 W
WGemini is one of the constellations of the zodiac and is located in the northern celestial hemisphere. It was one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. Its name is Latin for twins, and it is associated with the twins Castor and Pollux in Greek mythology. Its symbol is .
 W
W1 Geminorum is a star in the constellation Gemini. Its apparent magnitude is 4.15.
 W
W3 Geminorum is a blue supergiant star in the constellation Gemini. It is a small amplitude pulsating variable and a close double star, with a mean combined apparent visual magnitude of 5.75.
 W
W6 Geminorum is a variable star in the zodiac constellation of Gemini, located roughly 5,000 light years away from the Sun. It has the variable star designation BU Geminorum; 6 Geminorum is the Flamsteed designation. At its brightest this reddish hued star is barely visible to the naked eye but is readily visible with binoculars, found southwest of M 35, below WY Geminorum. It is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +27 km/s. The star is a member of the Gemini OB1 association.
 W
WBG Geminorum is an eclipsing binary star system in the constellation Gemini. It consists of a K0 supergiant with a more massive but unseen companion. The companion is likely to be either a black hole or class B star. Material from the K0 star is being transferred to an accretion disk surrounding the unidentified object.
 W
WCastor is the second-brightest object in the zodiac constellation of Gemini and one of the brightest stars in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation α Geminorum, which is Latinised to Alpha Geminorum and abbreviated Alpha Gem or α Gem. It appears singular to the naked eye, but it is actually a sextuple star system organized into three binary pairs, made up of the stars Castor Aa, Castor Ab, Castor Ba, Castor Bb, Castor Ca, and Castor Cb. Although it is the 'α' (alpha) member of the constellation, it is fainter than 'β' (beta) Geminorum, Pollux.
 W
WDelta Geminorum, formally named Wasat, is a triple star system in the constellation of Gemini.
 W
WAl-Dhira' and similar spellings is a disused name for the two pairs of stars α and β Canis Minoris and α and β Geminorum.
 W
WDN Geminorum or Nova Geminorum 1912 was a classical nova which lit up in 1912 in the constellation Gemini. It was discovered by Norwegian variable star observer Sigurd Einbu on March 12, 1912 before reaching peak brightness, which allowed early-stage spectra to be collected by Yerkes Observatory. The nova reached a maximum brightness of around 3.5 mag before declining, which means it was visible to the naked eye. Its brightness decreased over the following 36 days by 3 magnitudes as it gradually faded from sight. The light curve saw two maxima a few months after the outburst, along with strong oscillations. Today its brightness is visual magnitude 15.5.
 W
WEpsilon Geminorum, formally named Mebsuta, is a star in the constellation of Gemini, on the outstretched right 'leg' of the twin Castor. The apparent visual magnitude of +3.06 makes it one of the brighter stars in this constellation. The distance to this star can be determined by parallax measurements, giving a value of 840 light-years, with a margin of error of 40 ly (12 pc).
 W
WThe Eskimo Nebula, also known as the Clown-faced Nebula, Lion Nebula, or Caldwell 39, is a bipolar double-shell planetary nebula (PN). It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel in 1787. The formation resembles a person's head surrounded by a parka hood. It is surrounded by gas that composed the outer layers of a Sun-like star. The visible inner filaments are ejected by a strong wind of particles from the central star. The outer disk contains unusual, light-year-long filaments.
 W
WEta Geminorum, formally named Propus, is a triple star system in the constellation of Gemini. It is a naked-eye variable star around 380 light years from the Sun.
 W
WGamma Geminorum, formally named Alhena, is the third-brightest object in the constellation of Gemini. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 1.9, making it easily visible to the naked eye even in urban regions. Based upon parallax measurements with the Hipparcos satellite, it is located at a distance of roughly 109 light-years from the Sun.
 W
WGeminga is a neutron star approximately 250 parsecs from the Sun in the constellation Gemini. Its name, attributed by its discoverer Giovanni Bignami, is both a contraction of Gemini gamma-ray source, and a transcription of the words gh'è minga, meaning "it's not there" in the Milanese dialect of Lombard.
