 W
WDemography is the statistical study of populations, especially human beings.
 W
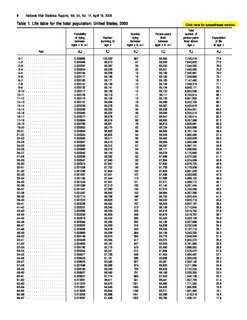
WActuarial notation is a shorthand method to allow actuaries to record mathematical formulas that deal with interest rates and life tables.
 W
WActuarial science is the discipline that applies mathematical and statistical methods to assess risk in insurance, finance, and other industries and professions. More generally, actuaries apply rigorous mathematics to model matters of uncertainty.
 W
WThe Berlin Demography Forum (BDF) is a global, non-partisan platform providing a new impetus to raise awareness of the significance of demographic change both at a national and international level. The forum brings together high-ranking politicians, scientists, business leaders, and representatives of international organisations and civil society to debate potential solutions and to contribute to sustainable development.
 W
WThe following is a list of the causes of human deaths worldwide for different years arranged by their associated mortality rates. In 2002, there were about 57 million deaths. In 2005, according to the World Health Organization (WHO) using the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD), about 58 million people died. In 2010, according to the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, 52.8 million people died. In 2016, the WHO recorded 56.7 million deaths with the leading cause of death as cardiovascular disease causing more than 17 million deaths as shown in the chart to the side.
 W
WIn demographics, the center of population of a region is a geographical point that describes a centerpoint of the region's population. There are several different ways of defining such a "center point", leading to different geographical locations; these are often confused.
 W
WThe Child Development Index (CDI) is an index combining performance measures specific to children—education, health and nutrition—to produce a score on a scale of 0 to 100. A zero score would be the best. The higher the score, the worse children are faring.
 W
WChild mortality is the mortality of children under the age of five. The child mortality rate, also under-five mortality rate, refers to the probability of dying between birth and exactly five years of age expressed per 1,000 live births.
 W
WIn statistics, marketing and demography, a cohort is a group of subjects who share a defining characteristic.
 W
WThe Crisis of the Late Middle Ages was a series of events in the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries that brought centuries of European stability to a halt. Three major crises led to radical changes in all areas of society: demographic collapse, political instabilities and religious upheavals.
 W
WDesakota is a term used in urban geography used to describe areas in the extended surroundings of large cities, in which urban and agricultural forms of land use and settlement coexist and are intensively intermingled.
 W
WIn demography and medical geography, epidemiological transition is a theory which "describes changing population patterns in terms of fertility, life expectancy, mortality, and leading causes of death." For example, a phase of development marked by a sudden increase in population growth rates brought by improved food security and innovations in public health and medicine, can be followed by a re-leveling of population growth due to subsequent declines in fertility rates. Such a transition can account for the replacement of infectious diseases by chronic diseases over time due to increased life span as a result of improved health care and disease prevention. This theory was originally posited by Abdel Omran in 1971.
 W
WThe Federal Institute for Population Research, abbreviated BiB, is research institute of the German federal government under the portfolio of the Federal Ministry of the Interior and has the task of providing scientific advice to the federal government on issues relating to demography and demographic trends in fertility, nuptiality, mortality, ageing and migration as well as global issues.
 W
WThe Gompertz curve or Gompertz function is a type of mathematical model for a time series, named after Benjamin Gompertz (1779–1865). It is a sigmoid function which describes growth as being slowest at the start and end of a given time period. The right-hand or future value asymptote of the function is approached much more gradually by the curve than the left-hand or lower valued asymptote. This is in contrast to the simple logistic function in which both asymptotes are approached by the curve symmetrically. It is a special case of the generalised logistic function. The function was originally designed to describe human mortality, but since has been modified to be applied in biology, with regard to detailing populations.
 W
WHuman migration involves the movement of people from one place to another with intentions of settling, permanently or temporarily, at a new location. The movement often occurs over long distances and from one country to another, but internal migration is also possible; indeed, this is the dominant form of human migration globally. Migration is often associated with better human capital at both individual and household level, and with better access to migration networks. Age is very also important for both work and non-work migration. People may migrate as individuals, in family units or in large groups. There are four major forms of migration: invasion, conquest, colonization and emigration/immigration.
