 W
WA unit of volume is a unit of measurement for measuring volume or capacity, the extent of an object or space in three dimensions. Units of capacity may be used to specify the volume of fluids or bulk goods, for example water, rice, sugar, grain or flour.
 W
WThe acre-foot is a non-SI unit of volume commonly used in the United States in reference to large-scale water resources, such as reservoirs, aqueducts, canals, sewer flow capacity, irrigation water, and river flows.
 W
WBags have been used as standard measures for a variety of commodities which were actually supplied in bags or sacks. These include:Cement is commonly sold in bags of 94 pounds weight, because this is about 1 cubic foot of powdered cement. Agricultural produce in England was sold in bags which varied in capacity depending on the place and the commodity. Examples include:a bag of wheat in Staffordshire would contain 3 Winchester bushels while a bag of oats would contain 6 standard bushels. in the West Country, apples would be sold in bags of from 16 to 24 gallons. A measure of 24 gallons was known as the Cornish bushel.Bags are used as units by the National Agricultural Statistics Service of the United States Department of Agriculture for the following commodities:coffee = 60 kg flour = 100 pounds grapefruit = 40 pounds rice = 100 pounds
 W
WA barrel is one of several units of volume applied in various contexts; there are dry barrels, fluid barrels, oil barrels, and so forth. For historical reasons the volumes of some barrel units are roughly double the volumes of others; volumes in common use range approximately from 100 to 200 litres. In many connections the term drum is used almost interchangeably with barrel.
 W
WA bushel is an imperial and US customary unit of volume based upon an earlier measure of dry capacity. The old bushel is equal to 2 kennings (obsolete), 4 pecks, or 8 dry gallons, and was used mostly for agricultural products, such as wheat. In modern usage, the volume is nominal, with bushels denoting a mass defined differently for each commodity.
 W
WThe cord is a unit of measure of dry volume used to measure firewood and pulpwood in the United States and Canada.
 W
WIn classical antiquity, the cotyla or cotyle was a measure of capacity among the Romans and Greeks: by the former it was also called hemina; by the latter, τρυβλίον and ἡμίνα or ἡμίμνα. It was the half of the sextarius or ξέστης, and contained six cyathi, or nearly half a pint English.
 W
WA cubic centimetre is a commonly used unit of volume that corresponds to the volume of a cube that measures 1 cm x 1 cm × 1 cm. One cubic centimetre corresponds to a volume of one millilitre. The mass of one cubic centimetre of water at 3.98 °C is closely equal to one gram.
 W
WThe cubic inch is a unit of volume in the Imperial units and United States customary units systems. It is the volume of a cube with each of its three dimensions being one inch long which is equivalent to 1/231 of a US gallon.
 W
WThe cubic metre or cubic meter is the SI derived unit of volume. Its SI symbol is m3. It is the volume of a cube with edges one metre in length. An alternative name, which allowed a different usage with metric prefixes, was the stère, still sometimes used for dry measure. Another alternative name, no longer widely used, was the kilolitre.
 W
WThe cup is a cooking measure of volume, commonly associated with cooking and serving sizes. It is traditionally equal to half a liquid pint in US customary units, or an amount between 200 ml and 250 ml in the metric system, which may vary due to location. Because actual drinking cups may differ greatly from the size of this unit, standard measuring cups are usually used instead.
 W
WThe demiard is a traditional unit of volume originating in pre-revolutionary France. After the revolution, when the metric system was introduced in France, the demiard persisted in Louisiana, Quebec, and other French-speaking areas of North America.
 W
WA dessert spoon is a spoon designed specifically for eating dessert and sometimes used for soup or cereals. Similar in size to a soup spoon but with an oval rather than round bowl, it typically has a capacity around twice that of a teaspoon.
 W
WA fifth is a unit of volume formerly used for wine and distilled beverages in the United States, equal to one fifth of a US liquid gallon, 4⁄5 quart, or 25 3⁄5 US fluid ounces (757 ml); it has been superseded by the metric bottle size of 750 mL, sometimes called a metric fifth, which is the standard capacity of wine bottles worldwide and is approximately 1% smaller.
 W
WThe firlot was a dry measure used in Scotland. For centuries it was the primary measure for all grains sold in the country. In the Scottish system a firlot was equal to 4 pecks, and the boll was equal to 4 firlots.
 W
WThe gallon is a unit of measurement for volume and fluid capacity in both the US customary units and the British imperial systems of measurement. Three significantly different sizes are in current use:the imperial gallon, defined as 4.54609 litres, which is used in the United Kingdom, Canada, and some Caribbean nations; the US gallon defined as 231 cubic inches, which is used in the US and some Latin American and Caribbean countries; and the US dry gallon ("usdrygal"), defined as 1⁄8 US bushel.
 W
WThe gill or teacup is a unit of measurement for volume equal to a quarter of a pint. It is no longer in common use, except in regard to the volume of alcoholic spirits measures.In imperial units In United States customary units
 W
WThe earliest recorded systems of weights and measures originate in the 3rd or 4th millennium BC. Even the very earliest civilizations needed measurement for purposes of agriculture, construction, and trade. Early standard units might only have applied to a single community or small region, with every area developing its own standards for lengths, areas, volumes and masses. Often such systems were closely tied to one field of use, so that volume measures used, for example, for dry grains were unrelated to those for liquids, with neither bearing any particular relationship to units of length used for measuring cloth or land. With development of manufacturing technologies, and the growing importance of trade between communities and ultimately across the Earth, standardized weights and measures became critical. Starting in the 18th century, modernized, simplified and uniform systems of weights and measures were developed, with the fundamental units defined by ever more precise methods in the science of metrology. The discovery and application of electricity was one factor motivating the development of standardized internationally applicable units.