 W
WNGC 2277 is what appears to be an open cluster in the constellation Gemini. It was first observed on 20 April 1865 by the German astronomer Heinrich Louis d'Arrest. However, it is simply an asterism formed by several stars in the sky appearing close together.
 W
WIC 443 is a galactic supernova remnant (SNR) in the constellation Gemini. On the plane of the sky, it is located near the star Eta Geminorum. Its distance is roughly 5,000 light years from Earth.
 W
WIC 444 is a small, 32 square arcminute reflection nebula in the constellation Gemini.
 W
WKoposov II is a low-luminosity globular cluster in the constellation Gemini in the halo of the Milky Way galaxy. It was discovered, along with globular cluster Koposov I by S. Koposov et al. in 2007. Koposov I and Koposov II were described by their discoverers as the "lowest luminosity globular clusters orbiting the Milky Way," along with AM 4, Palomar 1, and Whiting 1.
 W
WIn ancient Mesopotamian religion, Lugal-irra and Meslamta-ea are a set of twin gods who were worshipped in the village of Kisiga, located in northern Babylonia. They were regarded as guardians of doorways and they may have originally been envisioned as a set of twins guarding the gates of the Underworld, who chopped the dead into pieces as they passed through the gates. During the Neo-Assyrian period, small depictions of them would be buried at entrances, with Lugal-irra always on the left and Meslamta-ea always on the right. They are identical and are shown wearing horned caps and each holding an axe and a mace. They are identified with the constellation Gemini, which is named after them.
 W
WThe Medusa Nebula is a planetary nebula in the constellation of Gemini. It is also known as Abell 21 and Sharpless 2-274. It was originally discovered in 1955 by University of California, Los Angeles astronomer George O. Abell, who classified it as an old planetary nebula. Until the early 1970s, the nebula was thought to be a supernova remnant. With the computation of expansion velocities and the thermal character of the radio emission, Soviet astronomers in 1971 concluded that it was most likely a planetary nebula. As the nebula is so large, its surface brightness is very low, with surface magnitudes of between +15.99 and +25 reported.
 W
WMessier 35 or M35, also known as NGC 2168, is an open cluster of stars in the northern constellation of Gemini. It was discovered by Philippe Loys de Chéseaux around 1745 and independently discovered by John Bevis before 1750. The cluster is scattered over an area of the sky almost the size of the full moon and is located 3,870 light-years from Earth. The compact open cluster NGC 2158 lies directly southwest of M35.
 W
WMu Geminorum, formally named Tejat, is a single star in the northern constellation of Gemini. From parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is roughly 230 light-years distant from the Sun.
 W
WNGC 2129 is an open cluster in the constellation Gemini. It has an angular distance of 2.5 arcminutes and is approximately 2.2 ± 0.2 kpc from the Sun inside the Local spiral arm. At that distance, the angular size of the cluster corresponds to a diameter of about 10.4 light years. NGC 2129 is a very young cluster whose age has been estimated at 10 million years.
 W
WNGC 2158 is an open cluster in the constellation of Gemini. It is located southwest of open cluster Messier 35, and is believed to be about 2 billion years old. The two clusters are unrelated, as NGC 2158 is around 9,000 light years further away than M35.
 W
WNGC 2266 is an open cluster in the constellation Gemini. Its apparent size is 5 arc minutes. Its distance is 3,400 parsecs (11,000 ly). It was discovered by German-British astronomer William Herschel on 7 December 1785.
 W
WNGC 2291 is a lenticular galaxy in the constellation Gemini. It was discovered by John Herschel on January 22, 1827. The visual magnitude is 13, and the apparent size is 1.0 by 0.8 arc minutes.
 W
WNGC 2294 is an elliptical galaxy within the constellation Gemini, discovered by George Johnstone Stoney on February 22, 1849. The visual magnitude is 14, and the apparent size is 0.8 by 0.4 arc minutes.