 W
WStep migration is a migration pattern conceptualized in 1885 by Ernst Georg Ravenstein who observed migration as occurring stage by stage as rural inhabitants move closer to urban areas of growth. It is a migration pattern regarded by some scholars to be a widely popular form of international migration in the twenty-first century globalized world. There is a large breadth of study proving the existence of step migration in many international migration patterns, although there is lack of consensus over its exact specification and measurement. Step migration scholars deem it to be an important international trend that has the power to aid in the design of policy development efforts in both rural and urban areas worldwide.
 W
WIn demography, the field of study that deals with the study of populations), a Lexis diagram is a two dimensional diagram used to represent events that occur to individuals belonging to different cohorts. Calendar time is usually represented on the horizontal axis, while age is represented on the vertical axis. In some cases, the y-axis is plotted backwards, with age 0 at the top of the page and increasing downwards. Other arrangements of the axes are also seen. As an example the death of an individual in 2009 at age 80 is represented by the point (2009,80); the cohort of all persons born in 1929 is represented by a diagonal line starting at (1929,0) and continuing through (1930,1)., and so on.
 W
WLife expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, its current age, and other demographic factors including gender. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth (LEB), which can be defined in two ways. Cohort LEB is the mean length of life of an actual birth cohort and can be computed only for cohorts born many decades ago so that all their members have died. Period LEB is the mean length of life of a hypothetical cohort assumed to be exposed, from birth through death, to the mortality rates observed at a given year.
 W
WIn human reproduction, a live birth occurs when a fetus, whatever its gestational age, exits the maternal body and subsequently shows any sign of life, such as voluntary movement, heartbeat, or pulsation of the umbilical cord, for however brief a time and regardless of whether the umbilical cord or placenta are intact.
 W
WCouples living apart together (LAT) have an intimate relationship but live at separate addresses. It includes couples who wish to live together but are not yet able to, as well as couples who prefer live apart, for various reasons.
 W
WLongevity myths are traditions about long-lived people, either as individuals or groups of people, and practices that have been believed to confer longevity, but for which scientific evidence does not support the ages claimed or the reasons for the claims. While literal interpretations of such myths may appear to indicate extraordinarily long lifespans, many scholars believe such figures may be the result of incorrect translation of numbering systems through various languages coupled with the cultural and/or symbolic significance of certain numbers.
 W
WMarriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally recognised union between people, called spouses, that establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children, and between them and their in-laws. It is considered a cultural universal, but the definition of marriage varies between cultures and religions, and over time. Typically, it is an institution in which interpersonal relationships, usually sexual, are acknowledged or sanctioned. In some cultures, marriage is recommended or considered to be compulsory before pursuing any sexual activity. A marriage ceremony is called a wedding.
 W
WMaternal death or maternal mortality is defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) as "the death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, irrespective of the duration and site of the pregnancy, from any cause related to or aggravated by the pregnancy or its management but not from accidental or incidental causes."
 W
WThe Maternal Mortality and Morbidity Task Force was started by the Department of State in 2013 to help reduce maternal death in Texas. The task force and DSHS must submit a joint report on the findings of the task force and recommendations to the governor, lieutenant governor, speaker of the House of Representatives, and appropriate committees of the Texas Legislature by September 1 of each even-numbered year, beginning September 1, 2016. The maternal mortality ratio (MMR) for the state of Texas was concluded to be the highest in the developed world in 2016, with the maternal mortality rate (MMRate) of the state surging beyond the poor MMRate of 48 states of the US at 23.8% to a remarkably high 35.8%.
 W
WMortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of deaths per 1,000 individuals per year; thus, a mortality rate of 9.5 in a population of 1,000 would mean 9.5 deaths per year in that entire population, or 0.95% out of the total. It is distinct from "morbidity", which is either the prevalence or incidence of a disease, and also from the incidence rate.
 W
WThe number of people who died in the Paraguayan War (1864–1870) is unknown. Widely diverging estimates have been made. "Determining the size of Paraguay's population has always been an exercise in frustration." However, there is a widespread impression that the casualties were immense; there was also some population loss from non-lethal causes such as migration. The Dutch human geographer Jan Kleinpenning thought that Paraguay lost between a quarter and a half of its population, but much higher and lower estimates have been made. No academic demographic scholarship makes it less than 7% or greater than 69%.
