 W
WProteomics is the large-scale study of proteins. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, with many functions. The proteome is the entire set of proteins that is produced or modified by an organism or system. Proteomics has enabled the identification of ever increasing numbers of protein. This varies with time and distinct requirements, or stresses, that a cell or organism undergoes. Proteomics is an interdisciplinary domain that has benefitted greatly from the genetic information of various genome projects, including the Human Genome Project. It covers the exploration of proteomes from the overall level of protein composition, structure, and activity. It is an important component of functional genomics.
 W
WActivity-based proteomics, or activity-based protein profiling (ABPP) is a functional proteomic technology that uses chemical probes that react with mechanistically related classes of enzymes.
 W
WIn molecular biology, biochips are essentially miniaturized laboratories that can perform hundreds or thousands of simultaneous biochemical reactions. Biochips enable researchers to quickly screen large numbers of biological analytes for a variety of purposes, from disease diagnosis to detection of bioterrorism agents. Digital microfluidic biochips have become one of the most promising technologies in many biomedical fields. In a digital microfluidic biochip, a group of (adjacent) cells in the microfluidic array can be configured to work as storage, functional operations, as well as for transporting fluid droplets dynamically.
 W
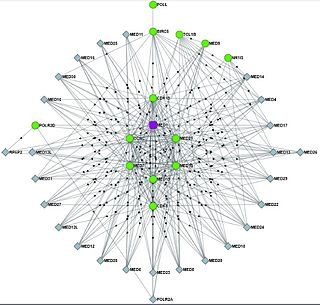
WBioPlex is an open access resource for studying protein-protein interactions. It is the result of collaborations between Harvard Medical School and Biogen. BioPlex 1.0 reported 23,744 interactions among 7,668 proteins. BioPlex 2.0 extended those observations to detect over 29,000 new interactions.
 W
WBottom-up proteomics is a common method to identify proteins and characterize their amino acid sequences and post-translational modifications by proteolytic digestion of proteins prior to analysis by mass spectrometry. The major alternative workflow used in proteomics is called top-down proteomics where intact proteins are purified prior to digestion and/or fragmentation either within the mass spectrometer or by 2D electrophoresis. Essentially, bottom-up proteomics is a relatively simple and reliable means of determining the protein make-up of a given sample of cells, tissues, etc.
 W
WDegradomics is a sub-discipline of biology encompassing all the genomic and proteomic approaches devoted to the study of proteases, their inhibitors, and their substrates on a system-wide scale. This includes the analysis of the protease and protease-substrate repertoires, also called "protease degradomes". The scope of these degradomes can range from cell, tissue, and organism-wide scales.
 W
WDeproteination is the process of eliminating protein from some live materials. This procedure is particularly common in studies on the inorganic part of bone, teeth and shells.
 W
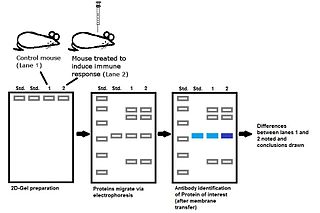
WAn electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) or mobility shift electrophoresis, also referred as a gel shift assay, gel mobility shift assay, band shift assay, or gel retardation assay, is a common affinity electrophoresis technique used to study protein–DNA or protein–RNA interactions. This procedure can determine if a protein or mixture of proteins is capable of binding to a given DNA or RNA sequence, and can sometimes indicate if more than one protein molecule is involved in the binding complex. Gel shift assays are often performed in vitro concurrently with DNase footprinting, primer extension, and promoter-probe experiments when studying transcription initiation, DNA replication, DNA repair or RNA processing and maturation, as well as pre-mRNA splicing. Although precursors can be found in earlier literature, most current assays are based on methods described by Garner and Revzin and Fried and Crothers.
 W
WFast parallel proteolysis (FASTpp) is a method to determine the thermostability of proteins by measuring which fraction of protein resists rapid proteolytic digestion.
 W
WThe Human Proteome Folding Project (HPF) is a collaborative effort between New York University, the Institute for Systems Biology (ISB) and the University of Washington, using the Rosetta software developed by the Rosetta Commons.
 W
WImmunoproteomics is the study of large sets of proteins (proteomics) involved in the immune response.
 W
WLys-N is a metalloendopeptidase found in the mushroom Grifola frondosa that cleaves proteins on the amino side of lysine residues.
 W
WPROSITE is a protein database. It consists of entries describing the protein families, domains and functional sites as well as amino acid patterns and profiles in them. These are manually curated by a team of the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics and tightly integrated into Swiss-Prot protein annotation. PROSITE was created in 1988 by Amos Bairoch, who directed the group for more than 20 years. Since July 2018, the director of PROSITE and Swiss-Prot is Alan Bridge.
 W
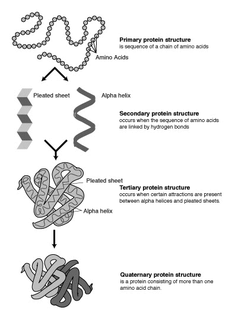
WProteins are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity.
 W
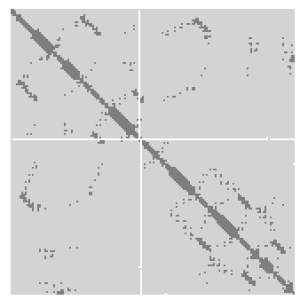
WA protein contact map represents the distance between all possible amino acid residue pairs of a three-dimensional protein structure using a binary two-dimensional matrix. For two residues and , the element of the matrix is 1 if the two residues are closer than a predetermined threshold, and 0 otherwise. Various contact definitions have been proposed: The distance between the Cα-Cα atom with threshold 6-12 Å; distance between Cβ-Cβ atoms with threshold 6-12 Å ; and distance between the side-chain centers of mass.
