academic research, teaching, and industrial engineering simulation contexts.
 W
WThe FEniCS Project is a collection of free and open-source software components with the common goal to enable automated solution of differential equations. The components provide scientific computing tools for working with computational meshes, finite-element variational formulations of ordinary and partial differential equations, and numerical linear algebra.
 W
WGerris is computer software in the field of computational fluid dynamics (CFD). Gerris was released as free and open-source software, subject to the requirements of the GNU General Public License (GPL), version 2 or any later.
 W
WGetFEM++ is a generic finite element C++ library with interfaces for Python, Matlab and Scilab. It aims at providing finite element methods and elementary matrix computations for solving linear and non-linear problems numerically. Its flexibility in choosing among different finite element approximations and numerical integration methods is one of its distinguishing characteristics.
 W
WGMS is water modeling application for building and simulating groundwater models from Aquaveo. It features 2D and 3D geostatistics, stratigraphic modeling and a unique conceptual model approach. Currently supported models include MODFLOW, MODPATH, MT3DMS, RT3D, FEMWATER, SEEP2D, and UTEXAS.
 W
WHEC-RAS is a computer program that models the hydraulics of water flow through natural rivers and other channels. Prior to the 2016 update to Version 5.0, the program was one-dimensional, meaning that there is no direct modeling of the hydraulic effect of cross section shape changes, bends, and other two- and three-dimensional aspects of flow. The release of Version 5.0 introduced two-dimensional modeling of flow as well as sediment transfer modeling capabilities. The program was developed by the United States Army Corps of Engineers in order to manage the rivers, harbors, and other public works under their jurisdiction; it has found wide acceptance by many others since its public release in 1995.
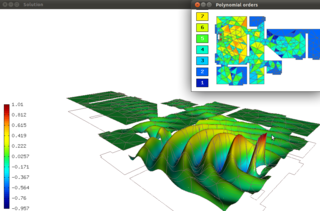 W
WHermes2D is a C++/Python library of algorithms for rapid development of adaptive hp-FEM solvers. hp-FEM is a modern version of the finite element method (FEM) that is capable of extremely fast, exponential convergence.
 W
WHydroGeoSphere (HGS) is a 3D control-volume finite element groundwater model, and is based on a rigorous conceptualization of the hydrologic system consisting of surface and subsurface flow regimes. The model is designed to take into account all key components of the hydrologic cycle. For each time step, the model solves surface and subsurface flow, solute and energy transport equations simultaneously, and provides a complete water and solute balance.
 W
Wlibrsb is an open-source parallel library for sparse matrix computations using the Recursive Sparse Blocks (RSB) matrix format.
 W
WLis is a scalable parallel software library for solving discretized linear equations and eigenvalue problems that mainly arise in the numerical solution of partial differential equations by using iterative methods. Although it is designed for parallel computers, the library can be used without being conscious of parallel processing.
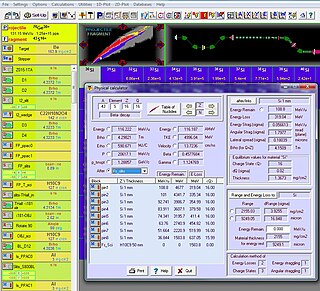 W
WThe program LISE++ is designed to predict the intensity and purity of radioactive ion beams (RIB) produced by In-flight separators. LISE++ also facilitates the tuning of experiments where its results can be quickly compared to on-line data. The program is constantly expanding and evolving from the feedback of its users around the world.
 W
WThe cosmic microwave background (CMB) is the thermal radiation assumed to be left over from the "Big Bang" of cosmology. The CMB is a snapshot of the oldest light in our universe, imprinted on the sky when the universe was just 380,000 years old. It shows tiny temperature fluctuations that correspond to regions of slightly different densities, representing the seeds of all future structure: the stars and galaxies of today. Therefore, analysis of the small anisotropies in the CMB helps us to understand the origin and the fate of our universe. In past few decades, there has been a lot of improvement in the observations and several experiments, performed to understand the basic structure of the universe. For analyzing data of different cosmological experiments and for understanding the theoretical nature of the universe many advanced methods and computing software are developed in and used by cosmologists for years. These software are widely used by the cosmologists across the globe.
 W
WMFEM is an open-source C++ library for solving partial differential equations using the finite element method, developed and maintained by researchers at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and the MFEM open-source community on GitHub. MFEM is free software released under a BSD license.
 W
WMOOSE is an object-oriented C++ finite element framework for the development of tightly coupled multiphysics solvers from Idaho National Laboratory. MOOSE makes use of the PETSc non-linear solver package and libmesh to provide the finite element discretization.
 W
WNEST is a simulation software for spiking neural network models, including large-scale neuronal networks. NEST was initially developed by Markus Diesmann and Marc-Oliver Gewaltig and is now developed and maintained by the NEST Initiative.
 W
WOpenFOAM is a C++ toolbox for the development of customized numerical solvers, and pre-/post-processing utilities for the solution of continuum mechanics problems, most prominently including computational fluid dynamics (CFD).
 W
WRange Software is finite element analysis software package.
 W
WRibbon diagrams, also known as Richardson diagrams, are 3D schematic representations of protein structure and are one of the most common methods of protein depiction used today. The ribbon shows the overall path and organization of the protein backbone in 3D, and serves as a visual framework on which to hang details of the full atomic structure, such as the balls for the oxygen atoms bound to the active site of myoglobin in the adjacent image. Ribbon diagrams are generated by interpolating a smooth curve through the polypeptide backbone. α-helices are shown as coiled ribbons or thick tubes, β-strands as arrows, and non-repetitive coils or loops as lines or thin tubes. The direction of the polypeptide chain is shown locally by the arrows, and may be indicated overall by a colour ramp along the length of the ribbon.
