 W
WA social network is a social structure made up of a set of social actors, sets of dyadic ties, and other social interactions between actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods for analyzing the structure of whole social entities as well as a variety of theories explaining the patterns observed in these structures. The study of these structures uses social network analysis to identify local and global patterns, locate influential entities, and examine network dynamics.
 W
WThis is a list of notable individuals who research complex networks, including social networks, biological networks, and semantic networks, among others. Individuals are categorized based on their background and training, or their area of focus.
 W
WAmino is an online application developed by Narvii, Inc. It was created by Yin Wang and Ben Anderson in 2014.
 W
WThe art world comprises everyone involved in producing, commissioning, presenting, preserving, promoting, chronicling, criticizing, buying and selling fine art. It is recognized that there are many art worlds, defined either by location or alternative definitions of fine art. Some may use the singular art world to refer only to the elite level of globalized fine art. The art world(s) are continually changing in response both to the creativity of those that create art and in response to social change.
 W
WThe Barabási–Albert (BA) model is an algorithm for generating random scale-free networks using a preferential attachment mechanism. Several natural and human-made systems, including the Internet, the world wide web, citation networks, and some social networks are thought to be approximately scale-free and certainly contain few nodes with unusually high degree as compared to the other nodes of the network. The BA model tries to explain the existence of such nodes in real networks. The algorithm is named for its inventors Albert-László Barabási and Réka Albert and is a special case of an earlier and more general model called Price's model.
 W
WThe Bianconi–Barabási model is a model in network science that explains the growth of complex evolving networks. This model can explain that nodes with different characteristics acquire links at different rates. It predicts that a node's growth depends on its fitness and can calculate the degree distribution. The Bianconi–Barabási model is named after its inventors Ginestra Bianconi and Albert-László Barabási. This model is a variant of the Barabási–Albert model. The model can be mapped to a Bose gas and this mapping can predict a topological phase transition between a "rich-get-richer" phase and a "winner-takes-all" phase.
 W
WIn network science, a biased random walk on a graph is a time path process in which an evolving variable jumps from its current state to one of various potential new states; unlike in a pure random walk, the probabilities of the potential new states are unequal.
 W
WCatfishing is a deceptive activity where a person creates a sockpuppet presence or fake identity on a social networking service, usually targeting a specific victim for abuse or fraud. The practice may be used for financial gain, to compromise a victim in some way, or simply as forms of trolling or wish fulfillment. Catfishing media has been produced, often featuring victims who wish to identify their catfisher. Celebrities have been targeted, which has brought media attention to catfishing practices.
 W
WEnterprise social networking focuses on the use of online social networks or social relations among people who share business interests and/or activities. Enterprise social networking is often a facility of enterprise social software, which is essentially social software used in "enterprise" (business/commercial) contexts. It encompasses modifications to corporate intranets and other classic software platforms used by large companies to organize their communication, collaboration and other aspects of their intranets. Enterprise social networking is also generally thought to include the use of a standard external social networking service to generate visibility for an enterprise.
 W
WThe Erdős number describes the "collaborative distance" between mathematician Paul Erdős and another person, as measured by authorship of mathematical papers. The same principle has been applied in other fields where a particular individual has collaborated with a large and broad number of peers.
 W
Werento is the largest online rental marketplace in Germany. The company considers itself at the forefront of the collaborative consumption movement, also known as the sharing economy. Founded in 2003 by Chris Müller and Uwe Kampschulte as a Berlin start-up, today erento is operating in the UK, Finland, Austria, Germany and Switzerland.
 W
WSilvio Pestrin Farina is is an Argentina businessman and systems developer. He is the creator of FictionCity, an online social network for artists founded in Buenos Aires. H
 W
WThe Fediverse is an ensemble of federated servers that are used for web publishing and file hosting, but which, while independently hosted, can communicate with each other. On different servers (instances), users can create so-called identities. These identities are able to communicate over the boundaries of the instances because the software running on the servers supports one or more communication protocols which follow an open standard. As an identity on the fediverse, users are able to post text and other media, or to follow posts by other identities. In some cases, users can even show or share data publicly or to a selected group of identities and allow other identities to edit other users' data.
 W
WGeewa is a Czech mobile games developer based in Prague. Founded in 2005, the company develops and publishes casual competitive multiplayer games for mobile devices. Geewa was awarded the Red Herring 100 Europe award in 2013 and is best known for their games Smashing Four and Pool Live Tour. In 2017 Geewa lost CZK 18 mio. on sales CZK 26 mio., cumulated loss increased to CZK 174 mio.
