 W
WThe scientific community examined several alternative approaches to redefining the kilogram before deciding on a redefinition of the SI base units in November 2018. Each approach had advantages and disadvantages.
The apothecaries' system, or apothecaries' weights and measures, is a historical system of mass and volume units that were used by physicians and apothecaries for medical recipes and also sometimes by scientists. The English version of the system is closely related to the English troy system of weights, the pound and grain being exactly the same in both. It divides a pound into 12 ounces, an ounce into 8 drachms, and a drachm into 3 scruples of 20 grains each. This exact form of the system was used in the United Kingdom; in some of its former colonies, it survived well into the 20th century. The apothecaries' system of measures is a similar system of volume units based on the fluid ounce. For a long time, medical recipes were written in Latin, often using special symbols to denote weights and measures.
 W
WThe avoirdupois system is a measurement system of weights which uses pounds and ounces as units. It was first commonly used in the 13th century AD and was updated in 1959.
 W
WThe candy or candee, also known as the maunee, was a traditional South Asian unit of mass, equal to 20 maunds and roughly equivalent to 500 pounds avoirdupois (227 kilograms). It was most used in southern India, to the south of Akbar's empire, but has been recorded elsewhere in South Asia. In Marathi, the same word was also used for a unit of area of 120 bighas, and it is also recorded as a unit of dry volume.
 W
WThe carat (ct) is a unit of mass equal to 200 mg (0.00705 oz) or 0.00643 troy oz, and is used for measuring gemstones and pearls. The current definition, sometimes known as the metric carat, was adopted in 1907 at the Fourth General Conference on Weights and Measures, and soon afterwards in many countries around the world. The carat is divisible into 100 points of 2 mg. Other subdivisions, and slightly different mass values, have been used in the past in different locations.
 W
WThe catty, kati or jin, symbol 斤, is a traditional Chinese unit of mass used across East and Southeast Asia, notably for weighing food and other groceries in some wet markets, street markets, and shops. Related units include the picul, equal to 100 catties, and the tael, which is 1⁄16 of a catty. A stone is a former unit used in Hong Kong equal to 120 catties and a gwan (鈞) is 30 catties. Catty or kati is still used in South East Asia as a unit of measurement in some contexts especially by the significant Overseas Chinese populations of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Singapore.
 W
WDirham, dirhem or dirhm is a silver coin. It is used as currency across the world. Throughout history, human civilizations have used silver and gold as currency. The name derives from the name of the ancient Greek currency, drachma.
 W
WEarth mass (ME or M⊕, where ⊕ is the standard astronomical symbol for planet Earth) is the unit of mass equal to that of Earth. The current best estimate for Earth mass is M⊕ = 5.9722×1024 kg, with a standard uncertainty of 6×1020 kg (relative uncertainty 10−4). The recommended value in 1976 was (5.9742±0.0036)×1024 kg. It is equivalent to an average density of 5515 kg.m−3.
 W
WA grain is a unit of measurement of mass, and in the troy weight, avoirdupois, and Apothecaries' system, equal to exactly 64.79891 milligrams. It is nominally based upon the mass of a single virtual ideal seed of a cereal. From the Bronze Age into the Renaissance the average masses of wheat and barley grains were part of the legal definitions of units of mass. Expressions such as "thirty-two grains of wheat, taken from the middle of the ear" appear to have been ritualistic formulas, essentially the premodern equivalent of legal boilerplate. Another source states that it was defined as the weight needed for 252.458 units to balance a cubic inch of distilled water at 30 inches of mercury pressure and 62 degrees Fahrenheit for both the air and water. Another book states that Captain Henry Kater, of the British Standards Commission, arrived at this value experimentally.
 W
WThe gram is a metric system unit of mass.
 W
WThe grave is the unit of mass used in the first metric system which was implemented in France in 1793. In 1795, the grave was renamed as the kilogram.
 W
WGrivna (гривна) was a currency as well as a measure of weight used in Kievan Rus' and other East Slavic countries since the 11th century.
 W
WThe grzywna was a measure of weight, mainly for silver, commonly used throughout medieval central and eastern Europe, particularly in the Kingdom of Poland and Kingdom of Bohemia.
 W
WThe earliest recorded systems of weights and measures originate in the 3rd or 4th millennium BC. Even the very earliest civilizations needed measurement for purposes of agriculture, construction, and trade. Early standard units might only have applied to a single community or small region, with every area developing its own standards for lengths, areas, volumes and masses. Often such systems were closely tied to one field of use, so that volume measures used, for example, for dry grains were unrelated to those for liquids, with neither bearing any particular relationship to units of length used for measuring cloth or land. With development of manufacturing technologies, and the growing importance of trade between communities and ultimately across the Earth, standardized weights and measures became critical. Starting in the 18th century, modernized, simplified and uniform systems of weights and measures were developed, with the fundamental units defined by ever more precise methods in the science of metrology. The discovery and application of electricity was one factor motivating the development of standardized internationally applicable units.
 W
WThe hundredweight, formerly also known as the centum weight or quintal, is a British imperial and US customary unit of weight or mass. Its value differs between the US and British imperial systems. The two values are distinguished in American English as the "short" and "long" hundredweight and in British English as the "cental" and the "imperial hundredweight".The short hundredweight or cental of 100 pounds (45.36 kg) is used in the United States. The long or imperial hundredweight of 8 stone or 112 pounds (50.80 kg) is defined in the imperial system.
