 W
WThe Ames Research Center (ARC), also known as NASA Ames, is a major NASA research center at Moffett Federal Airfield in California's Silicon Valley. It was founded in 1939 as the second National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) laboratory. That agency was dissolved and its assets and personnel transferred to the newly created National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) on October 1, 1958. NASA Ames is named in honor of Joseph Sweetman Ames, a physicist and one of the founding members of NACA. At last estimate NASA Ames has over US$3 billion in capital equipment, 2,300 research personnel and a US$860 million annual budget.
 W
WThe Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory is a not-for-profit university-affiliated research center (UARC) in Howard County, Maryland. It is affiliated with Johns Hopkins University and employs 7,200 people (2020). The lab serves as a technical resource for the Department of Defense, NASA, and other government agencies. APL has developed numerous systems and technologies in the areas of air and missile defense, surface and undersea naval warfare, computer security, and space science and spacecraft construction. While APL provides research and engineering services to the government, it is not a traditional defense contractor, as it is a UARC and a division of Johns Hopkins University. APL is a scientific and engineering research and development division, rather than an academic division, of Johns Hopkins.
 W
WThe NASA Neil A. Armstrong Flight Research Center (AFRC) is an aeronautical research center operated by NASA. Its primary campus is located inside Edwards Air Force Base in California and is considered NASA's premier site for aeronautical research. AFRC operates some of the most advanced aircraft in the world and is known for many aviation firsts, including critical support for the first crewed airplane to exceed the speed of sound in level flight with the Bell X-1, highest speed ever recorded by a crewed, powered aircraft, the first pure digital fly-by-wire aircraft, and many others. AFRC also operates a second site in Palmdale, Ca. known as Building 703, once the former Rockwell International/North American Aviation production facility, next to Air Force Plant 42. There, AFRC houses and operates several of NASA's Science Mission Directorate aircraft including SOFIA, a DC-8 Flying Laboratory, a Gulfstream C-20A UAVSAR and ER-2 High Altitude Platform. David McBride is currently the center's director.
 W
WRobert Aubinière (1912-2001) was a French military, born in Paris. He was director of CNES (1961-1972) and ELDO Secretaries General (1972-1975).
 W
WThe British National Space Centre (BNSC) was an agency of the Government of the United Kingdom, organised in 1985, that coordinated civil space activities for the UK. It was replaced on 1 April 2010 by the United Kingdom Space Agency (UKSA).
 W
WChōfu Aerospace Center is the headquarters and main development facility for the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA).
 W
WThe Columbus Control Centre also known by its radio callsign, Mission Control Munich, is the mission control centre which is used to control the Columbus research laboratory, which is part of the International Space Station (ISS). The control centre is located at the German Aerospace Center (DLR) facility in Oberpfaffenhofen near Munich, Germany. The centre is operated by the DLR, under contract from the European Space Agency (ESA).
 W
WEdwards Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force installation located in Kern County in Edwards, California, about 22 miles (35 km) northeast of Lancaster, 15 miles (24 km) east of Rosamond and 5.5 miles (8.9 km) south of California City.
 W
WThe European Astronaut Centre (EAC), is an establishment of the European Space Agency and home of the European Astronaut Corps. It is near to Cologne, Germany, and is subdivided into six separate arms, these being Astronaut Training, Space Medicine, Astronaut Management, Human Exploration of the Moon as part of the Spaceship EAC initiative and Communications. It provides training facilities for European and international partner astronauts, particularly regarding ESA hardware for the ISS such as Columbus and formerly the ATV. The overall European Astronaut Centre organisation is also in charge of the organisation of the training of European astronauts in the centers of other partners, such as the United States, Russia, Canada (Saint-Hubert) or Japan (Tsukuba).
 W
WThe European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) serves as the main mission control centre for the European Space Agency (ESA) and is located in Darmstadt, Germany. ESOC's primary function is the operation of unmanned spacecraft on behalf of ESA and the launch and early orbit phases (LEOP) of ESA and third-party missions. The Centre is also responsible for a range of operations-related activities within ESA and in cooperation with ESA's industry and international partners, including ground systems engineering, software development, flight dynamics and navigation, development of mission control tools and techniques and space debris studies.
 W
WThe European Space Research and Technology Centre (ESTEC) is the European Space Agency's main technology development and test centre for spacecraft and space technology. It is situated in Noordwijk, South Holland, in the western Netherlands, although several kilometers off the village but immediately linked to the most Northern district of the nearby town Katwijk.
 W
WThe Flight Research Laboratory at NASA's Langley Research Center houses fixed and rotary wing aircraft used in atmospheric and flight research. It also housed simulation equipment used during the Gemini and Apollo programs such as the Rendezvous Docking Simulator and Projector Planetarium.
 W
WThe German Aerospace Center, abbreviated DLR, is the national center for aerospace, energy and transportation research of Germany. Its headquarters are located in Cologne and it has multiple other locations throughout Germany. The DLR is engaged in a wide range of research and development projects in national and international partnerships. In addition to conducting its own research projects, DLR also acts as the German space agency. As such, it is responsible for planning and implementing the German space programme on behalf of the German federal government. As a project management agency, DLR also coordinates and answers the technical and organisational implementation of projects funded by a number of German federal ministries.
