 W
WBradley K. Alpert is a computational scientist at NIST. He is probably best known for co-developing fast spherical filters. His fast spherical filters were critical in the construction of the most efficient three-dimensional fast multipole methods (FMMs) for solving the Helmholtz equation and Maxwell's equations. Other well-known work of his includes contributions to computational methods for time-domain wave propagation, quadratures for singular integrals, and multiwavelets.
 W
WNikolai Sergeevich Bakhvalov was a Soviet and Russian mathematician.
 W
WFranco Brezzi is an Italian mathematician.
 W
WAnnalisa Buffa is an Italian mathematician, specializing in numerical analysis and PDEs.
 W
WJohn Charles Butcher is a New Zealand mathematician who specialises in numerical methods for the solution of ordinary differential equations. Butcher works on multistage methods for initial value problems, such as Runge-Kutta and general linear methods. The Butcher group and the Butcher tableau are named after him.
 W
WPafnuty Lvovich Chebyshev was a Russian mathematician and considered to be the founding father of Russian mathematics.
 W
WAlexandre Joel Chorin is known for his contributions to computational fluid mechanics, turbulence, and computational statistical mechanics.
 W
WPhillip Colella is an American applied mathematician and a member of the Applied Numerical Algorithms Group at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. He has also worked at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. He is known for his fundamental contributions in the development of mathematical methods and numerical tools used to solve partial differential equations, including high-resolution and adaptive mesh refinement schemes. Colella is a member of the US National Academy of Sciences.
 W
WGeorge Bernard Dantzig was an American mathematical scientist who made contributions to industrial engineering, operations research, computer science, economics, and statistics.
 W
WCarl-Wilhelm Reinhold de Boor is a German-American mathematician and professor emeritus at the University of Wisconsin–Madison.
 W
WJames Weldon Demmel Jr. is an American mathematician and computer scientist, the Dr. Richard Carl Dehmel Distinguished Professor of Mathematics and Computer Science at the University of California, Berkeley.
 W
WIain S. Duff is a British mathematician and computer scientist, known for his work in numerical methods and software for solving problem with sparse matrices, in particular the Harwell Subroutine Library. From 1986–2009, he was the Group Leader of Numerical Analysis at Harwell Laboratory, which has moved in 1990 to the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory. He is also the Project Leader for the Parallel Algorithms Group at CERFACS in Toulouse.
 W
WIoana Dumitriu is a Romanian-American mathematician who works as a professor of mathematics at the University of California, San Diego. Her research interests include the theory of random matrices, numerical analysis, scientific computing, and game theory.
 W
WBjörn Engquist has been a leading contributor in the areas of multiscale modeling and scientific computing, and a productive educator of applied mathematicians.
 W
WAlessandro Faedo was an Italian mathematician and politician, born in Chiampo. He is known for his work in numerical analysis, leading to the Faedo–Galerkin method: he was one of the pupils of Leonida Tonelli and, after his death, he succeeded him on the chair of mathematical analysis at the University of Pisa, becoming dean of the faculty of sciences and then rector and exerting a strong positive influence on the development of the university.
 W
WPaul Roesel Garabedian was a mathematician and numerical analyst. Garabedian was the Director-Division of Computational Fluid Dynamics at the Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University. He is known for his contributions to the fields of computational fluid dynamics and plasma physics, which ranged from elegant existence proofs for potential theory and conformal mappings to the design and optimization of stellarators. Garabedian was elected a member of the National Academy of Sciences in 1975.
 W
WSergei Konstantinovich Godunov is professor at the Sobolev Institute of Mathematics of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Novosibirsk, Russia.
 W
WGene Howard Golub, Fletcher Jones Professor of Computer Science at Stanford University, was one of the preeminent numerical analysts of his generation.
 W
WMax D. Gunzburger, Francis Eppes Distinguished Professor of Mathematics at Florida State University, is an American mathematician and computational scientist affiliated with the Florida State interdisciplinary Department of Scientific Computing. He was the 2008 winner of the SIAM W.T. and Idalia Reid Prize in Mathematics. His seminal research contributions include flow control, finite element analysis, superconductivity and Voronoi tessellations. He has also made contributions in the areas of aerodynamics, materials, acoustics, climate change, groundwater, image processing and risk assessment.
 W
WRichard Wesley Hamming was an American mathematician whose work had many implications for computer engineering and telecommunications. His contributions include the Hamming code, the Hamming window, Hamming numbers, sphere-packing, and the Hamming distance.
 W
WDouglas Rayner Hartree was an English mathematician and physicist most famous for the development of numerical analysis and its application to the Hartree–Fock equations of atomic physics and the construction of a differential analyser using Meccano.
 W
WPeter Karl Henrici was a Swiss mathematician best known for his contributions to the field of numerical analysis.