 W
WNGC 2355 is an old open cluster in the constellation Gemini.
 W
WNGC 2357 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation of Gemini. It was discovered by Édouard Stephan on 6 February 1885.
 W
WNGC 2371-2 is a dual lobed planetary nebula located in the constellation Gemini. Visually, it appears like it could be two separate objects; therefore, two entries were given to the planetary nebula by John Louis Emil Dreyer in the New General Catalogue, so it may be referred to as NGC 2371, NGC 2372, or variations on this name.
 W
WNu Geminorum is a binary, and possibly a multiple star system in the constellation Gemini. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.16, which is bright enough to be visible to the naked eye on a dark night. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 5.99 mas, it is located at a distance of roughly 540 light years from the Sun.
 W
WOmega Geminorum, Latinized from ω Geminorum, is a star located in the middle of the northern zodiac constellation of Gemini. With an apparent visual magnitude of 5.18, it is faintly visible to the naked eye. According to the Bortle scale, it can be viewed from dark suburban skies. With an annual parallax shift of just 2.19 mas, it is located about 1,500 light years from the Sun.
 W
WPollux b, also designated β Geminorum b and HD 62509 b, formally named Thestias, is an extrasolar planet approximately 34 light-years away in the constellation of Gemini. This planet was discovered orbiting the star Pollux in 2006 by astronomer Artie P. Hatzes, confirming his hypothesis originally published in 1993. The planet has at least twice the mass of Jupiter. It moves around Pollux in 1.61 years at a distance of 1.64 AU in a nearly circular orbit.
 W
WPunarvasu) is a Nakshatra in Hindu astrology, which refers to the two brightest stars in the constellation of Gemini: Castor and Pollux.
 W
WRho Geminorum is a star system that lies approximately 59 light-years away in the constellation of Gemini, about 5 arcminutes east of Castor. The system consists of a primary bright enough to be seen with the naked eye, a faint secondary which has rarely been observed even professionally, and a distant, somewhat bright tertiary which requires telescopic equipment for observation.
 W
WSigma Geminorum is a binary star system in the constellation Gemini, just to the northeast of Pollux. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.20. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 26.08 mas, it is located 125 light years from the Sun.
 W
WTau Geminorum, Latinized from τ Geminorum, is a star in the northern zodiac constellation of Gemini. It has the apparent visual magnitude of +4.42, making it visible to the naked eye under suitably good seeing conditions. This star is close enough to the Earth that its distance can be measured using the parallax technique, which yields a value of roughly 321 light-years.
 W
WTV Geminorum is a variable red supergiant in the constellation Gemini. Its visual magnitude varies from 6.3 to 7.5.
 W
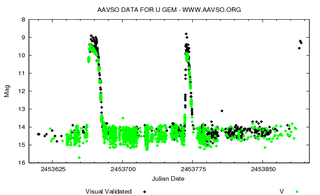
WU Geminorum, in the constellation Gemini, is an archetypal example of a dwarf nova. The binary star system consists of a white dwarf closely orbiting a red dwarf. Every few months it undergoes an outburst that greatly increases its brightness. The dwarf nova class of variable stars are often referred to as U Geminorum variables after this star.
 W
WXi Geminorum, formally named Alzirr, is a star in the zodiac constellation of Gemini. It forms one of the four feet of the outline demarcating the Gemini twins. The star has an apparent visual magnitude of 3.35, which is bright enough for it to be seen with the naked eye. From stellar parallax measurements, its distance from the Sun can be estimated as 58.7 light-years.
 W
WZeta Geminorum is a bright star with cluster components, distant optical components and a likely spectroscopic partner in the zodiac constellation of Gemini — in its south, on the left 'leg' of the twin Pollux. It is a classical Cepheid variable star, of which over 800 have been found in our galaxy. As such its regular pulsation and luminosity and its relative proximity means the star is a useful calibrator in computing the cosmic distance ladder. Based on parallax measurements, it is approximately 1,200 light-years from the Sun.