 W
WAndromeda is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy, and one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, it is named for Andromeda, daughter of Cassiopeia, in the Greek myth, who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus. Andromeda is most prominent during autumn evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with several other constellations named for characters in the Perseus myth. Because of its northern declination, Andromeda is visible only north of 40° south latitude; for observers farther south, it lies below the horizon. It is one of the largest constellations, with an area of 722 square degrees. This is over 1,400 times the size of the full moon, 55% of the size of the largest constellation, Hydra, and over 10 times the size of the smallest constellation, Crux.
 W
WAquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for "water-carrier" or "cup-carrier", and its symbol is , a representation of water. Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.
 W
WAquila is a constellation on the celestial equator. Its name is Latin for 'eagle' and it represents the bird that carried Zeus/Jupiter's thunderbolts in Greek-Roman mythology.
 W
WAra, the southern constellation between Scorpius, Telescopium, Triangulum Australe and Norma, was one of the Greek bulk described by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union.
 W
WArgo Navis, or simply Argo, was a large constellation in the southern sky. The genitive was "Argus Navis", abbreviated "Arg". Flamsteed and other early modern astronomers called it Navis, genitive "Navis", abbreviated "Nav".
 W
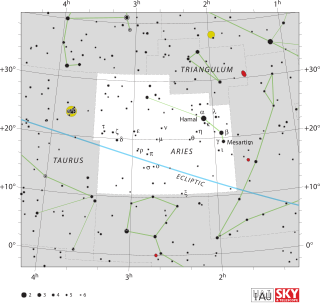
WAries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the Northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is , representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees.
 W
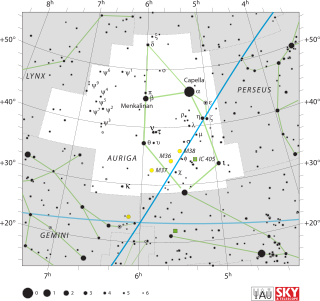
WAuriga is one of the 88 modern constellations; it was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy. It is north of the celestial equator. Its name is Latin for “(the) charioteer”, associating it with various mythological beings, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the northern Hemisphere, as are five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest, Hydra.
 W
WBoötes is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs 'herdsman' or 'plowman'.
 W
WCancer is one of the twelve constellations of the zodiac and is located in the Northern celestial hemisphere. Its name is Latin for crab and it is commonly represented as one. Its astrological symbol is♋. Cancer is a medium-size constellation with an area of 506 square degrees and its stars are rather faint, its brightest star Beta Cancri having an apparent magnitude of 3.5. It contains two stars with known planets, including 55 Cancri, which has five: one super-earth and four gas giants, one of which is in the habitable zone and as such has expected temperatures similar to Earth. At the (angular) heart of this sector of our celestial sphere is Praesepe, one of the closest open clusters to Earth and a popular target for amateur astronomers.
 W
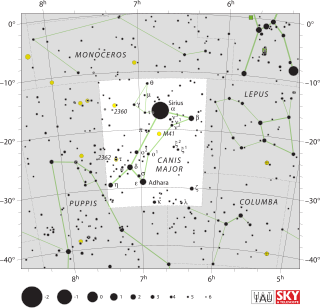
WCanis Major is a constellation in the southern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for "greater dog" in contrast to Canis Minor, the "lesser dog"; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter through the sky. The Milky Way passes through Canis Major and several open clusters lie within its borders, most notably M41.
 W
WCanis Minor is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for "lesser dog", in contrast to Canis Major, the "greater dog"; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.
 W
WCapricornus is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for "horned goat" or "goat horn" or "having horns like a goat's", and it is commonly represented in the form of a sea goat: a mythical creature that is half goat, half fish. Its symbol is .
 W
WCassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivaled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars.
 W
WCentaurus is a bright constellation in the southern sky. One of the largest constellations, Centaurus was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. In Greek mythology, Centaurus represents a centaur; a creature that is half human, half horse. Notable stars include Alpha Centauri, the nearest star system to the Solar System, its neighbour in the sky Beta Centauri, and V766 Centauri, one of the largest stars yet discovered. The constellation also contains Omega Centauri, the brightest globular cluster as visible from Earth and the largest identified in the Milky Way, possibly a remnant of a dwarf galaxy.