 W
WNASA John H. Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field is a NASA center within the cities of Brook Park and Cleveland between Cleveland Hopkins International Airport and the Rocky River Reservation of Cleveland Metroparks, with a subsidiary facility in Sandusky, Ohio. Its director is Marla E. Pérez-Davis. Glenn Research Center is one of ten major NASA facilities, whose primary mission is to develop science and technology for use in aeronautics and space. As of May 2012, it employed about 1,650 civil servants and 1,850 support contractors on or near its site.
 W
WThe Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) is a laboratory in the Earth Sciences Division of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center affiliated with the Columbia University Earth Institute. The institute is located at Columbia University in New York City.
 W
WThe Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately 6.5 miles (10.5 km) northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC employs approximately 10,000 civil servants and contractors. It is one of ten major NASA field centers, named in recognition of American rocket propulsion pioneer Robert H. Goddard. GSFC is partially within the former Goddard census-designated place; it has a Greenbelt mailing address.
 W
WIndian Institute of Space Science and Technology (IIST) is a government-aided institute and deemed university for the study and research of space science, located at Valiamala, Nedumangad, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala. It is the first university in Asia to be solely dedicated to the study and research of Outer space. It was inaugurated on 14 September 2007 by G. Madhavan Nair, the then Chairman of ISRO. IIST was set up by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) under the Department of Space, Government of India. A. P. J. Abdul Kalam, former President of India, was the Chancellor of IIST. IIST offers regular engineering undergraduate, postgraduate and doctorate programmes with focus on space science, technology and applications.
 W
WThe ISRO Propulsion Complex (IPRC), located at Mahendragiri of Tamil Nadu, is an Indian Space Research Organisation centre involved in testing, assembling, and integrating propulsion systems and stages that are developed at ISRO's Liquid Propulsion Systems Centres. Formerly, IPRC was known as LPSC, Mahendragiri, functioning under LPSC. It was elevated as an independent centre and renamed as IPRC with effect from 1 February 2014.
 W
WThe Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a federally funded research and development center and NASA field center in the city of La Cañada Flintridge, with a Pasadena mailing address, in California, United States.
 W
WThe Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center (JSC) is NASA's center for human spaceflight, where human spaceflight training, research, and flight control are conducted. It was built and leased to NASA by Joseph L. Smith & Associates, Inc. It was renamed in honor of the late US president and Texas native, Lyndon B. Johnson, by an act of the United States Senate on February 19, 1973.
 W
WThe buildings in the Johnson Space Center house facilities of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's human spaceflight activities. The center consists of a complex of 100 buildings constructed on 1,620 acres (656 ha) located in southeast Houston, Texas.
 W
WKakuda Space Center is a facility of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), located in the city of Kakuda in Miyagi Prefecture in northern Japan, specializing in the development and testing of rocket engines and space propulsion systems. The LE-5, and the LE-7 rocket enginese were developed at the Kakuda Space Center.
 W
WNASA's Independent Verification & Validation (IV&V) Program was established in 1993 as part of an agency-wide strategy to provide the highest achievable levels of safety and cost-effectiveness for mission critical software. NASA's IV&V Program was founded under the NASA Office of Safety and Mission Assurance (OSMA) as a direct result of recommendations made by the National Research Council (NRC) and the Report of the Presidential Commission on the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster.
 W
WThe Langley Research Center located in Hampton, Virginia, United States, is the oldest of NASA's field centers. It directly borders Langley Air Force Base and the Back River on the Chesapeake Bay. LaRC has focused primarily on aeronautical research, but has also tested space hardware at the facility, such as the Apollo Lunar Module. In addition, a number of the earliest high-profile space missions were planned and designed on-site, and Langley was considered a potential site for the NASA's Manned Space Center prior to the eventual selection of Houston.
 W
WLiège Space Center is a research center of the University of Liège in Belgium. It holds a hundred people, half of whom are engineers and scientists. The activities of the CSL are specialized in optics, space technologies and space environment testing.
 W
WThe Lviv Centre of the Space Research Institute of the NASU and NSAU is a Lviv branch of the actual institute.
 W
WThe George C. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), located in Huntsville, Alabama, is the U.S. government's civilian rocketry and spacecraft propulsion research center. As the largest NASA center, MSFC's first mission was developing the Saturn launch vehicles for the Apollo program. Marshall has been the lead center for the Space Shuttle main propulsion and external tank; payloads and related crew training; International Space Station (ISS) design and assembly; computers, networks, and information management; and the Space Launch System (SLS). Located on the Redstone Arsenal near Huntsville, MSFC is named in honor of General of the Army George Marshall.
 W
WThe Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF) is an 832-acre (337 ha) manufacturing complex owned by NASA in New Orleans East, a district within New Orleans, Louisiana, in the United States. Organizationally it is part of NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, and is currently a multi-tenant complex to allow commercial and government contractors, as well as government agencies, to use the site.