 W
WGeosocial networking is a type of social networking in which geographic services and capabilities such as geocoding and geotagging are used to enable additional social dynamics. User-submitted location data or geolocation techniques can allow social networks to connect and coordinate users with local people or events that match their interests. Geolocation on web-based social network services can be IP-based or use hotspot trilateration. For mobile social networks, texted location information or mobile phone tracking can enable location-based services to enrich social networking.
 W
WA global network is any communication network which spans the entire Earth. The term, as used in this article refers in a more restricted way to bidirectional communication networks, and to technology-based networks. Early networks such as international mail and unidirectional communication networks, such as radio and television, are described elsewhere.
 W
WHierarchical network models are iterative algorithms for creating networks which are able to reproduce the unique properties of the scale-free topology and the high clustering of the nodes at the same time. These characteristics are widely observed in nature, from biology to language to some social networks.
 W
WImgur is an American online image sharing community and image host founded by Alan Schaaf in 2009. The service has been popular with hosting viral images and memes, particularly those posted on Reddit.
 W
WIn graph theory, the Katz centrality of a node is a measure of centrality in a network. It was introduced by Leo Katz in 1953 and is used to measure the relative degree of influence of an actor within a social network. Unlike typical centrality measures which consider only the shortest path between a pair of actors, Katz centrality measures influence by taking into account the total number of walks between a pair of actors.
 W
WMain path analysis is a mathematical tool, first proposed by Hummon and Doreian in 1989, to identify the major paths in a citation network, which is one form of a directed acyclic graph (DAG). The method begins by measuring the significance of all the links in a citation network through the concept of ‘traversal count’ and then sequentially chains the most significant links into a "main path", which is deemed the most significant historical path in the target citation network. The method is applicable to any human activity that can be organized in the form of a citation network. The method is commonly applied to trace the knowledge flow paths or development trajectories of a science or technology field, through bibliographic citations or patent citations. It has also been applied to judicial decisions to trace the evolving changes of legal opinions. Main path analysis has attracted scholars attention recently. Academic research related to main path analysis saw a fast growing since 2007. A list of academic articles that introduce, explain, apply, modify, or extend the method originated in Hummon and Doreian can be found here.
 W
WMobile social networking (MSN) is social networking where individuals with similar interests converse and connect with one another through their mobile phone and/or tablet. Much like web-based social networking, mobile social networking occurs in virtual communities.
 W
WTheneeds is an online and mobile content discovery platform that helps its users discover articles, news, videos, social posts, and other media tailored to their specific interests.
 W
WOdnoklassniki is a social network service used mainly in Russia and former Soviet Republics. The site was developed by Albert Popkov and launched on March 4, 2006.
 W
WPersonal media are media of communication which are used by an individual rather than by a corporation or institution. They are generally contrasted with mass media which are produced by teams of people and broadcast to a general population. In other words, personal media allow individuals, as opposed to corporate entities, to contribute knowledge and opinion to the public. The term dates from the 1980s.
 W
WPheme is a 36-month research project begun in 2014 into establishing the veracity of claims made on the internet.
 W
WRoposo, is an Indian video-sharing social media platform, owned by Glance Digital Experience Pvt. Ltd having its registered office at Bengaluru, India. It is a platform where people express visually with homemade videos and photos. Catering to users aged between 15 and 35 years, the app offers a TV-like browsing experience with user-generated content on its channels. Users can also use editing tools on the platform and upload their content..
 W
WScientific collaboration network is a social network where nodes are scientists and links are co-authorships as the latter is one of the most well documented forms of scientific collaboration.It is an undirected, scale-free network where the degree distribution follows a power law with an exponential cutoff – most authors are sparsely connected while a few authors are intensively connected. The network has an assortative nature – hubs tend to link to other hubs and low-degree nodes tend to link to low-degree nodes. Assortativity is not structural, meaning that it is not a consequence of the degree distribution, but it is generated by some process that governs the network’s evolution.
 W
WA sexual network is a social network that is defined by the sexual relationships within a set of individuals.
 W
WSix degrees of separation is the idea that all people on average are six, or fewer, social connections away from each other. Also known as the 6 Handshakes rule. As a result, a chain of "a friend of a friend" statements can be made to connect any two people in a maximum of six steps.
 W
WThe small-world experiment comprised several experiments conducted by Stanley Milgram and other researchers examining the average path length for social networks of people in the United States. The research was groundbreaking in that it suggested that human society is a small-world-type network characterized by short path-lengths. The experiments are often associated with the phrase "six degrees of separation", although Milgram did not use this term himself.