 W
WCepheus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after Cepheus, a king of Aethiopia in Greek mythology.
 W
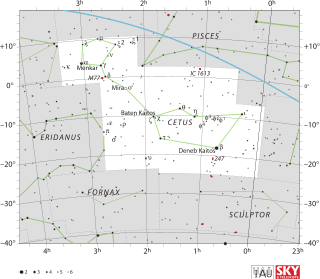
WCetus is a constellation. (The) Cetus was a sea monster in Greek mythology as both Perseus and Heracles needed to slay, sometimes in English called 'the whale'. Cetus is in the region of the sky that contains other water-related constellations: Aquarius, Pisces and Eridanus.
 W
WCorona Australis is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means "southern crown", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.
 W
WCorona Borealis is a small constellation in the Northern Celestial Hemisphere. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Its brightest stars form a semicircular arc. Its Latin name, inspired by its shape, means "northern crown". In classical mythology Corona Borealis generally represented the crown given by the god Dionysus to the Cretan princess Ariadne and set by him in the heavens. Other cultures likened the pattern to a circle of elders, an eagle's nest, a bear's den, or even a smokehole. Ptolemy also listed a southern counterpart, Corona Australis, with a similar pattern.
 W
WCorvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name means "crow" in Latin. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it depicts a raven, a bird associated with stories about the god Apollo, perched on the back of Hydra the water snake. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi, form a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky.
 W
WCrater is a small constellation in the southern celestial hemisphere. Its name is the latinization of the Greek krater, a type of cup used to water down wine. One of the 48 constellations listed by the second-century astronomer Ptolemy, it depicts a cup that has been associated with the god Apollo and is perched on the back of Hydra the water snake.
 W
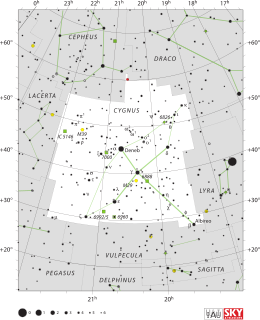
WCygnus is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. Cygnus is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, and it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross. Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.
 W
WDelphinus is a small constellation in the Northern Celestial Hemisphere, close to the celestial equator. Its name is the Latin version for the Greek word for dolphin (δελφίνι). It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. It is one of the smaller constellations, ranked 69th in size. Delphinus' five brightest stars form a distinctive asterism symbolizing a dolphin with four stars representing the body and one the tail. It is bordered by Vulpecula, Sagitta, Aquila, Aquarius, Equuleus and Pegasus.
 W
WDraco is a constellation in the far northern sky. Its name is Latin for dragon. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. The north pole of the ecliptic is in Draco. Draco is circumpolar, and can be seen all year from northern latitudes.
 W
WEquuleus is a constellation. Its name is Latin for "little horse", a foal. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is the second smallest of the modern constellations, spanning only 72 square degrees. It is also very faint, having no stars brighter than the fourth magnitude.
 W
WEridanus is a constellation in the southern celestial hemisphere. It is represented as a river. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is the sixth largest of the modern constellations. The same name was later taken as a Latin name for the real Po River and also for the name of a minor river in Athens.
 W
WGemini is one of the constellations of the zodiac and is located in the northern celestial hemisphere. It was one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. Its name is Latin for twins, and it is associated with the twins Castor and Pollux in Greek mythology. Its symbol is .
 W
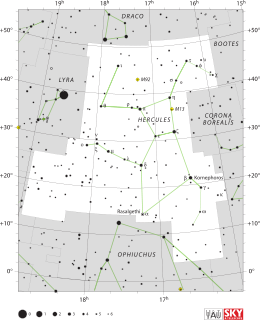
WHercules is a constellation named after Hercules, the Roman mythological hero adapted from the Greek hero Heracles. Hercules was one of the 48 constellations listed by the second-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is the fifth-largest of the modern constellations and is the largest of the 50 which have no stars brighter than apparent magnitude +2.5.