 W
WMarlis Hochbruck is a German applied mathematician and numerical analyst known for her research on matrix exponentials, exponential integrators, and their applications to the numerical solution of differential equations. She is a professor in the Institute for Applied and Numerical Mathematics at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology.
 W
WOlga Holtz is a Russian mathematician specializing in numerical analysis. She received the Sofia Kovalevskaya Award in 2006 and the European Mathematical Society Prize (2008). Since 2008, she is a member of the Young Academy of Germany.
 W
WFritz John was a German-born mathematician specialising in partial differential equations and ill-posed problems. His early work was on the Radon transform and he is remembered for John's equation. He was a 1984 MacArthur Fellow.
 W
WWilliam "Velvel" Morton Kahan is a Canadian mathematician and computer scientist, who received the Turing Award in 1989 for "his fundamental contributions to numerical analysis", was named an ACM Fellow in 1994, and inducted into the National Academy of Engineering in 2005.
 W
WAndrei (Andrew) Knyazev is a Russian-American mathematician. He graduated from the Faculty of Computational Mathematics and Cybernetics of Moscow State University under the supervision of Evgenii Georgievich D'yakonov in 1981 and obtained his PhD in Numerical Mathematics at the Russian Academy of Sciences under the supervision of Vyacheslav Ivanovich Lebedev in 1985. He worked at the Kurchatov Institute in 1981–1983, and then to 1992 at the Marchuk Institute of Numerical Mathematics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, headed by Gury Marchuk.
 W
WErvand George Kogbetliantz was an Armenian-American mathematician and the first president of the Yerevan State University. He left Russia in 1918. He received a Doctorate in mathematics from the University of Paris in 1923. His mathematical work was mainly on infinite series, on the theory of orthogonal polynomials, on an algorithm for singular value decomposition which bears his name, on algorithms for the evaluation of elementary functions in computers, and on the enumeration of prime elements of the Gaussian integers. He also invented a three-dimensional version of chess, and was working at his death with Bobby Fischer on a game of chess for three people. When he first went to America (1941), he taught Mathematics at Lehigh University. In the early 1950s, he was a consultant for IBM in New York City and taught at Columbia University. Prior to moving back to Paris and retiring, he was a professor at Rockefeller University.
 W
WAleksandr (Alexander) Semenovich Kronrod was a Soviet mathematician and computer scientist, best known for the Gauss-Kronrod quadrature formula which he published in 1964. Earlier, he worked on computational solutions of problems emerging in theoretical physics. He is also known for his contributions to economics, specifically for proposing corrections and calculating price formation for the USSR. Later, Kronrod gave his fortune and life to medicine to care for terminal cancer patients. Kronrod is remembered for his captivating personality and was admired as a student, teacher and leader.
 W
WMartin Wilhelm Kutta was a German mathematician.
 W
WCornelius (Cornel) Lanczos was a Hungarian mathematician and physicist, who was born in Székesfehérvár, Fejér County, Kingdom of Hungary on February 2, 1893, and died on June 25, 1974. According to György Marx he was one of The Martians.
 W
WPeter David Lax is a Hungarian-born American mathematician working in the areas of pure and applied mathematics.
 W
WVyacheslav Ivanovich Lebedev was a Soviet and Russian mathematician, known for his work on numerical analysis.
 W
WBram van Leer is Arthur B. Modine Emeritus Professor of aerospace engineering at the University of Michigan, in Ann Arbor. He specializes in Computational fluid dynamics (CFD), fluid dynamics, and numerical analysis. His most influential work lies in CFD, a field he helped modernize from 1970 onwards. An appraisal of his early work has been given by C. Hirsch (1979)
 W
WClaude Lemaréchal is a French applied mathematician, and former senior researcher at INRIA near Grenoble, France.
 W
WChristian Lubich is an Austrian mathematician, specializing in numerical analysis.
 W
WVolker Ludwig Mehrmann is a German mathematician.
 W
WPhyllis Nicolson was a British mathematician most known for her work on the Crank–Nicolson method together with John Crank.
 W
WJohn E. Osborn was an American mathematician. He obtained B.S. (1958), M.S. (1963), and Ph.D. (1965) degrees at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. His Ph.D. adviser was Hans Weinberger. Osborn made fundamental contributions to computational mathematics, especially to the theory of numerical solution of partial differential equations, eigenvalue approximations, and the finite element method. He also co-authored several textbooks on differential equations and numerical computation with the goal of introducing computation into sophomore level differential equations courses.
 W
WStanley Osher is an American mathematician, known for his many contributions in shock capturing, level-set methods, and PDE-based methods in computer vision and image processing. Osher is a professor at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), Director of Special Projects in the Institute for Pure and Applied Mathematics (IPAM) and member of the California NanoSystems Institute (CNSI) at UCLA. He has a daughter, Kathryn, and a son, Joel.