 W
WThere are NASA facilities across the United States and around the world. NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC provides overall guidance and political leadership to the agency. There are 10 NASA field centers, which provide leadership for and execution of NASA's work. All other facilities fall under the leadership of at least one of these field centers. Some facilities serve more than one application for historic or administrative reasons. NASA has used or supported various observatories and telescopes, and an example of this is the NASA Infrared Telescope Facility. In 2013 a NASA Office of the Inspector General's (OIG) Report recommended a Base Realignment and Closure Commission (BRAC) style organization to consolidate NASA's little used facilities. The OIG determined at least 33 of NASA's 155 facilities were underutilized.
 W
WThe Noshiro Rocket Testing Center is a facility of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), located on the coast of the Sea of Japan in the city of Noshiro in Akita Prefecture, Japan.
 W
WThe Russian Space Research Institute is the leading organization of the Russian Academy of Sciences on space exploration to benefit fundamental science. It was formerly known as the Space Research Institute of the USSR Academy of Sciences.
 W
WSagamihara Campus is a facility of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) in Sagamihara, Kanagawa Prefecture.
 W
WThe Space Applications Centre (SAC) is an institution of research in Ahmedabad under the aegis of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). It is one of the major centres of ISRO that is engaged in the research, development and demonstration of applications of space technology in the field of telecommunications, remote sensing, meteorology and satellite navigation. This includes research and development of on-board systems, ground systems and end user equipment hardware and software.
 W
WThe John C. Stennis Space Center (SSC) is a NASA rocket testing facility in Hancock County, Mississippi, on the banks of the Pearl River at the Mississippi–Louisiana border. As of 2012, it is NASA's largest rocket engine test facility. There are over 30 local, state, national, international, private, and public companies and agencies using SSC for their rocket testing facilities.
 W
WThe University of Surrey is a public research university in Guildford, England. The university received its royal charter in 1966, along with a number of other institutions following recommendations in the Robbins Report. The institution was previously known as Battersea College of Technology and was located in Battersea Park, London. Its roots however, go back to Battersea Polytechnic Institute, founded in 1891 to provide further and higher education in London, including its poorer inhabitants. The university's research output and global partnerships have led to it being regarded as one of the UK's leading research universities.
 W
WThe Swamp Works is a lean-development, rapid innovation environment at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. It was founded in 2012, when four laboratories in the Surface Systems Office were merged into an enlarged facility with a modified philosophy for rapid technology development. Those laboratories are the Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations Lab, the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Lab, the Applied Chemistry Lab, and the Life Support and Habitation Systems (LSHS) team. The first two of these are located inside the main Swamp Works building, while the other two use the facility although their primary work is located elsewhere. The team developed the Swamp Works operating philosophy from Kelly Johnson's Skunk Works, including the "14 Rules of Management", from the NASA development shops of Wernher von Braun, and from the innovation culture of Silicon Valley. The team prototypes space technologies rapidly to learn early in the process how to write better requirements, enabling them to build better products, rapidly, and at reduced cost. It was named the Swamp Works for similarity with the Skunk Works and the Phantom Works, but branded by the widespread marshes (swamps) on the Cape Canaveral property of the Kennedy Space Center. The Swamp Works was co-founded by NASA engineers and scientists Jack Fox, Rob Mueller, and Philip Metzger. The logo, a robotic alligator, was designed by Rosie Mueller, a professional designer and the spouse of Rob Mueller.
 W
WThe Toulouse Space Centre is a research and development centre of CNES. Founded on September 1968, it is located in the Rangueil-Lespinet district of Toulouse in the Haute-Garonne department in the Occitanie region. More than 1,700 employees are responsible for the development of most of the work for which CNES is responsible, with the exception of launch vehicles and their launches.
 W
WTÜBİTAK Space Technologies Research Institute or TÜBİTAK UZAY for short, is a Turkish institution carrying out research and development projects on space technology, electronics, information technology and related fields. It was established in 1985, under the name "Ankara Electronics Research and Development Institute" within the campus of Middle East Technical University (ODTÜ) in cooperation with the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey and the university in Ankara. In 1995, the organization was renamed. Since 1998, the institute houses a new building in the campus.
 W
WUsuda Deep Space Center is a facility of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. It is a spacecraft tracking station in Saku, Nagano, opened in October, 1984. The main feature of the station is a 64-meter beam waveguide antenna.
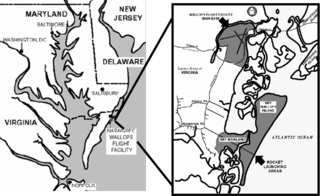 W
WWallops Flight Facility (WFF) is a rocket launch site on Wallops Island on the Eastern Shore of Virginia, United States, just east of the Delmarva Peninsula and approximately 100 miles (160 km) north-northeast of Norfolk. The facility is operated by the Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and primarily serves to support science and exploration missions for NASA and other Federal agencies. WFF includes an extensively instrumented range to support launches of more than a dozen types of sounding rockets; small expendable suborbital and orbital rockets; high-altitude balloon flights carrying scientific instruments for atmospheric and astronomical research; and, using its Research Airport, flight tests of aeronautical research aircraft, including unmanned aerial vehicles.