 W
WHydra is the largest of the 88 modern constellations, measuring 1303 square degrees, and also the longest at over 100 degrees. Its southern end borders Libra and Centaurus and its northern end borders Cancer. It was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy. It is commonly represented as a water snake. It is located in the southern hemisphere.
 W
WLeo is one of the constellations of the zodiac, lying between Cancer the crab to the west and Virgo the maiden to the east. It is located in the Northern celestial hemisphere. Its name is Latin for lion, and to the ancient Greeks represented the Nemean Lion killed by the mythical Greek hero Heracles meaning 'Glory of Hera' as one of his twelve labors. Its symbol is . One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, Leo remains one of the 88 modern constellations today, and one of the most easily recognizable due to its many bright stars and a distinctive shape that is reminiscent of the crouching lion it depicts. The lion's mane and shoulders also form an asterism known as "The Sickle," which to modern observers may resemble a backwards "question mark."
 W
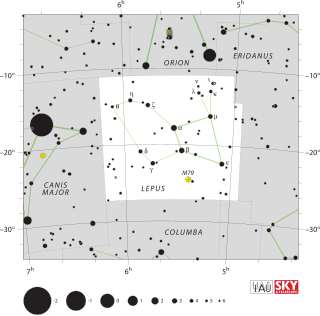
WLepus is a constellation lying just south of the celestial equator. Its name is Latin for hare. It is located below—immediately south—of Orion, and is sometimes represented as a hare being chased by Orion or by Orion's hunting dogs.
 W
WLibra is a constellation of the zodiac and is located in the Southern celestial hemisphere. Its name is Latin for weighing scales, and its symbol is . It is fairly faint, with no first magnitude stars, and lies between Virgo to the west and Scorpius to the east. Beta Librae, also known as Zubeneschamali, is the brightest star in the constellation. Three star systems are known to have planets.
 W
WLupus is a constellation of the mid-Southern Sky. Its name is Latin for wolf. Lupus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations, but was long an asterism associated with the just westerly, larger constellation Centaurus.
 W
WLyra is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence is sometimes referred to as Vultur Cadens or Aquila Cadens, respectively. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is nearly overhead in temperate northern latitudes shortly after midnight at the start of summer. From the equator to about the 40th parallel south it is visible low in the northern sky during the same months.
 W
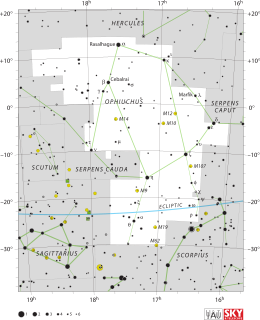
WOphiuchus is a large constellation straddling the celestial equator. Its name is from the Greek Ὀφιοῦχος, and it is commonly represented as a man grasping a snake. The serpent is represented by the constellation Serpens. Ophiuchus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It was formerly referred to as Serpentarius.
 W
WOrion is a prominent constellation located on the celestial equator and visible throughout the world. It is one of the most conspicuous and recognizable constellations in the night sky. It is named after Orion, a hunter in Greek mythology. Its brightest stars are blue-white Rigel and red Betelgeuse.
 W
WPegasus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the winged horse Pegasus in Greek mythology. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognised today.
 W
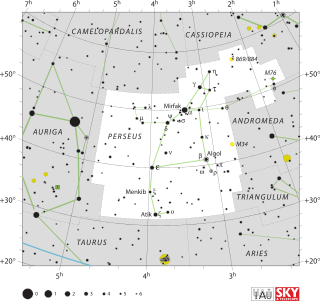
WPerseus is a constellation in the northern sky, being named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus. It is one of the 48 ancient constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located near several other constellations named after ancient Greek legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west. Some star atlases during the early 19th century also depicted Perseus holding the disembodied head of Medusa, whose asterism was named together as Perseus et Caput Medusae; however, this never came into popular usage.
