 W
W1390 Abastumani is a very large and dark background asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 3 October 1935, by Russian astronomer Pelageya Shajn at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. The primitive P-type asteroid has a rotation period of 17.1 hours and measures approximately 101 kilometers in diameter. It was named for the Georgian town of Abastumani.
 W
W1150 Achaia ; prov. designation: 1929 RB) is a stony background asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered by Karl Reinmuth at Heidelberg Observatory on 2 September 1929. The S-type asteroid has a notably long rotation period of hours 61 hours and measures approximately 7.8 kilometers in diameter. It is named for the Greek region of Achaia.
 W
W6522 Aci is an elongated Phocaea asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 9 July 1991, by American astronomer Eleanor Helin at Palomar Observatory in California, United States. The likely stony S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 5.65 hours and measures approximately 6 kilometers in diameter. It was named for the Jaci river at Acireale in Italy, and refers to the myth of Acis and Galatea.
 W
W744 Aguntina, provisional designation 1913 QW, is a rare-type carbonaceous asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, about 60 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered by Austrian astronomer Joseph Rheden at Vienna Observatory, Austria, on 26 February 1913.
 W
WAlma is an asteroid from the intermediate asteroid belt, approximately 24 kilometers in diameter. It was Guillaume Bigourdan's only asteroid discovery. He discovered it on 24 March 1894 in Paris.
 W
WAmherstia was the 8th asteroid discovered by Raymond Smith Dugan, and was named after Amherst College, his alma mater. Amherstia is a large M-type asteroid, with an estimated diameter of 73 km. It follows an eccentric orbit between Jupiter and Mars, with an orbital period of 4.39 years.
 W
W1957 Angara is a stony Eos asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 18 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 1 April 1970, by Soviet astronomer Lyudmila Chernykh at the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory in Nauchnyj, and named after the Siberian Angara River.
 W
WAngelina is an asteroid from the central region of the asteroid belt, approximately 50 kilometers in diameter. It is an unusually bright form of E-type asteroid.
 W
W791 Ani is a very large asteroid of the Meliboea family, located in the outer regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 29 June 1914, by Russian astronomer Grigory Neujmin at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. The dark carbonaceous C-type asteroid has a rotation period of 11.2 hours and measures approximately 65.7 × 103.5 kilometers, with a mean-diameter of 100 km (62 mi). It was named after the historic Armenian city of Ani.
 W
W1457 Ankara, provisional designation 1937 PA, is a stony asteroid from the central region of the asteroid belt, approximately 18 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 3 August 1937, by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth at Heidelberg Observatory in southwest Germany, and later named for the Turkish capital city of Ankara.
 W
W1294 Antwerpia (prov. designation: 1933 UB1) is a dark background asteroid from the central regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 24 October 1933, by astronomer Eugène Delporte at the Royal Observatory of Belgium in Uccle. The carbonaceous C-type asteroid has a rotation period of 6.6 hours and measures approximately 35 kilometers (22 miles) in diameter. It was named for the Belgian city of Antwerp.
 W
W1768 Appenzella is a rare-type Nysian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 20 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 23 September 1965, by Swiss astronomer Paul Wild at Zimmerwald Observatory near Bern, Switzerland. It was later named after the Swiss canton of Appenzell.
 W
WAusonia is a stony Vestian asteroid from the inner region of the asteroid belt, approximately 100 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered by Italian astronomer Annibale de Gasparis on 10 February 1861, from the Astronomical Observatory of Capodimonte, in Naples, Italy. The initial choice of name for the asteroid was "Italia", after Italy, but this was modified to Ausonia, an ancient classical name for the Italian region.
 W
W333 Badenia is a large background asteroid, approximately 72 kilometers in diameter, located the outer region of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 22 August 1892, by astronomer Max Wolf at the Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory in southwest Germany. The carbonaceous C-type asteroid has a rotation period of 9.9 hours. It was named after the historical Grand Duchy of Baden that existed until 1918, and where the discovering observatory is located. Badenia was the first asteroid to receive a provisional designation.
 W
W770 Bali is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. It is a member of the Flora family. It was discovered on 31 October 1913, by German astronomer Adam Massinger at the Heidelberg Observatory in southwest Germany. The asteroid was probably named after the Indonesian island of Bali, as the discoverer had named a couple other asteroids after places in Indonesia. The alternative hypothesis is that it was named after Bali, king of the Daityas in Hindu mythology.
 W
WBamberga is one of the largest asteroids in the asteroid belt. It was discovered by Johann Palisa on 25 February 1892 in Vienna. It is one of the top-20 largest asteroids in the asteroid belt. Apart from the near-Earth asteroid Eros, it was the last asteroid which is ever easily visible with binoculars to be discovered.
 W
WBavaria is a carbonaceous background asteroid from the intermediate asteroid belt, approximately 54 kilometers. It was discovered by Johann Palisa on 16 November 1890 in Vienna.