 W
WThe International Prototype of the Kilogram is an object that was used to define the magnitude of the mass of the kilogram from 1889, when it replaced the Kilogramme des Archives, until 2019, when it was replaced by a new definition of the kilogram based on physical constants. During that time, the IPK and its duplicates were used to calibrate all other kilogram mass standards on Earth.
 W
WJupiter mass, also called Jovian mass, is the unit of mass equal to the total mass of the planet Jupiter. This value may refer to the mass of the planet alone, or the mass of the entire Jovian system to include the moons of Jupiter. Jupiter is by far the most massive planet in the Solar System. It is approximately 2.5 times as massive as all of the other planets in the Solar System combined.
 W
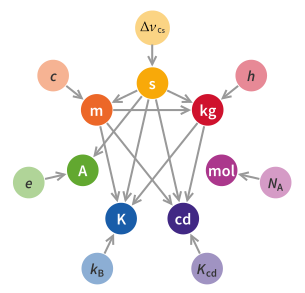
WThe kilogram is the base unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI), the current metric system, having the unit symbol kg. It is a widely used measure in science, engineering and commerce worldwide, and is often simply called a kilo in everyday speech.
 W
WThe maund is the anglicized name for a traditional unit of mass used in British India, and also in Afghanistan, Persia and Arabia: the same unit in the Moghul Empire was sometimes written as mann or mun in English, while the equivalent unit in the Ottoman Empire and Central Asia was called the batman. At different times, and in different South Asian localities, the mass of the maund has varied, from as low as 25 pounds (11 kg) to as high as 160 pounds (72½ kg): even greater variation is seen in Persia and Arabia.
 W
WMithqāl is a unit of mass equal to 4.25 grams which is mostly used for measuring precious metals, such as gold, and other commodities, like saffron.
 W
WA picul or tam is a traditional Asian unit of weight, defined as "as much as a man can carry on a shoulder-pole".
 W
WPood, is a unit of mass equal to 40 funt. Plural: pudi or pudy. Since 1899 It is approximately set to 16.38 kilograms. It was used in Russia, Belarus, and Ukraine. Pood was first mentioned in a number of 12th-century documents. Unlike funt, which came at least in the 14th century from Middle High German: phunt, Old East Slavic: пудъ pud is a much older borrowing from Old Norse: pund which in turn came through the mediation of Old English: pund from Latin: pondus "weight".
 W
WRatti is a traditional Indian unit of measurement for mass. Based on the nominal weight of a Gunja seed, it measured approximately 1.8 or 1.75 grains or 0.1215 g as modern standardized weight. It is still used by the jewellers in the Indian Subcontinent.
 W
WThe measures of the old Romanian system varied greatly not only between the three Romanian states, but sometimes also inside the same country. The origin of some of the measures are the Latin, Slavic, Greek and Turkish systems.
 W
WA Seer is a traditional unit of mass and volume used in large parts of Asia prior to the middle of the 20th century. It remains in use only in a few countries such as Afghanistan, Iran, and parts of India although in Iran it indicates a smaller unit of weight than the one used in India.
 W
WShekel or sheqel is an ancient Near Eastern coin, usually of silver. A shekel was first a unit of weight-very roughly 11 grams (0.39 oz)-and became currency in ancient Tyre and ancient Carthage and then in ancient Israel under the Maccabees.
 W
WThe solar mass (M☉) is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately 2×1030 kg. It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. It is approximately equal to the mass of the Sun. This equates to about two nonillion (short scale) or two quintillion (long scale) kilograms:M☉ = (1.98847±0.00007)×1030 kg
 W
WThe stone or stone weight is an English and imperial unit of mass equal to 14 pounds. The stone continues in customary use in the United Kingdom and Ireland for body weight.
 W
WThis article is about the society of the Mongol Empire.
 W
WThe baht is the official currency of Thailand. It is divided into 100 satang. The issuance of currency is the responsibility of the Bank of Thailand.
 W
WThe tola also transliterated as tolah or tole, is a traditional Ancient Indian and South Asian unit of mass, now standardised as 180 troy grains or exactly 3/8 troy ounce. It was the base unit of mass in the British Indian system of weights and measures introduced in 1833, although it had been in use for much longer. It was also used in Aden and Zanzibar: in the latter, one tola was equivalent to 175.90 troy grains.
 W
WThe ton is a unit of measure. It has a long history and has acquired a number of meanings and uses over the years. It is used principally as a unit of mass. Its original use as a measurement of volume has continued in the capacity of cargo ships and in terms such as the freight ton. Recent specialised uses include the ton as a measure of energy and for truck classification. It is also a colloquial term.
 W
WThe tonne is a metric unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is commonly referred to as a metric ton in the United States. It is equivalent to approximately 2,204.6 pounds, 1.102 short tons (US) or approximately 0.984 long tons (UK). The official SI unit is the megagram, a less common way to express the same mass.
 W
WTroy weight is a system of units of mass that originated in 15th-century England, and is primarily used in the precious metals industry. The Troy weights are the grain, the pennyweight, the troy ounce, and the troy pound. The troy grain is equal to the grain-unit of the avoirdupois system, the troy ounce is heavier than the avoirdupois ounce, yet the troy pound is lighter than the avoirdupois pound.
 W
WA truss is a tight bundle of hay or straw. It would usually be cuboid, for storage or shipping, and would either be harvested into such bundles or cut from a large rick.