 W
WPisces is a constellation of the zodiac. Its vast bulk – and main asterism viewed in most European cultures per Greco-Roman antiquity as a distant pair of fishes connected by one cord each that join at an apex – are in the Northern celestial hemisphere. Its name is the Latin plural for fish. It is between Aquarius, of similar size, to the southwest and Aries, which is smaller, to the east. The ecliptic and the celestial equator intersect within this constellation and in Virgo. This means the sun passes directly overhead of the equator, on average, at approximately this point in the sky, at the March equinox.
 W
WPiscis Austrinus is a constellation in the southern celestial hemisphere. The name is Latin for "the southern fish", in contrast with the larger constellation Pisces, which represents a pair of fishes. Before the 20th century, it was also known as Piscis Notius. Piscis Austrinus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The stars of the modern constellation Grus once formed the "tail" of Piscis Austrinus. In 1597, Petrus Plancius carved out a separate constellation and named it after the crane.
 W
WSagitta is a dim but distinctive constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for 'arrow', not to be confused with the significantly larger constellation Sagittarius 'the archer'. It was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. Although it dates to antiquity, Sagitta has no star brighter than 3rd magnitude and has the third-smallest area of any constellation.
 W
WSagittarius is one of the constellations of the zodiac and is located in the Southern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for "archer", and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur pulling back a bow. It lies between Scorpius and Ophiuchus to the west and Capricornus and Microscopium to the east.
 W
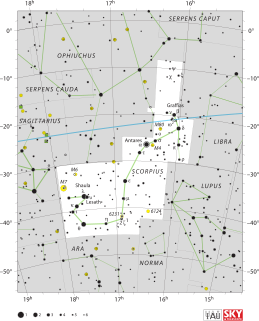
WScorpius is one of the constellations of the zodiac and is located in the Southern celestial hemisphere. Its name is Latin for scorpion, and its symbol is . Scorpius is one of the 48 constellations identified by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy in the second century. It is an ancient constellation that pre-dates the Greeks. It lies between Libra to the west and Sagittarius to the east. It is a large constellation located in the southern hemisphere near the center of the Milky Way.
 W
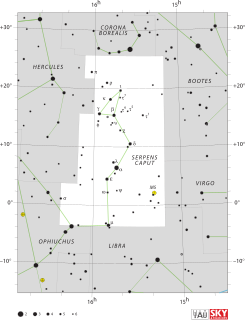
WSerpens is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput to the west and Serpens Cauda to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the "Serpent-Bearer". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.
 W
WTaurus is one of the constellations of the zodiac and is located in the Northern celestial hemisphere. Taurus is a large and prominent constellation in the northern hemisphere's winter sky. It is one of the oldest constellations, dating back to at least the Early Bronze Age when it marked the location of the Sun during the spring equinox. Its importance to the agricultural calendar influenced various bull figures in the mythologies of Ancient Sumer, Akkad, Assyria, Babylon, Egypt, Greece, and Rome. The symbol representing Taurus is , which resembles a bull's head.
 W
WTriangulum is a small constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for "triangle", derived from its three brightest stars, which form a long and narrow triangle. Known to the ancient Babylonians and Greeks, Triangulum was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy. The celestial cartographers Johann Bayer and John Flamsteed catalogued the constellation's stars, giving six of them Bayer designations.
 W
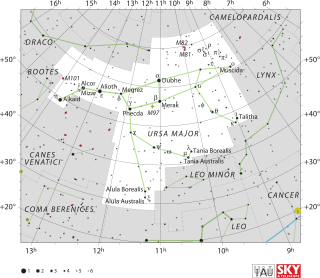
WUrsa Major is a constellation in the northern sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater she-bear," referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa Minor, the lesser bear. In antiquity, it was one of the original 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD. Today it is the third largest of the 88 modern constellations.
 W
WUrsa Minor, also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the Northern Sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the North American name, Little Dipper: seven stars with four in its bowl like its partner the Big Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, because of Polaris being the north pole star.
 W
WVirgo is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for virgin, and its symbol is . Lying between Leo to the west and Libra to the east, it is the second-largest constellation in the sky and the largest constellation in the zodiac. The ecliptic intersects the celestial equator within this constellation and Pisces. Underlying these technical two definitions, the sun passes directly overhead of the equator, within this constellation, at the September equinox. Virgo can be easily found through its brightest star, Spica.