 W
WA hogshead is a large cask of liquid. More specifically, it refers to a specified volume, measured in either imperial or US customary measures, primarily applied to alcoholic beverages, such as wine, ale, or cider.
 W
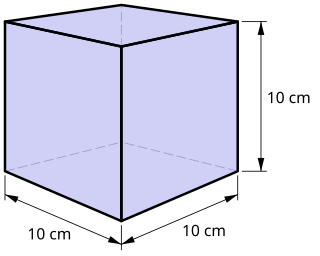
WThe litre or liter is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metre (m3). A cubic decimetre occupies a volume of 10 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm and is thus equal to one-thousandth of a cubic metre.
 W
WMaß or Mass is the German word describing the amount of beer in a regulation mug; in modern times exactly 1 liter (33.8 U.S. fl oz). The same word is also often used as an abbreviation for Maßkrug, the handled drinking vessel containing it, ubiquitous in Bavarian beer gardens and beer halls, and a staple of Oktoberfest. This vessel is often referred to as a beer mug by English speakers, and can be correctly called a beer stein if made of stoneware and capable of holding a regulation Maß of beer.
 W
WA masu was originally a square wooden box used to measure rice in Japan during the feudal period. Masu existed in many sizes, typically covering the range from one to to one gō.
 W
WA measuring cup or measuring jug is a kitchen utensil used primarily to measure the volume of liquid or bulk solid cooking ingredients such as flour and sugar, especially for volumes from about 50 mL (2 fl oz) upwards. Measuring cups are also used to measure washing powder, liquid detergents and bleach for clothes washing. The cup will usually have a scale marked in cups and fractions of a cup, and often with fluid measure and weight of a selection of dry foodstuffs.
 W
WA measuring spoon is a spoon used to measure an amount of an ingredient, either liquid or dry, when cooking. Measuring spoons may be made of plastic, metal, and other materials. They are available in many sizes, including the teaspoon and tablespoon.
 W
WA fluid ounce is a unit of volume typically used for measuring liquids. Various definitions have been used throughout history, but only two are still in common use: the British Imperial and the United States customary fluid ounce.
 W
WA peck is an imperial and United States customary unit of dry volume, equivalent to 2 dry gallons or 8 dry quarts or 16 dry pints. An imperial peck is equivalent to 9.09 liters and a US customary peck is equivalent to 8.81 liters. Two pecks make a kenning (obsolete), and four pecks make a bushel. Although the peck is no longer widely used, some produce, such as apples, are still often sold by the peck in the USA.
 W
WThe pint is a unit of volume or capacity in both the imperial and United States customary measurement systems. In both of those systems it is traditionally one eighth of a gallon. The British imperial pint is about 1⁄5 larger than the American pint because the two systems are defined differently. Almost all other countries have standardized on the metric system, so the size of what may be called a pint varies depending on local custom.
 W
WThe measures of the old Romanian system varied greatly not only between the three Romanian states, but sometimes also inside the same country. The origin of some of the measures are the Latin, Slavic, Greek and Turkish systems.
 W
WThe Sāʿ
 W
WA Seer is a traditional unit of mass and volume used in large parts of Asia prior to the middle of the 20th century. It remains in use only in a few countries such as Afghanistan, Iran, and parts of India although in Iran it indicates a smaller unit of weight than the one used in India.
 W
WA ser is an obsolete unit of dry volume in India. In 1871 it was defined as being exactly 1 litre. After metrication in the mid-20th century, the unit became obsolete.It was the unit in pre-modern India which was so close to the metric values of volume approx equal to a litre.
 W
WA standard or standard hundred was a measure of timber used in trade.
 W
WA standard drink is a measure of alcohol consumption representing a hypothetical beverage which contains a fixed amount of pure alcohol. A standard drink varies in volume depending on the alcohol concentration of the beverage, but it always contains the same amount of alcohol and therefore produces the same amount of drunkenness.
 W
WThe stere or stère (st) is a unit of volume in the original metric system equal to one cubic metre. The name was coined from the Greek στερεός stereos, "solid", in 1793 France as a metric analogue to the cord. The stère is typically used for measuring large quantities of firewood or other cut wood, while the cubic meter is used for uncut wood. It is not part of the modern metric system (SI).
 W
WStuck was a form occasionally found in English writing as a corruption of the German "Stück", itself an abbreviation of Stückfass, referring to the volume of a wine cask of around 1000-1200 litres. It was normally used in reference to German wine production.
 W
WA tablespoon is a large spoon. In many English-speaking regions, the term now refers to a large spoon used for serving; however, in some regions, it is the largest type of spoon used for eating.
 W
WA teaspoon (tsp.) is an item of cutlery. It is a small spoon that can be used to stir a cup of tea or coffee, or as a tool for measuring volume. The size of teaspoons ranges from about 2.5 to 7.3 mL. For cooking purposes and, more importantly, for dosing of medicine, a teaspoonful is defined as 5 mL, and standard measuring spoons are used.
 W
WTmcft, (Tmc ft), (TMC), (tmc), is the abbreviation of one thousand million cubic feet (1,000,000,000 = 109 = 1 billion), commonly used in India in reference to volume of water in a reservoir or river flow.
 W
WThe ton is a unit of measure. It has a long history and has acquired a number of meanings and uses over the years. It is used principally as a unit of mass. Its original use as a measurement of volume has continued in the capacity of cargo ships and in terms such as the freight ton. Recent specialised uses include the ton as a measure of energy and for truck classification. It is also a colloquial term.