 W
W1349 Bechuana, provisional designation 1934 LJ, is a background asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 26 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 13 June 1934, by South-African astronomer Cyril Jackson at the Union Observatory in Johannesburg. The asteroid was named for the former Bechuanaland, what is now the Republic of Botswana.
 W
WBohemia is a sizeable Main belt asteroid. It was discovered by Auguste Charlois on 16 July 1893 in Nice.
 W
W361 Bononia is a very large, resonant Hilda asteroid located in the outermost region of the asteroid belt. It is classified as a D-type asteroid and is probably composed of organic rich silicates, carbon and anhydrous silicates. It was discovered by Auguste Charlois on 11 March 1893, in Nice, and assigned the prov. designations A893 EF and 1893 P.
 W
W3544 Borodino (prov. designation: 1977 RD4) is a stony background asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 9 kilometers (5.6 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 7 September 1977, by Soviet astronomer Nikolai Chernykh at the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory in Nauchnij, on the Crimean peninsula. The likely elongated S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 5.44 hours. It was named for the Russian village of Borodino where the Battle of Borodino took place.
 W
WBruna is a main belt asteroid that was discovered on 20 March 1890 by Johann Palisa, an Austrian astronomer at the Vienna Observatory.
 W
WCalifornia is an asteroid belonging to the Flora family in the Main Belt. It has an unusually high albedo.
 W
W1245 Calvinia is a stony Koronian asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 30 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 26 May 1932, by South African astronomer Cyril Jackson at the Union Observatory in Johannesburg. The S-type asteroid is likely elongated and has a rotation period of 4.9 hours. It was named for the city of Calvinia in South Africa.
 W
WCampania is a large main belt asteroid that was discovered by French astronomer Auguste Charlois on 20 September 1893 in Nice.
 W
W1391 Carelia is a stony background asteroid from the central region of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 16 February 1936, by Finnish astronomer Yrjö Väisälä at Turku Observatory in Southwest Finland. The S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 5.9 hours and measures approximately 11 kilometers in diameter. It was named for the Northeast European region of Karelia.
 W
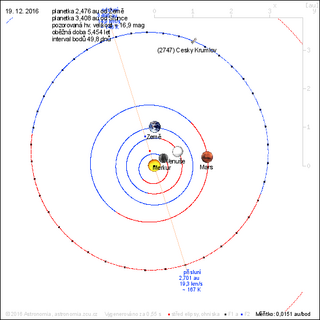
W2747 Český Krumlov, provisional designation 1980 DW, is a carbonaceous asteroid and slow rotator from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 22 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered by Czech astronomer Antonín Mrkos at Kleť Observatory on 19 February 1980, and named for the Czech town of Český Krumlov.
 W
W1333 Cevenola, provisional designation 1934 DA, is a binary Eunomian asteroid from the asteroid belt, approximately 15 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 20 February 1934, by French astronomer Odette Bancilhon at Algiers Observatory, Algeria in Northern Africa. It was named after the French mountain-range Cévennes, via the Occitan feminine adjective/demonym cevenòla.
 W
WChicago is a very large main-belt asteroid. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of carbonaceous material.
 W
W1633 Chimay, provisional designation 1929 EC, is a Themistian asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 37 kilometers in diameter.
 W
W1125 China (prov. designation: 1957 UN1) is a dark background asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 30 October 1957, by astronomer Zhāng Yùzhé (Y. C. Chang,张钰哲) at the Chinese Purple Mountain Observatory(紫金山天文台) in Nanjing, and named in honor of the country China. The assumed C-type asteroid has a short rotation period of 5.4 hours and measures approximately 26 kilometers (16 miles) in diameter. Its name and number were actually taken from another asteroid that was considered a lost asteroid at the time, but was eventually rediscovered and given the new designation 3789 Zhongguo. "Zhongguo" means "China" in Chinese (1928 UF).
 W
W1135 Colchis ; prov. designation: 1929 TA) is a background asteroid from the central region of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 3 October 1929, by Soviet astronomer Grigory Neujmin at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. The X-type asteroid has a rotation period of hours 23.5 and measures approximately 49 kilometers in diameter. It was named for the ancient Kingdom of Colchis.
 W
WComacina is a minor planet orbiting the Sun.
 W
WCremona is a minor planet orbiting the Sun.
 W
W1140 Crimea, provisional designation 1929 YC, is a stony asteroid from the middle region of the asteroid belt, approximately 28 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 30 December 1929, by Soviet astronomer Grigory Neujmin at Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula, after which it was named.
 W
W1419 Danzig is a highly elongated Flora asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 5 September 1929, by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth at Heidelberg Observatory in southwest Germany. The stony S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 8.1 hours and measures approximately 14 kilometers in diameter. It was named for the city of Gdańsk.
 W
W1244 Deira is a dark background asteroid and slow rotator from the inner region of the asteroid belt. The X-type asteroid has an exceptionally long rotation period of 210.6 hours and measures approximately 31 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 25 May 1932, by English-born South African astronomer Cyril Jackson at the Union Observatory in Johannesburg, who named it after Deira, an old kingdom near his birthplace, the market town of Ossett, located in West Yorkshire, England.