 W
WAlexander Markowich Ostrowski was a mathematician.
 W
WTiberiu Popoviciu was a Romanian mathematician and the namesake of Popoviciu's inequality and Popoviciu's inequality on variances.
 W
WRolf Rannacher is a German mathematician and a professor of numerical analysis at Heidelberg University.
 W
WWerner Romberg was a German mathematician and physicist.
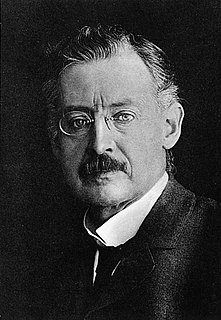 W
WCarl David Tolmé Runge was a German mathematician, physicist, and spectroscopist.
 W
WAhmed Hamdy Mohamed Sameh is the Samuel D. Conte Professor of Computer Science at Purdue University. He is known for his contributions to parallel algorithms in numerical linear algebra.
 W
WDaniel Shanks was an American mathematician who worked primarily in numerical analysis and number theory. He is best known as the first to compute π to 100,000 decimal places, and for his book Solved and Unsolved Problems in Number Theory.
 W
WStephen Smale is an American mathematician, known for his research in topology, dynamical systems and mathematical economics. He was awarded the Fields Medal in 1966 and spent more than three decades on the mathematics faculty of the University of California, Berkeley.
 W
WJosef Stoer is a German mathematician specializing in numerical analysis and professor emeritus of the Institut für Mathematik of Universität Würzburg.
 W
WEndre Süli is a mathematician. He is Professor of Numerical Analysis in the Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford, Fellow and Tutor in Mathematics at Worcester College, Oxford and Supernumerary Fellow of Linacre College, Oxford. He was educated at the University of Belgrade and, as a British Council Visiting Student, at the University of Reading and St Catherine's College, Oxford. His research is concerned with the mathematical analysis of numerical algorithms for nonlinear partial differential equations.
 W
WEitan Tadmor is a distinguished university professor at the University of Maryland, College Park, known for his contributions to the theory and computation of PDEs with diverse applications to shock wave, kinetic transport, incompressible flows, image processing, and self-organized collective dynamics.
 W
WJohn (Jack) Todd was a Northern Irish mathematician most of whose career was spent in England and the USA; he was a pioneer in the field of numerical analysis.
 W
WRichard Steven Varga is an American mathematician who specializes in numerical analysis and linear algebra. He is currently an Emeritus University Professor of Mathematical Sciences at Kent State University and an adjunct Professor at Case Western Reserve University. Varga is known for his contributions to many areas of mathematics, including matrix analysis, complex analysis, approximation theory, and scientific computation. He is the author of the classic textbook Matrix Iterative Analysis. Varga has been the Editor-in-Chief of the journal Electronic Transactions on Numerical Analysis (ETNA).
 W
WSir Edmund Taylor Whittaker FRS FRSE LL.D. Sc.D. was an early 20th-century British mathematician, physicist, and historian of science. Whittaker was a leading mathematical scholar of the early twentieth century who contributed widely to applied mathematics and was renowned for his research in mathematical physics and numerical analysis, including the theory of special functions, along with his contributions to astronomy, celestial mechanics, the history of physics, and digital signal processing. Among the most influential publications in Whittaker’s bibliography, he authored several popular reference works in mathematics, physics, and the history of science, including A Course of Modern Analysis, Analytical Dynamics of Particles and Rigid Bodies, and A History of the Theories of Aether and Electricity. Whittaker is also remembered for his role in the relativity priority dispute, as he credited Henri Poincaré and Hendrik Lorentz for developing special relativity in the second volume of his History, a dispute which has lasted several decades, though scientific consensus has remained with Einstein. Whittaker served as the Royal Astronomer of Ireland early in his career, a position he held from 1906 through 1912, before moving on to the chair of mathematics at the University of Edinburgh for the next three decades and, towards the end of his career, received the Copley Medal and was knighted. The School of Mathematics of the University of Edinburgh holds The Whittaker Colloquium, a yearly lecture, in his honour and the Edinburgh Mathematical Society promotes an outstanding young Scottish mathematician once every four years with the Sir Edmund Whittaker Memorial Prize, also given in his honour.
 W
WJames Hardy Wilkinson FRS was a prominent figure in the field of numerical analysis, a field at the boundary of applied mathematics and computer science particularly useful to physics and engineering.
 W
WMax August Zorn was a German mathematician. He was an algebraist, group theorist, and numerical analyst. He is best known for Zorn's lemma, a method used in set theory that is applicable to a wide range of mathematical constructs such as vector spaces, ordered sets and the like. Zorn's lemma was first postulated by Kazimierz Kuratowski in 1922, and then independently by Zorn in 1935.