 W
WProtein mass spectrometry refers to the application of mass spectrometry to the study of proteins. Mass spectrometry is an important method for the accurate mass determination and characterization of proteins, and a variety of methods and instrumentations have been developed for its many uses. Its applications include the identification of proteins and their post-translational modifications, the elucidation of protein complexes, their subunits and functional interactions, as well as the global measurement of proteins in proteomics. It can also be used to localize proteins to the various organelles, and determine the interactions between different proteins as well as with membrane lipids.
 W
WProtein sequencing is the practical process of determining the amino acid sequence of all or part of a protein or peptide. This may serve to identify the protein or characterize its post-translational modifications. Typically, partial sequencing of a protein provides sufficient information to identify it with reference to databases of protein sequences derived from the conceptual translation of genes.
 W
WThis list of protein structure prediction software summarizes notable used software tools in protein structure prediction, including homology modeling, protein threading, ab initio methods, secondary structure prediction, and transmembrane helix and signal peptide prediction.
 W
WProtein–protein interactions (PPIs) are physical contacts of high specificity established between two or more protein molecules as a result of biochemical events steered by interactions that include electrostatic forces, hydrogen bonding and the hydrophobic effect. Many are physical contacts with molecular associations between chains that occur in a cell or in a living organism in a specific biomolecular context.
 W
WProteogenomics is a field of biological research that utilizes a combination of proteomics, genomics, and transcriptomics to aid in the discovery and identification of peptides. Proteogenomics is used to identify new peptides by comparing MS/MS spectra against a protein database that has been derived from genomic and transcriptomic information. Proteogenomics often refers to studies that use proteomic information, often derived from mass spectrometry, to improve gene annotations. Genomics deals with the genetic code of entire organisms, while transcriptomics deals with the study of RNA sequencing and transcripts. Proteomics utilizes tandem mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography to identify and study the functions of proteins. Proteomics is being utilized to discover all the proteins expressed within an organism, known as its proteome. The issue with proteomics is that it relies on the assumption that current gene models are correct and that the correct protein sequences can be found using a reference protein sequence database; however, this is not always the case as some peptides cannot be located in the database. In addition, novel protein sequences can occur through mutations. these issues can be fixed with the use of proteomic, genomic, and trancriptomic data. The utilization of both proteomics and genomics led to proteogenomics which became its own field in 2004..
 W
WThe proteome is the entire set of proteins that is, or can be, expressed by a genome, cell, tissue, or organism at a certain time. It is the set of expressed proteins in a given type of cell or organism, at a given time, under defined conditions. Proteomics is the study of the proteome.
 W
WQuantitative proteomics is an analytical chemistry technique for determining the amount of proteins in a sample. The methods for protein identification are identical to those used in general proteomics, but include quantification as an additional dimension. Rather than just providing lists of proteins identified in a certain sample, quantitative proteomics yields information about the physiological differences between two biological samples. For example, this approach can be used to compare samples from healthy and diseased patients. Quantitative proteomics is mainly performed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) or mass spectrometry (MS). However, a recent developed method of quantitative dot blot (QDB) analysis is able to measure both the absolute and relative quantity of an individual proteins in the sample in high throughput format, thus open a new direction for proteomic research. In contrast to 2-DE, which requires MS for the downstream protein identification, MS technology can identify and quantify the changes.
 W
WSelected reaction monitoring (SRM) is a method used in tandem mass spectrometry in which an ion of a particular mass is selected in the first stage of a tandem mass spectrometer and an ion product of a fragmentation reaction of the precursor ion is selected in the second mass spectrometer stage for detection.
 W
WStable Isotope Labeling by/with Amino acids in Cell culture (SILAC) is a technique based on mass spectrometry that detects differences in protein abundance among samples using non-radioactive isotopic labeling. It is a popular method for quantitative proteomics.
 W
WTop-down proteomics is a method of protein identification that either uses an ion trapping mass spectrometer to store an isolated protein ion for mass measurement and tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) analysis or other protein purification methods such as two-dimensional gel electrophoresis in conjunction with MS/MS. Top-down proteomics is capable of identifying and quantitating unique proteoforms through the analysis of intact proteins. The name is derived from the similar approach to DNA sequencing. During mass spectrometry intact proteins are typically ionized by electrospray ionization and trapped in a Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance, quadrupole ion trap or Orbitrap mass spectrometer. Fragmentation for tandem mass spectrometry is accomplished by electron-capture dissociation or electron-transfer dissociation. Effective fractionation is critical for sample handling before mass-spectrometry-based proteomics. Proteome analysis routinely involves digesting intact proteins followed by inferred protein identification using mass spectrometry (MS). Top-down MS (non-gel) proteomics interrogates protein structure through measurement of an intact mass followed by direct ion dissociation in the gas phase.
 W
WUniProt is a freely accessible database of protein sequence and functional information, many entries being derived from genome sequencing projects. It contains a large amount of information about the biological function of proteins derived from the research literature. It is maintained by the UniProt consortium, which consists of several European bioinformatics organisations and a foundation from Washington, DC, United States.
 W
WZFP82 zinc finger protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZFP82 gene.
 W
WZinc finger protein 112 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF112 gene.
 W
WZinc finger protein 180 is a protein that is encoded in humans by the ZNF180 gene.
 W
WZinc finger protein 208 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF208 gene.
 W
WZinc finger protein 226 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF226 gene.
 W
WZinc finger protein 395 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF395 gene.
 W
WZinc finger protein 426 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF426 gene.
 W
WZinc finger protein 557 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF557 gene.
 W
WZinc finger protein 576 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF576 gene.
 W
WZinc finger protein 613 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF613 gene.
 W
WZinc finger protein 839 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF839 gene.