 W
WA runoff model is a mathematical model describing the rainfall–runoff relations of a rainfall catchment area, drainage basin or watershed. More precisely, it produces a surface runoff hydrograph in response to a rainfall event, represented by and input as a hyetograph. In other words, the model calculates the conversion of rainfall into runoff. A well known runoff model is the linear reservoir, but in practice it has limited applicability. The runoff model with a non-linear reservoir is more universally applicable, but still it holds only for catchments whose surface area is limited by the condition that the rainfall can be considered more or less uniformly distributed over the area. The maximum size of the watershed then depends on the rainfall characteristics of the region. When the study area is too large, it can be divided into sub-catchments and the various runoff hydrographs may be combined using flood routing techniques.
 W
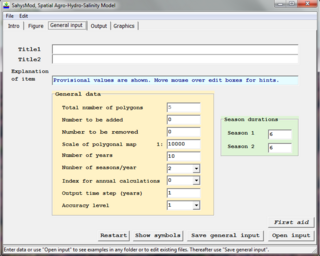
WSahysMod is a computer program for the prediction of the salinity of soil moisture, groundwater and drainage water, the depth of the watertable, and the drain discharge in irrigated agricultural lands, using different hydrogeologic and aquifer conditions, varying water management options, including the use of ground water for irrigation, and several crop rotation schedules, whereby the spatial variations are accounted for through a network of polygons.
 W
WSaltMod is computer program for the prediction of the salinity of soil moisture, groundwater and drainage water, the depth of the watertable, and the drain discharge (hydrology) in irrigated agricultural lands, using different (geo)hydrologic conditions, varying water management options, including the use of ground water for irrigation, and several cropping rotation schedules. The water management options include irrigation, drainage, and the use of subsurface drainage water from pipe drains, ditches or wells for irrigation.
 W
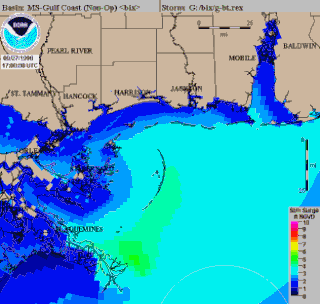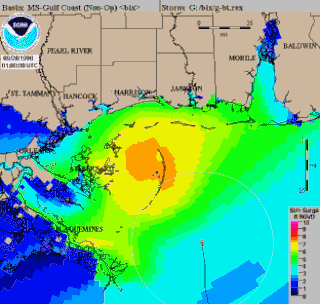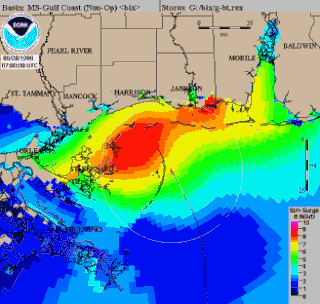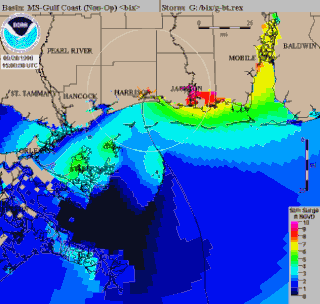
WSea, Lake, and Overland Surge from Hurricanes (SLOSH) is a computerized model developed by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), United States Army Corps of Engineers (USACE), and the National Weather Service (NWS), to estimate storm surge depths resulting from historical, hypothetical, or predicted hurricanes. The model functions by taking into account a storm's pressure, size, forward speed, forecast track, wind speeds, and topographical data.
 W
WSIESTA is an original method and its computer program implementation, to perform efficient electronic structure calculations and ab initio molecular dynamics simulations of molecules and solids. SIESTA's efficiency stems from the use of strictly localized basis sets and from the implementation of linear-scaling algorithms which can be applied to suitable systems. A very important feature of the code is that its accuracy and cost can be tuned in a wide range, from quick exploratory calculations to highly accurate simulations matching the quality of other approaches, such as plane-wave and all-electron methods.
 W
WSimThyr is a free continuous dynamic simulation program for the pituitary-thyroid feedback control system. The open-source program is based on a nonlinear model of thyroid homeostasis. In addition to simulations in the time domain the software supports various methods of sensitivity analysis. It provides a GUI, which allows for visualising time series, modifying constant structure parameters of the feedback loop, storing parameter sets as XML files and exporting results of simulations in various formats that are suitable for statistical software. SimThyr is primarily intended for educational purposes and in-silico research.
 W
WSU2 is a suite of open-source software tools written in C++ for the numerical solution of partial differential equations (PDE) and performing PDE-constrained optimization. The primary applications are computational fluid dynamics and aerodynamic shape optimization, but has been extended to treat more general equations such as electrodynamics and chemically reacting flows. SU2 supports continuous and discrete adjoint for calculating the sensitivities/gradients of a scalar field.
 W
WTITAN2D is a geoflow simulation software application, intended for geological researchers. It is distributed as free software.
 W
WVisual MODFLOW (VMOD) is a software program developed by Waterloo Hydrogeologic. Originally released in 1994, Visual MODFLOW was the first commercially available graphical interface for the open source groundwater modeling engine called MODFLOW. As of May 2012, a newer .NET version of the software was rebranded as Visual MODFLOW Flex. The program also combines proprietary extensions, such as MODFLOW-SURFACT, MT3DMS and a three-dimensional model explorer. Visual MODFLOW supports MODFLOW-2000, MODFLOW-2005, MODFLOW-NWT, MODFLOW-LGR, MODFLOW-SURFACT, and SEAWAT.
 W
WWMS is a watershed computer simulation and modeling software application from Aquaveo. It was originally created in the early 1990s at the Engineering Computer Graphics Laboratory at Brigham Young University.