 W
WIn biology, a population is a number of all the organisms of the same group or species who live in a particular geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with individuals from other areas.
 W
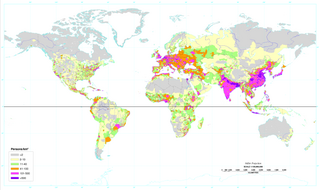
WPopulation density is a measurement of population per unit area, or exceptionally unit volume; it is a quantity of type number density. It is frequently applied to living organisms, most of the time to humans. It is a key geographical term. In simple terms, population density refers to the number of people living in an area per square kilometre.
 W
WPopulation health has been defined as "the health outcomes of a group of individuals, including the distribution of such outcomes within the group". According to Akarowhe (2018), the working definition of population health is expressed thus; population health as an art, simply means that it is geared towards equal health care delivery to an anticipated group of people in a particular geographical location; as a science, it implies that it adopt scientific approach of preventive, therapeutic, and diagnostic service in proffering medical treatment to the health problem of people; as a product, it means that population health is directed toward overall health performance of people through health satisfaction within the said geographical area; and as a process it entails effective and efficient running of a health management/population health management system to cater for the health needs of the people. It is an approach to health that aims to improve the health of an entire human population. This concept does not refer to animal or plant populations. It has been described as consisting of three components. These are "health outcomes, patterns of health determinants, and policies and interventions". A priority considered important in achieving the aim of Population Health is to reduce health inequities or disparities among different population groups due to, among other factors, the social determinants of health, SDOH. The SDOH include all the factors that the different populations are born into, grow up and function with throughout their lifetimes which potentially have a measurable impact on the health of human populations. The Population Health concept represents a change in the focus from the individual-level, characteristic of most mainstream medicine. It also seeks to complement the classic efforts of public health agencies by addressing a broader range of factors shown to impact the health of different populations. The World Health Organization's Commission on Social Determinants of Health, reported in 2008, that the SDOH factors were responsible for the bulk of diseases and injuries and these were the major causes of health inequities in all countries. In the US, SDOH were estimated to account for 70% of avoidable mortality.
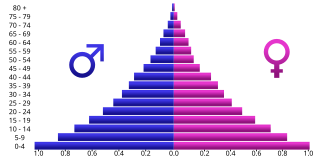 W
WA population pyramid, also called an "age-gender-pyramid", is a graphical illustration that shows the distribution of various age groups in a population, which forms the shape of a pyramid when the population is growing. Males are conventionally shown on the left and females on the right, and they may be measured by raw number or as a percentage of the total population. This tool can be used to visualize the age of a particular population. It is also used in ecology to determine the overall age distribution of a population; an indication of the reproductive capabilities and likelihood of the continuation of a species.
 W
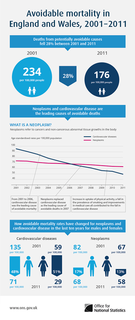
WPreventable causes of death are causes of death related to risk factors which could have been avoided. The World Health Organization has traditionally classified death according to the primary type of disease or injury. However, causes of death may also be classified in terms of preventable risk factors—such as smoking, unhealthy diet, sexual behavior, and reckless driving—which contribute to a number of different diseases. Such risk factors are usually not recorded directly on death certificates, although they are acknowledged in medical reports.
 W
WThe sector model, also known as the Hoyt model, is a model of urban land use proposed in 1939 by land economist Homer Hoyt. It is a modification of the concentric zone model of city development. The benefits of the application of this model include the fact it allows for an outward progression of growth. As with all simple models of such complex phenomena, its validity is limited.
 W
WThe Tortilla Wall is a term given to a 14-mile section of United States border fence between the Otay Mesa Border Crossing in San Diego, California and the Pacific Ocean.
 W
WUSAFacts is a non-profit organization and website that provides data and reports on the US population, its government's finances, and government's impact on society.
 W
WThe World Economy: Historical Statistics is a landmark book by Angus Maddison. Published in 2004 by the OECD Development Centre, it studies the growth of populations and economies across the centuries: not just the world economy as it is now, but how it was in the past.