 W
WSocial capital is the effective functioning of social groups through interpersonal relationships, a shared sense of identity, a shared understanding, shared norms, shared values, trust, cooperation, and reciprocity. Social capital is a measure of the value of resources, both tangible and intangible, and the impact that these relationships have on the resources involved in each relationship, and on larger groups. It is generally seen as a form of capital that produces public goods for a common purpose.
 W
WThe social graph is a graph that represents social relations between entities. In short, it is a model or representation of a social network, where the word graph has been taken from graph theory. The social graph has been referred to as "the global mapping of everybody and how they're related".
 W
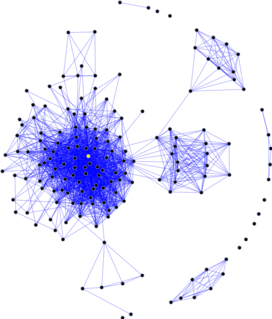
WSocial network analysis (SNA) is the process of investigating social structures through the use of networks and graph theory. It characterizes networked structures in terms of nodes and the ties, edges, or links that connect them. Examples of social structures commonly visualized through social network analysis include social media networks, memes spread, information circulation, friendship and acquaintance networks, business networks, knowledge networks, difficult working relationships, social networks, collaboration graphs, kinship, disease transmission, and sexual relationships. These networks are often visualized through sociograms in which nodes are represented as points and ties are represented as lines. These visualizations provide a means of qualitatively assessing networks by varying the visual representation of their nodes and edges to reflect attributes of interest.
 W
WCognitive social structures (CSS) is the focus of research that investigates how individuals perceive their own social structure. It is part of social network research and uses social network analysis to understand how various factors affect one's cognitive representation of the network. Importantly, an individual's perception of the network may be different than reality. In fact, these differences between the perceived network and the actual network are the focus of many studies that seek insight into how we think about others and our relationships.
 W
WSocial support is the perception and actuality that one is cared for, has assistance available from other people, and most popularly, that one is part of a supportive social network. These supportive resources can be emotional, informational, or companionship ; tangible or intangible. Social support can be measured as the perception that one has assistance available, the actual received assistance, or the degree to which a person is integrated in a social network. Support can come from many sources, such as family, friends, pets, neighbors, coworkers, organizations, etc.
 W
Wsocialblood is a Facebook application that connects blood donors and recipients of the same blood type through Facebook. socialblood, has created a social space for thousands of potential blood donors and recipients to meet and potentially donate.
 W
WThe sociology of the Internet involves the application of sociological theory and method to the Internet as a source of information and communication. Sociologists are concerned with the social implications of the technology; new social networks, virtual communities and ways of interaction that have arisen, as well as issues related to cyber crime.
 W
WStructural endogamy is a network concept that provides a means of finding the boundaries of endogamy in a community, using simply the genealogical and marriage linkages. The concept is related to that of structural cohesion. The examples are made with free tool Pajek. Another name for structural endogamy is (marital) relinking, which comes out of French social anthropology, and the study of how communities are formed through couples marrying who are already linked: linked, that is, by chains of kinship and marriage, as in circles of intermarrying families, or marriages between people with one or more ancestors in common. Many of the marriages represented in the Turkish nomads figure are with cousins, for example. But relinking also occurs without blood marriages, as in the example from the Mexican village of Belén Atzitzi-mititlán within Apetatitlán de Antonio Carvajal.
 W
WStudyPlaces is an international education portal in India. It is run by Savvica Inc., an online learning company based in Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
 W
WTargeted immunization strategies are approaches designed to increase the immunization level of populations and decrease the chances of epidemic outbreaks. Though often in regards to use in healthcare practices and the administration of vaccines to prevent biological epidemic outbreaks, these strategies refer in general to immunization schemes in complex networks, biological, social or artificial in nature. Identification of at-risk groups and individuals with higher odds of spreading the disease often plays an important role in these strategies.
 W
WThe Watts–Strogatz model is a random graph generation model that produces graphs with small-world properties, including short average path lengths and high clustering. It was proposed by Duncan J. Watts and Steven Strogatz in their joint 1998 Nature paper. The model also became known as the (Watts) beta model after Watts used to formulate it in his popular science book Six Degrees.
 W
WZachary's karate club is a social network of a university karate club, described in the paper "An Information Flow Model for Conflict and Fission in Small Groups" by Wayne W. Zachary. The network became a popular example of community structure in networks after its use by Michelle Girvan and Mark Newman in 2002.